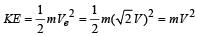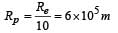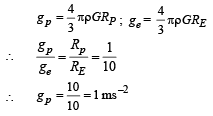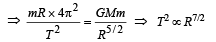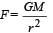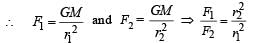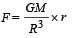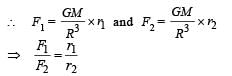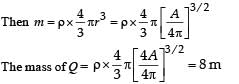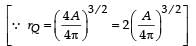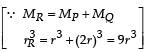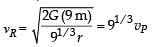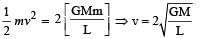JEE Advanced (Single Correct MCQs): Gravitation - JEE MCQ
16 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Advanced (Single Correct MCQs): Gravitation
If the radius of the earth were to shrink by one percent, its mass remaining the same, the acceleration due to gravity on the earth’s surface would
If g is the acceleration due to gravity on the earth’s surface, the gain in the potential energy of an object of mass m raised from the surface of the earth to a height equal to the radius R of the earth, is
If the distance between the earth and the sun were half its present value, the number of days in a year would have been
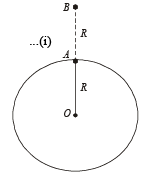
A geo-stationary satellite orbits around the earth in a circular orbit of radius 36,000km. Then, the time period of a spy satellite orbiting a few hundred km above the earth's surface (Rearth = 6,400km) will approximately be
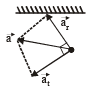
A simple pendulum is oscillating without damping. When the displacement of the bob is less than maximum, its acceleration vector ar is correctly shown in :
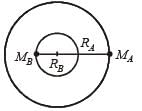
A binary star system consists of two stars A and B which have time period TA and TB, radius RA and RB and mass MA and MB. Then
A spherically symmetric gravitational system of particles has a mass density 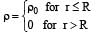 where ρ0 is a constant. A test mass can undergo circular motion under the influence of the gravitational field of particles. Its speed v as a function of distance r (0 < r < ∞) from the centre of the system is represented by –
where ρ0 is a constant. A test mass can undergo circular motion under the influence of the gravitational field of particles. Its speed v as a function of distance r (0 < r < ∞) from the centre of the system is represented by –
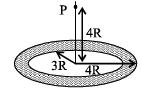
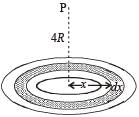
A thin uniform annular disc (see figure) of mass M has outer radius 4R and inner radius 3R. The work required to take a unit mass from point P on its axis to infinity is
A satellite is moving with a constant speed ‘V’ in a circular orbit about the earth. An object of mass ‘m’ is ejected from the satellite such that it just escapes from the gravitational pull of the earth. At the time of its ejection, the kinetic energy of the object is
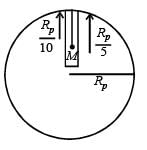
A planet of radius 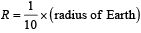 has the same mass density as Earth. Scientists dig a well of depth R/5 onit and lower a wire of the same length and a linear mass density 10–3 kg m–1 into it. If the wire is not touching anywhere, the force applied at the top of the wire by a person holding it in place is (take the radius of Earth = 6 × 106 m and the acceleration due to gravity on Earth is 10 ms–2)
has the same mass density as Earth. Scientists dig a well of depth R/5 onit and lower a wire of the same length and a linear mass density 10–3 kg m–1 into it. If the wire is not touching anywhere, the force applied at the top of the wire by a person holding it in place is (take the radius of Earth = 6 × 106 m and the acceleration due to gravity on Earth is 10 ms–2)
Imagine a light planet revolving around a very massive star in a circular orbit of radius R with a period of revolution T. If the gravitational force of attraction between the planet and the star is proportional to R–5/2
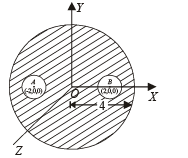
A solid sphere of uniform density and radius 4 units is located with its centre at the origin O of coordinates. Two spheres of equal radii 1 unit, with their centres at A (–2, 0 ,0) and B (2, 0, 0) respectively, are taken out of the solid leaving behind spherical cavities as shown in fig Then :
The magnitudes of the gravitational field at distance r1 and r2 from the centre of a uniform sphere of radius R and mass m are F1 and F2 respectively. Then:
A satellite S is moving in an elliptical orbit around the earth. The mass of the satellite is very small compared to the mass of the earth.
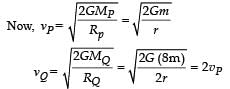
Two spherical planets P and Q have the same uniform density ρ, masses MP and MQ and surface areas A and 4A respectively. A spherical planet R also has uniform density ρ and its mass is (MP + MQ). The escape velocities from the planets P, Q and R are VP, VQ and VR, respectively. Then
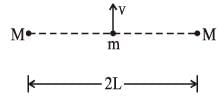
Two bodies, each of mass M, are kept fixed with a separation 2L. A particle of mass m is projected from the midpoint of the line joining their centres, perpendicular to the line. The gravitational constant is G. The correct statement(s) is (are)


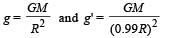
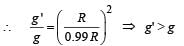
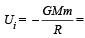 Initial potential energy of the system.
Initial potential energy of the system.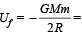 Final P.E. of the system.
Final P.E. of the system.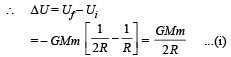
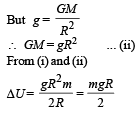

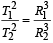
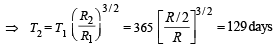
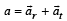
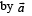
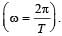
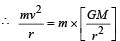 where M is the total mass of the
where M is the total mass of the
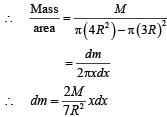
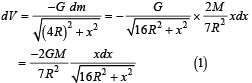
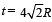
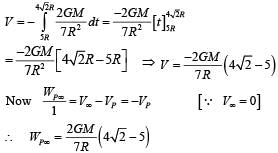
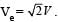 The kinetic energy at the time of ejection
The kinetic energy at the time of ejection