Test: Animal Life - 2 - Class 5 MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Animal Life - 2
The surroundings in which an animal lives and grows is called its
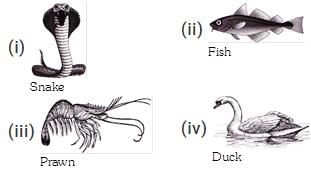
Which of the following is correct statement regarding the given animals?
Which of the following animals is an example of an arboreal animal?
Which of the following is the purpose of migration in animals?
Grass-hopper protects itself from being eaten by its predator -
Camouflage phenomena is seen in which one of the following animals?
Following are adaptation of animals for terrestrial habitat.
(i) They have strong claws that can be withdrawn inside their toes
(ii) They have eyes on both the sides of their heads.
(iii) They are light brown in color.
(iv)They have strong, flat hind teeth for chewing.
(v) They move in herds
(vi) They have eyes in front of their faces.
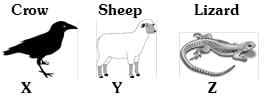
Q. Select the option that correctly categories the given adaptation for predator and prey animals.