DC Pandey Test: Current Electricity - JEE MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test Physics for JEE Main & Advanced - DC Pandey Test: Current Electricity
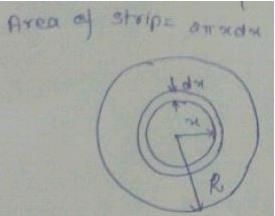
A brass disc and a carbon disc of same radius are assembled alternatively to make a cylindrical conductor. The resistance of the cylinder is independent of the temperature. The ratio of thickness of the brass disc to that of the carbon disc is ______. α is temperature coefficient of resistance & Neglect linear expansion
Out of the following which is not a poor conductor ?
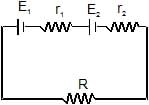
Under what condition current passing through the resistance R can be increased by short circuiting the battery of emf E2. The internal resistances of the two batteries are r1 and r2 respectively.
ABCD is a square where each side is a uniform wire of resistance 1Ω. A point E lies on CD such that if a uniform wire of resistance 1W is connected across AE and constant potential difference is applied across A and C then B and E are equipotential.
Two current elements P and Q have current voltage characteristics as shown below :
Which of the graphs given below represents current voltage characteristics when P and Q are in series.
A battery is of emf E is being charged from a charger such that positive terminal of the battery is connected to terminal A of charger and negative terminal of the battery is connected to terminal B of charger. The internal resistance of the battery is r.
Which of the following quantities do not change when a resistor connected to a battery is heated due to the current?
A metallic conductor of irregular cross-section is as shown in the figure. A constant potential difference is applied across the ends (1) and (2). Then :
A current passes through a wire of nonuniform cross section. Which of the following quantities are independent of the cross-section?
A simple circuit contains an ideal battery and a resistance R. If a second resistor is placed in parallel with the first.
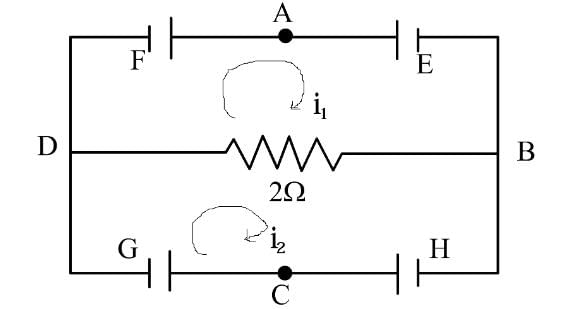
In the circuit shown E, F, G and H are cells of e.m.f. 2V, 1V, 3V and 1V respectively and their internal resistances are 2W, 1W, 3W and 1W respectively.
The equivalent resistance of a group of resistances is R. If another resistance is connected in parallel to the group, its new equivalent becomes R1 & if it is connected in series to the group, its new equivalent becomes R2 we have
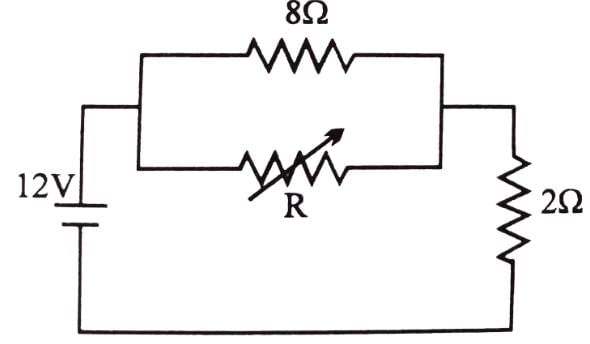
The value of the resistance R in figure is adjusted such that power dissipated in the 2W resistor is maximum. Under this condition
Statement-1 : When two conducting wires of different resistivity having same cross section area are joined in series, the electric field in them would be equal when they carry current.
Statement-2 : When wires are in series they carry equal current.
Statement-1 : Potential difference across the terminals of a battery is always less than its emf.
Statement-2 : A battery always has some internal resistance.
Statement-1 : Knowing that rating is done at steady state of the filament, an electric bulb connected to a source having rated voltage consumes more than rated power just after it is switched on.
Statement-2 : When filament is at room temperature its resistance is less than its resistance when the bulb is fully illuminated
Statement-1 : When a battery is supplying power to a circuit, work done by electrostatic forces on electrolyte ions inside the battery is positive
Statement-2 : Electric field is directed from positive to negative electrode inside a battery
Statement-1 : Conductivity of a metallic conductor decreases with increase in temperature.
Statement-2 : On increasing temperature the number of free electrons in the metallic conductar decreases.
A current of 0.50 ampere is passing through a CuSO4 solution. How many Cu++ions will be deposited on cathode in 10 seconds ?
A copper wire of radius 0.1 mm and resistance 1 kW is connected across a power supply of 20 V. How many electrons are transferred per second between the supply and the wire at one end ?
A wire has a length of 2.0 m and a resistance of 5.0 W. Find the electric field existing inside the wire if it carries a current of 10 A.
A car has a fresh storage battery of emf 12 V and internal resistance 5.0 × 10-2W. If the starter draws a current of 90 A, what is the terminal voltage of the battery when the starter is on ?
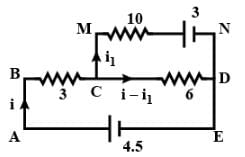
Find the current through the 10 W resistor shown in figure.
|
289 videos|635 docs|184 tests
|





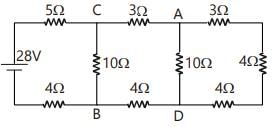 RAD=1/(1/10)+(1/3+4+3)=5Ω
RAD=1/(1/10)+(1/3+4+3)=5Ω