Test: Transcription (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 12 - Test: Transcription (NCERT)
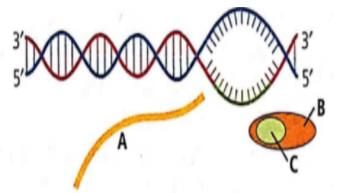
During transcription, the site of DNA molecule at which RNA polymerase binds is called
If the sequence of bases in DNA is GCTTAGGCAA then the sequence of bases in its transcript will be
Menthyl guanosine triphosphate is added to the 5' end of hnRNA in a process of
In transcription in eukaryotes, heterogenous nuclear RNA (hn RNA) is transcribed by
The structural genes, in eukaryotes possess coding and non-coding sequences called as (i) and (ii) respectively.
What is the main difference between monocistronic and polycistronic structural genes?
Where are polycistronic structural genes mostly found?
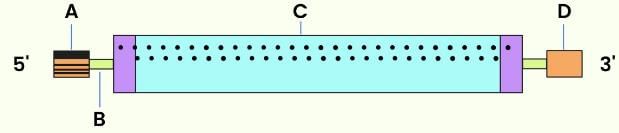
The given figure represents the process of transcription in bacteria.
Select the option which correctly labels A, B and C.
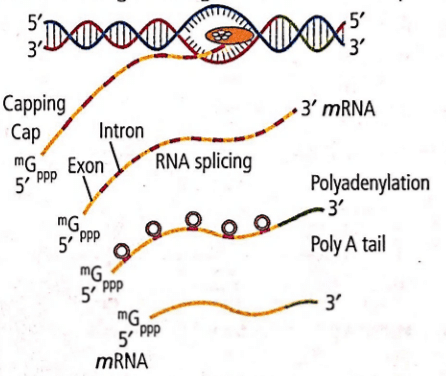
In eukaryotes, the process of processing of primary transcript involves
The process of copying genetic information from one strand of DNA to RNA is termed as __________
What is the function of exons in eukaryotic gene expression?
The fully processed hnRNA is called (i) and is transported out of the (ii) into (iii) for translation.
|
78 videos|277 docs|174 tests
|