Test: Principles of Inheritance & Variation - 2 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 12 - Test: Principles of Inheritance & Variation - 2
The innate tendency of offspring to resemble their parents is called?
Who is regarded as the father of genetics?
Material used for conducting experiments on genetic traits by Mendel was _________.
The physical expression or appearance of a character is called as:
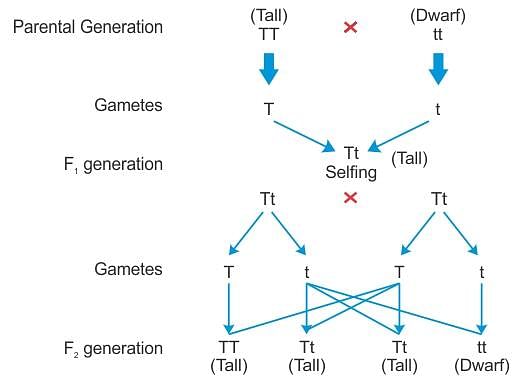
F2 generation is obtained by _________.
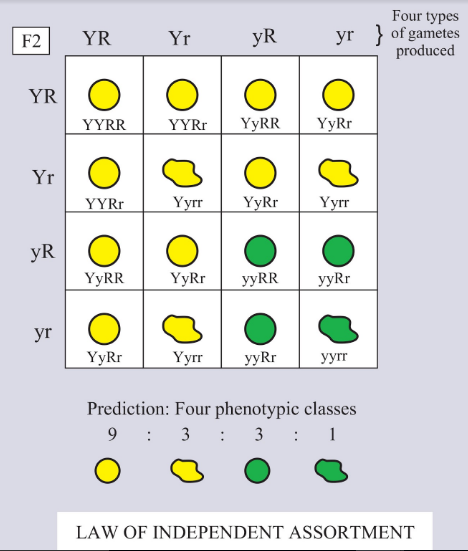
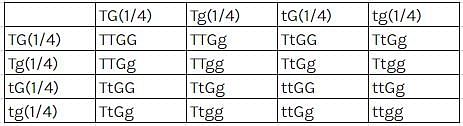
Dihybrid cross proves the law of _________.
In pea plants, yellow seeds are dominant to green, If a heterozygous yellow seeded plant is crossed with a green seeded plant, what ratio of yellow and green seeded plants would you expect in F1 generation?
In a cross between a pure tall plant with green pod and a pure short plant with yellow pod. How many short plants are produced in F2 generation out of 16?
The test cross is used to determine the ________.
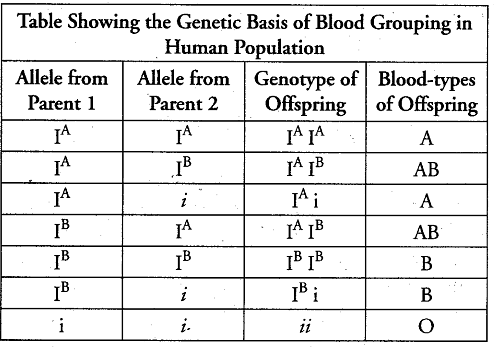
The genotypes of a husband and wife are IA IB and IAi. Among the blood types of their children how many different genotypes and phenotypes are possible?
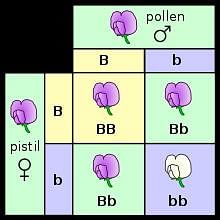
Which of the following is an example of co-dominance?
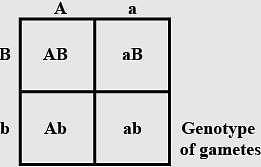
A human male produces sperms with the genotypes AB, Ab, aB, ab pertaining to two diallelic characters in equal proportions. What is the corresponding genotype of this person?
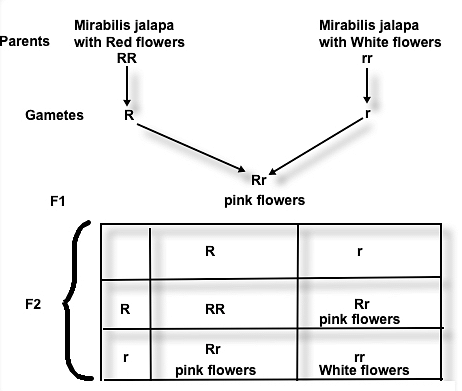
In Mirabilis jalapa, when two F1 pink flowered plants were crossed with each other, the F2 generation produced 40 red, 80 pink and 40 white flowering plants. This a case of:
Assertion: The cross between red and white flower-bearing snapdragon plants results in pink coloured flower.
Reason: Incomplete dominance of red and white flower results in pink coloured flowers.
When two genes are situated very close to one another on a chromosome _________.
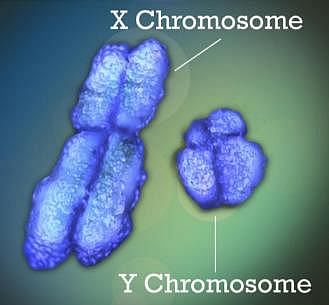
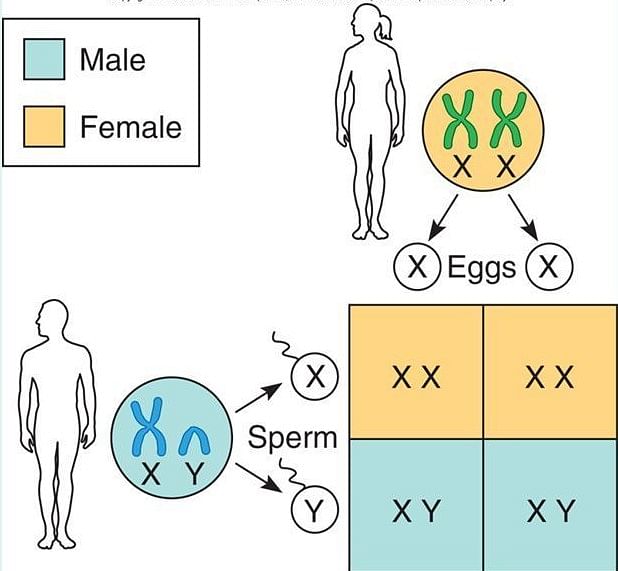
XY chromosome that determine the sex in human beings are:
Statement I: The bridge between one generation and the next is sperm and ovum.
Statement II: Both sperm and ovum contribute equally to heredity.
Statement III: Somatic diploid cells possess two chromosomes as well as two mendelian factors of each type.
Sex determination in human beings is _________.
In the case of Co-dominance when red and white flowers is crossed, the F1 generation resembles:
In human beings, if ovum fertilizes with a sperm carrying X-chromosome, the zygote develops into _________.
A colour blind girl is rare because she will be born only when
Which of the following is a recessive trait for a character chosen by Mendel in garden pea?
Identify the incorrect statement:
The ultimate source of allelic variation is:
According to the Law of Dominance, which of the following statements is true?
In the inheritance of flower color in the dog flower (snapdragon or Antirrhinum sp.), what is observed when a true-breeding red-flowered (RR) plant is crossed with a true-breeding white-flowered (rr) plant?
In the context of co-dominance, what happens when both the IA and IB alleles are present in an individual?
How does the Law of Segregation explain the inheritance of traits in offspring?
|
78 videos|277 docs|174 tests
|


![SOLVED] What will be the ratio of tall and dwarf plants in the - Self Study 365](https://edurev.gumlet.io/ApplicationImages/Temp/6b6380c6-c572-47ff-b447-e7f8f4bcfd3c_lg.jpg)