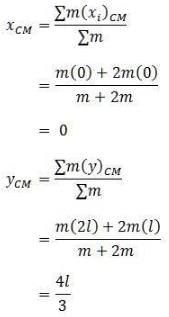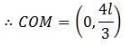JEE Previous Year Questions: Rotational Motion - NEET MCQ
21 Questions MCQ Test Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET - JEE Previous Year Questions: Rotational Motion
A solid sphere, a hollow sphere and a ring are released from top of an inclined plane (frictionless) so that they slide down the plane. Then maximum acceleration down the plane is for (no rolling)
[AIEEE 2002]
Moment of inertia of a circular wire of mass M and radius R about its diameter is
[AIEEE 2002]
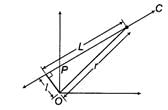
A particle of mass m moves along line PC with velocity v as shown. What is the angular momentum of the particle about O ?
[AIEEE 2002]

Initial angular velocity of a circular disc of mass M is w1. Then two small spheres of mass m are attached gently to two diametrically opposite points on the edge of the disc. What is the final angular velocity of the disc ?
[AIEEE 2002]
Let be the force acting on a particle having position vector
and
be the torque of this force about the origin. Then
[AIEEE 2003]
A particle performing uniform circular motion has angular momentum L. If its angular frequency is doubled and its kinetic energy halved, then the new angular momentum is
[AIEEE 2003]
A solid sphere is rotating in free space. If the radius of the sphere is increased keeping mass same, which one of the following will not be affected ?
[AIEEE 2004]
One solid sphere A and another hollow sphere B are of same mass and same outer radii. Their moment of inertia about their diameters are respectively IA and IB such that
[AIEEE 2004]
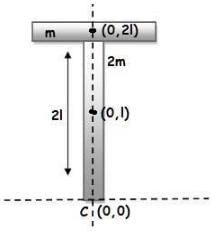
A T shaped object with dimensions shown in the figure, is lying on a smooth floor. A force is applied at the point P parallel to AB, such that the object has only the translational motion without rotation. Find the location of P with respect to C.
[AIEEE 2005]
The moment of inertia of uniform semicircular disc of mass M and radius r about a line perpendicular to the plane of the disc through the centre is
[AIEEE 2005]
An angular ring with inner and outer radii R1 and R2 is rolling without slipping with a uniform angular speed. The ratio of the forces experienced by the two particles situated on the inner and outer parts of the ring, is
[AIEEE 2005]
A thin circular ring of mass m and radius R is rotating about its axis with a constant angular velocity w. Two objects each of mass M are attached gently to the opposite ends of a diameter of the ring. The ring now rotates with an angular velocity w' =
[AIEEE 2006]
Four point masses, each of value m, are placed at the corners of a square ABCD of side l. The moment of inertia of this system about an axis passing through A and parallel to BD is
[AIEEE 2006]
Angular momentum of the particle rotating with a central force is constant due to
[AIEEE 2007]
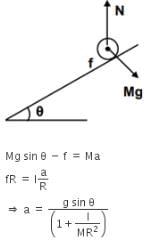
A round uniform body of radius R, mass M and moment of inertia I, rolls down (without slipping) an inclined plane making an angle q with the horizontal. Then its acceleration is
[AIEEE 2007]
For the given uniform square lamina ABCD, whose centre is O
[AIEEE 2007]
Consider a uniform square plate of side a and mass m. The moment of inertia of this plate about an axis perpendicular to its plane and passing through one of its corners is
[AIEEE 2008]
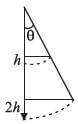
A thin uniform rod of length l and mass m is swinging freely about a horizontal axis passing through its end. Its maximum angular speed is w. Its centre of mass rises to maximum height of
[AIEEE 2009]
A pulley of radius 2 m is rotated about its axis by a force F = (20t _ 5t2) N (where t is measured in seconds) applied tangentially. It the moment of inertia of the pulley about its axis of rotation is 10 kg-m2 the number of rotations made by the pulley before its direction of motion if reserved, is
[AIEEE 2011]
A thin horizontal circular disc is rotating about a vertical axis passing through its centre. An insect is at rest at a point near the rim of the disc. The insect now moves along a diameter of the disc to reach its other end. During the journey of the insect, the angular speed of the disc.
[AIEEE 2011]
A hoop of radius r and mass m rotating with an angular velocity w0 is placed on a rough horizontal surface. The initial velocity of the centre of the hoop is zero. What will be the velocity of the centre of the hoop when it cases to slip ?
[JEE Mains 2013]
|
9 docs|1259 tests
|