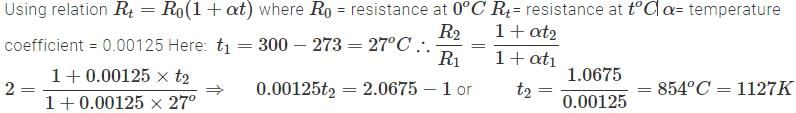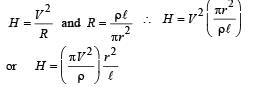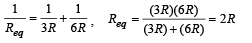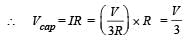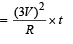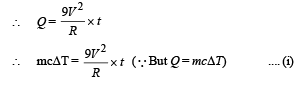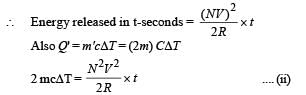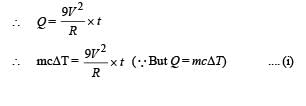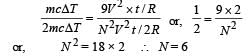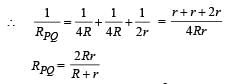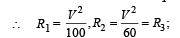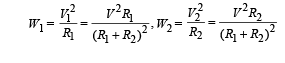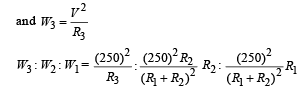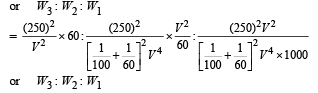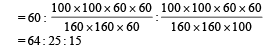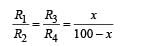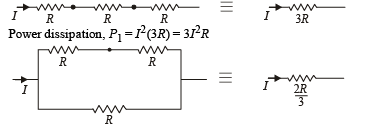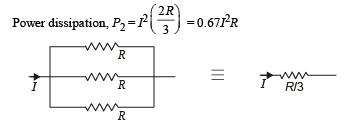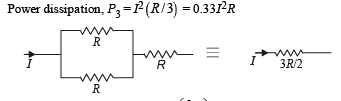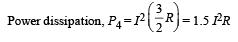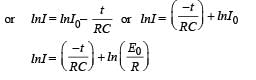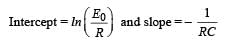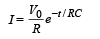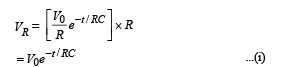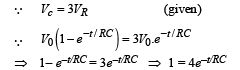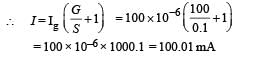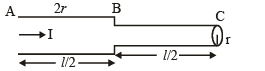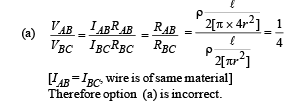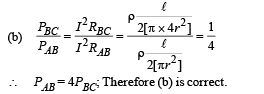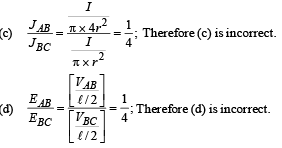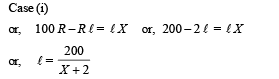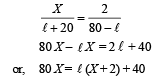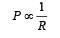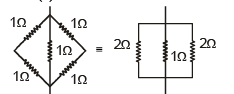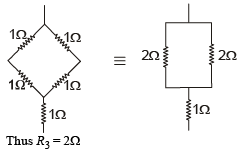JEE Advanced (Single Correct MCQs): Current Electricity - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced - JEE Advanced (Single Correct MCQs): Current Electricity
The temperature coefficient of resistance of a wire is 0.00125 per °C. At 300 K, its resistance is 1 ohm. This resistance of the wire will be 2 ohm at.
A constant voltage is applied between the two ends of a uniform metallic wire. Some heat is developed in it. The heat developed is doubled if
The electrostatic field due to a point charge depends on the distance r as 1/r2 . Indicate which of the following quantities shows same dependence on r.
In the circuit shown in fig the heat produced in the 5 ohm resistor due to the current flowing through it is 10 calories per second.
The heat generated in the 4 ohms resistor is
The current i in the circuit (see Fig) is
A piece of copper and another of germanium are cooled from room temperature to 80° K. The resistance of
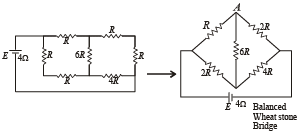
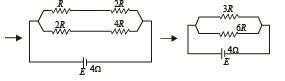
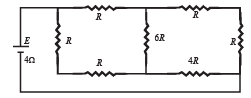
A battery of internal resistance 4Ω is connected to the network of resistances as shown. In order that the maximum power can be delivered to the network, the value of R in Ω should be
In the circuit P≠R , the reading of the galvanometer is same with switch S open or closed. Then

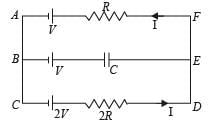
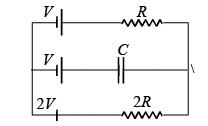
In the given circuit, with steady current, the potential drop across the capacitor must be
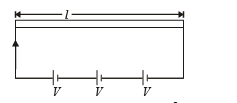
A wire of length L and 3 identical cells of negligible internal resistances are connected in series. Due to the current, the temperature of the wire is raised by ΔT in a time t. A number N of similar cells is now connected in series with a wire of the same material and cross-section but of length 2L. The temperature of the wire is raised by the same amount ΔT in the same time t. the value of N is
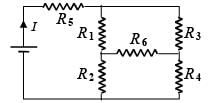
In the given circuit, it is observed that the current I is independent of the value of the resistance R6. Then the resistance values must satisfy
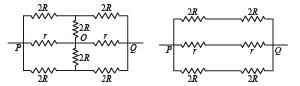
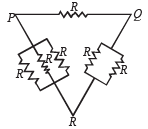
The effective resistance between points P and Q of the electrical circuit shown in the figure is

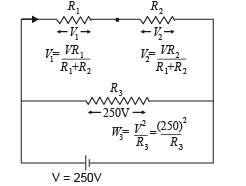
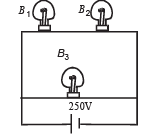
A 100 W bulb B1, and two 60 W bulb B2 an d B3, are connected to a 250 V source, as shown in figure. Now W1, W2 and W3 are the output powers of the bulbs B1, B2 and B3, respectively. Then
Express which of the following set ups can be used to verify Ohm’s law?
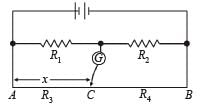
In the shown arrangement of the experiment of the meter bridge if AC corresponding to null deflection of galvanometer is x, what would be its value if the radius of the wire AB is doubled?

The three resistance of equal value are arranged in the different combinations shown below. Arrange them in increasing order of power dissipation.
Shown in figure is a Post Office box. In order to calculate the value of external resistance, it should be connected between
Six identical resistors are connected as shown in the figure.The equivalent resistance will be
A capacitor is charged using an exter nal batter y with a resistance x in series. The dashed line shows the variation of ln I with respect to time. If the resistance is changed to 2x, the new graph will be 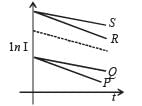
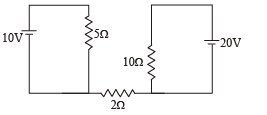
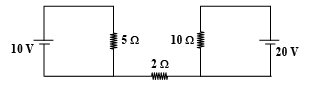
Find out the value of current through 2Ω resistance for the given circuit.
A 4 μF capacitor, a resistance of 2.5 MΩ is in series with 12 V battery. Find the time after which the potential difference across the capacitor is 3 times the potential difference across the resistor. [Given ln(2) = 0.693]
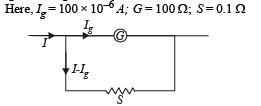
A moving coil galvanometer of resistance 100 Ω is used as an ammeter using a resistance 0.1 Ω. The maximum deflection current in the galvanometer is 100 μA. Find the minimum current in the circuit so that the ammeter shows maximum deflection
An ideal gas is filled in a closed rigid and thermally insulated container. A coil of 100 Ω resistor carrying current 1 A for 5 minutes supplies heat to the gas. The change in internal energy of the gas is
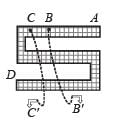
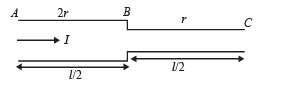
If a steady current I is flowing through a cylindrical element ABC. Choose the correct relationship
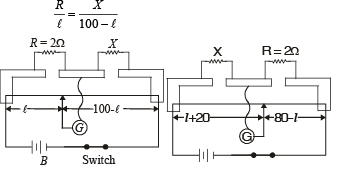
A resistance of 2Ω is connected across one gap of a metrebridge (the length of the wire is 100 cm) and an unknown resistance, greater than 2Ω, is connected across the other gap. When these resistances are interchanged, the balance point shifts by 20 cm. Neglecting any corrections, the unknown resistance is
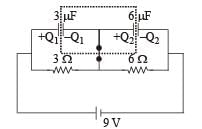
A circuit is connected as shown in the figure with the switch S open. When the switch is closed, the total amount of charge that flows from Y to X is
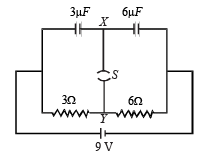
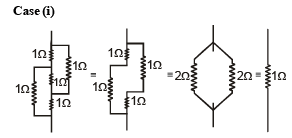
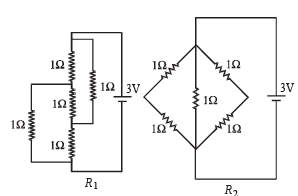
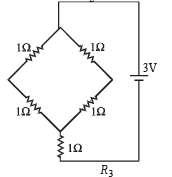
Figure shows three resistor configurations R1, R2 and R3 connected to 3V battery. If the power dissipated by the configuration R1, R2 and R3, is P1, P2 and P3, respectively, then –
Incandescent bulbs are designed by keeping in mind that the resistance of their filament increases with the increase in temperature. If at room temperature, 100 W, 60 W and 40 W bulbs have filament resistances R100, R60 and R40, respectively, the relation between these resistances is
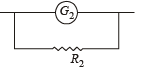
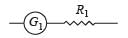
To verify Ohm’s law, a student is provided with a test resistor RT, a high resistance R1, a small resistance R2, two identical galvanometers G1 and G2, and a variable voltage source V. The correct circuit to carry out the experiment is
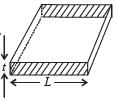
Consider a thin square sheet of side L and thickness t, made of a material of resistivity ρ. The resistance between two opposite faces, shown by the shaded areas in the figure is
|
446 docs|930 tests
|