Test: Means of Transport (Old NCERT) - JAMB MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Biology for JAMB - Test: Means of Transport (Old NCERT)
The movement of the molecules of solids, gases or liquids from the region of their higher concentration to the region of their lower concentration is known as:
The type of diffusion in which substances move across the membrane along their concentration gradient in the presence of certain carriers or transport proteins is called as
When transport proteins simultaneously move two molecules across a membrane in the same direction, the process is called
Smaller, lipid soluble molecules diffuse faster through cell membrane, but the movement of hydrophilic substances is facilitated by certain transporters which are chemically
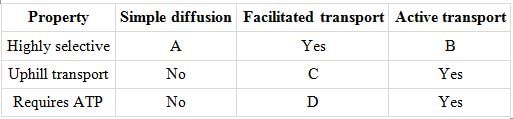
Refer to the given table and select the option that correctly fills the blanks in it.
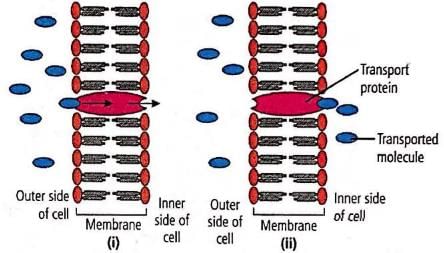
Refer the given figure. What does it represent?
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1 : The process of diffusion does not require any input of energy.
Statement 2 : Diffusion involves movement of particles from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration.
Uphill transport i.e., movement of substances from their lower concentration to their higher concentration occurs in
|
224 videos|175 docs|151 tests
|




















