Test: Respiration & Enzymes - 1 - ACT MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Respiration & Enzymes - 1
What is the importance of respiration in organisms?
Which of the following is/are not produced from two acetyl-CoA molecules at the end of Kreb's cycle?
Energy obtained by a cell from catabolic reaction is stored immediately in the form of
Which of the following is the source of respiration?
R.Q. is less than one at the time of respiration of –
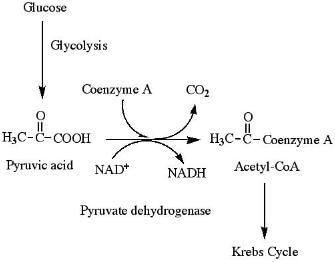
Number of ATP produced from one pyruvic acid during conversion to acetyl Co-A –
All enzymes of the TCA cycle are located in the mitochondrial matrix, except one which is located in inner mitochondrial membranes in eukaryotes. This enzyme is
Which of the following sentences about oxidative phase of pentose phosphate pathway is correct?
According to chemiosmotic theory of P. Mitchell (1978), ATPs are synthesised on membranes due to the :
During oxidative phosphorylation, proton gradient is not generated by
During glycolysis, one NADH is equivalent to _______ number of ATP.
Where does the second process of aerobic respiration take place?
Which of the following is a crucial event in aerobic respiration?
Conversion of pyruvic acid into ethyl alcohol is mediated by –
How many ATP molecules are utilised during glycolysis?
The formation of Acetyl Co-A from pyruvic acid is the result of its
Which of the following is link between carbohydrate and fat metabolism ?
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is used in converting –
Where does the synthesis of enzyme occur in a cell
Oxidation of one molecule of glucose in aerobic respiration results in the production of
The electron transport system in mitochondria is located in the: