Heredity - 3 - Class 10 MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Science Class 10 - Heredity - 3
Which of the following statement is not correct regarding variation in species?
Some dinosaurs had feathers although they could not fly but birds have feathers that help them to fly. In the context of evolution this means that
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
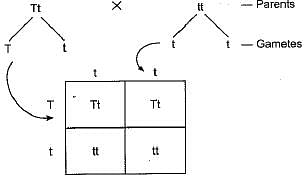
One tall pea plant and one dwarf pea plant on crossing resulted in 50% tall and 50% dwarf pea plant. The plants which were crossed were
Wild cabbage has evolved into new varieties fike cabbage, broccoli and cauliflower by
A cross between a tall plant (TT) and short pea plant (tt) resulted in progeny that were all tall plants because
If yellow seeded wrinkled pea plant (YYrr) is crossed with green seeded round pea plant (yyRR), the seeds produced in F1 generation are
Natural selection is called ‘survival of the fittest'.Which of the following statements best describes an organism?
A zygote which has an X chromosome inherited from the father will develop into a
Which concept was not included in Charles Darwin’s theory of Natural Selection?
In human males all the chromosomes are paired perfectly except
(i) 21st chromosome
(ii) Y chromosome
(iii) small chromosome
(iv) X chromosome
What is the difference between genetic drift and change due to natural selection?
To study the natural phenomenon of inheritance, Mendel selected the pea plants. Which of the following properties were suitable for their studies?
(i) Plants would easily self pollinate or cross pollinate in nature.
(ii) Plants were easily grown in garden soil with a considerably shorter generation time.
(iii) Pea plants do not require the true-breeding for hybridisation experiments.
(iv) Many parts of the plant such as pod, seed, flower, cotyledons showed distinct phenotypes.
|
85 videos|437 docs|75 tests
|