Test: Plant Water Relations (Old NCERT) - Grade 12 MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Biology for Grade 12 - Test: Plant Water Relations (Old NCERT)
A flowering plant is planted in an earthen pot and irrigated. Urea is added in high amounts to make the plant grow faster, but after some time the plant died. This may be due to
Absorption of water from soil by seeds increases the______ thus helping seedlings to come out of soil.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Read the given statements and select the correct ones.
(i) A membrane which permits the passage of pure solvent molecules to pass through it and not the solute particles is called semi-permeable.
(ii) A membrane which allows some substances to pass through it more readily than others is known as selectively/ differentially permeable.
(iii) All living biological membranes are perfectly semipermeable.
Movement of solvent molecule from a region of its higher concentration to a region of its lower concentration through a semipermeable membrane, is referred to as
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
(i) Pure water has the highest water potential i.e., zero.
(ii) Process of diffusion does not require any input of energy.
(iii) Water moves from the system containing water at higher water potential to the one having lower water potential.
If ψw = water potential; ψs = solute potential; ψρ = pressure potential, then select the correct equation showing their inter- relation
If DPD represents diffusion pressure deficit OP is the osmotic pressure and TP is the turgor pressure, then which of the following equation is correct?
Which of the following occupies the space between the cell wall and the shrunken protoplast in a plasmo lysed cell?
Two adjacent cells A and B are being studied. Cell A has OP of 10 atm and TP of 6 atm. Cell B has OP of 10 atm and TP of 4 atm.
Movement of water will occur from
If a cell A with DPD = 5 bars is connected to cells B, C and D, whose OP and TP are respectively 5 and 5, 10 and 4, and 8 and 3, the flow of water will be
The plant cell cytoplasm is surrounded by both cell wall and cell membrane. The specificity of transport of substances is mostly across the cell membrane, because
If some solute is dissolved in pure water, its water potential
A plasmolysed cell can be deplasmolysed by placing it in
Water potential of a flaccid cell will be:
Salt is added to preserve meat, pickles, etc. because salting kills bacteria by the process of
Select the incorrect statement regarding imbibition.
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1 : Plant cells do not rupture when placed in distilled water.
Statement 2 : Animal cells rupture when placed in distilled water.
Which of the following statments is/are correct?
Which option is true for a fully turgid cell?
The cell A has an osmotic potential of −20 bars and a pressure potential of +6 bars. What will be its water potential?
Use of excessive fertilisers causes wilting due to
The practice of breaking of rocks during rainy season by inserting wooden pegs in them is based on the phenomenon of
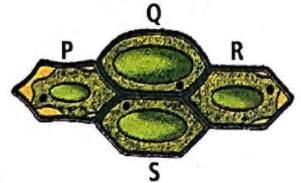
Which out of the four plant cells (P, Q, R and S) would not exhibit any wall pressure?
Given figure represents demonstration of osmosis by egg membrane osmoscope.
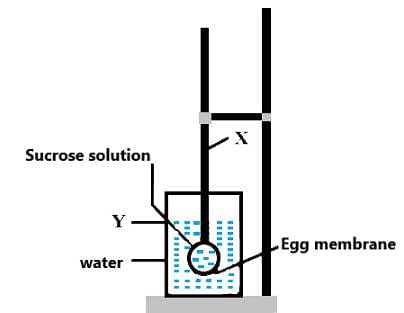
After few days, which of the following would have occurred ?
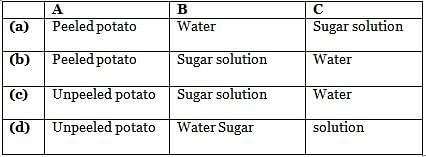
The given figure shows set up of potato osmoscope experiment. Select the option that correctly identifies the labels A, B and C.
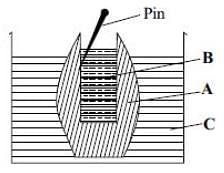
Read the given statments and select the correct option.
Statement 1: It becomes difficult to open and shut the wooden doors and windows during rainy season.
Statement 2: Wooden doors and windows imbibe water in rainy season and thus their volume is increased.
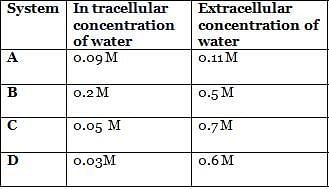
The given table shows properties of four cells systems A, B, C and D. The maximum rate of inward diffusion of water will be observed in which of these systems?
The concentration of solute in four cells is 0.4M. They are placed in four separate containers I, II, III and IV, filled with saline water of concentrations 0.1M, 0.4M, 2M and 3M respectively. In which container will the cell swell?
|
122 videos|161 docs|138 tests
|
|
122 videos|161 docs|138 tests
|












