R.C. Mukherjee Test: Chemical Equilibrium - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET - R.C. Mukherjee Test: Chemical Equilibrium
For the reaction equilibrium :
N2O4 (g) 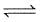 2NO2(g) ; the concentration of N2O4 and NO2 at equilibrium are 4.8 × 10-2 and 1.2 × 10-2 mol/L respectively. The value of Kc for the reaction is :
2NO2(g) ; the concentration of N2O4 and NO2 at equilibrium are 4.8 × 10-2 and 1.2 × 10-2 mol/L respectively. The value of Kc for the reaction is :
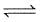 2NO2(g) ; the concentration of N2O4 and NO2 at equilibrium are 4.8 × 10-2 and 1.2 × 10-2 mol/L respectively. The value of Kc for the reaction is :
2NO2(g) ; the concentration of N2O4 and NO2 at equilibrium are 4.8 × 10-2 and 1.2 × 10-2 mol/L respectively. The value of Kc for the reaction is :What is the equilibrium constant for the reaction P4(s) + 5O2(g) 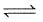 P4O10(s) :
P4O10(s) :
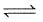 P4O10(s) :
P4O10(s) :The equilibrium constant for the reaction :
N2(g) + O2(g)  2NO(g) at temperature
2NO(g) at temperature
T is 4 × 10-4. The value of Kc for the reaction.
NO(g) 
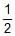 N2(g) +
N2(g) + 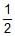 O2(g) at the same temperature is :
O2(g) at the same temperature is :
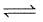 2NO(g) at temperature
2NO(g) at temperature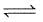
The equilibrium constant for the given reaction :
SO3(g) 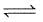 SO2(g) +
SO2(g) + O2(g); Kc = 4.9 × 10-2
The value of Kc for the reaction :
2SO2(g) + O2(g) 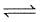 2SO3(g), will be
2SO3(g), will be
For the following three reactions 1, 2 and 3, equilibrium constants are given :
(1) CO(g) + H2O(g)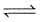 CO2(g)+H2(g) ; K1
CO2(g)+H2(g) ; K1
(2) CH4(g)+H2O(g)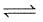 CO(g)+3H2(g) ; K2
CO(g)+3H2(g) ; K2
(3) CH4(g)+2H2O(g)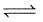 CO2(g)+4H2(g) ; K3
CO2(g)+4H2(g) ; K3
Which of the following relations is correct ?
Consider following reactions in equilbrium with equilibrium concentration 0.01M of every species
(I) PCl5(g)  PCl3(g) + Cl2(g)
PCl3(g) + Cl2(g)
(II) 2HI(g)  H2(g) + I2(g)
H2(g) + I2(g)
(III) N2(g) + 3H2 (g)  2NH3(g)
2NH3(g)
Extent of the reactions taking place is :
A definite amount of solid NH4HS is placed in a flask already containing ammonia gas at a certain temperature and 0.50 atm pressure. NH4HS decomposes to give NH3 and H2S and at equilibrium total pressure in flask is 0.84 atm. The equilibrium constant for the reaction is :
For the reaction 3A(g) + B(g) 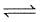 2C(g) at a given temperature, Kc = 9.0. What must be the volume of the flask, if a mixture of 2.0 mol each of A, B and C exist in equilibrium ?
2C(g) at a given temperature, Kc = 9.0. What must be the volume of the flask, if a mixture of 2.0 mol each of A, B and C exist in equilibrium ?
Sulfide ion in alkaline solution reacts with solid sulfur to form polysulfide ions having formulas S22-, S32-, S42- and so on. The equilibrium constant for the formation of S22- is 12 (K1) & for the formation of S32- is 132 (K2), both from S and S2-. What is the equilibrium constant for the formation of S32- from S22- and S
1 mole N2 and 3 mol H2 are placed in a closed container at a pressure of 4 atm. The pressure falls to 3 atm at the same temperature when the following equilibrium is attained.
N2(g) + 3H2(g) 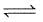 2NH3(g). The equilibrium constant Kp for dissociation of NH3 is :
2NH3(g). The equilibrium constant Kp for dissociation of NH3 is :
One mole of N2O4(g) at 300 K is left in a closed container under one atm. It is heated to 600 K when 20% by mass of N2O4 (g) decomposes to NO2(g). The resultant pressure is :
For the following gases equilibrium. N2O4(g) 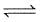 2NO2(g) Kp is found to be equal to Kc. This is attained when temperature is
2NO2(g) Kp is found to be equal to Kc. This is attained when temperature is
For the reaction :
CO(g) + O2(g)
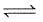 CO2(g), Kp/Kc is :
CO2(g), Kp/Kc is :
For the reaction :
2NO2(g) 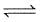 2NO(g) + O2(g) Kc = 1.8 × 10-6 at 184°C and R = 0.083 JK-1mol-1. When Kp and Kc are compared at 184°C, it is found that :
2NO(g) + O2(g) Kc = 1.8 × 10-6 at 184°C and R = 0.083 JK-1mol-1. When Kp and Kc are compared at 184°C, it is found that :
PCl5 dissociation a closed container as :
PCl5(g) 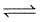 PCl3(g) + Cl2(g)
PCl3(g) + Cl2(g)
If total pressure at equilibrium of the reaction mixture is P and degree of dissociation of PCl5 is α, the partial pressure of PCl3 will be :
For the reaction : 2HI (g)  H2(g) + I2(g), the degree of dissociated (α) of HI(g) is related to equilibrium constant Kp by the expression :
H2(g) + I2(g), the degree of dissociated (α) of HI(g) is related to equilibrium constant Kp by the expression :
The equilibrium constant for the reaction
A(g) + 2B(g) 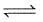 C(g) is 0.25 dm6 mol-2. In a volume of 5 dm3, what amount of A must be mixed with 4 mol of B to yield 1 mol of C at equilibrium
C(g) is 0.25 dm6 mol-2. In a volume of 5 dm3, what amount of A must be mixed with 4 mol of B to yield 1 mol of C at equilibrium
For the reaction
A(g) + 2B(g) 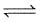 C(g) + D(g); Kc = 1012 If the initial moles of A, B, C and D are 0.5, 1, 0.5 and 3.5 moles respectively in a one litre vessel. What is the equilibrium concentration of B ?
C(g) + D(g); Kc = 1012 If the initial moles of A, B, C and D are 0.5, 1, 0.5 and 3.5 moles respectively in a one litre vessel. What is the equilibrium concentration of B ?
The equilibrium constant Kc for the reaction,
A(g) + 2B(g) 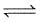 3C(g) is 2 × 10-3
3C(g) is 2 × 10-3
What would be the equilibrium partial pressure of gas C if initial pressure of gas A & B are 1 & 2 atm respectively.
A 20.0 litre vessel initially contains 0.50 mole each of H2 and I2 gases. These substances react and finally reach an equilibrium condition. Calculate the equilibrium concentration of HI if Keq = 49 for the reaction H2 + I2 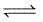 2HI.
2HI.
A vessel of 250 litre was filled with 0.01 mole of Sb2S3 and 0.01 mole of H2 to attain the equilibrium at 440°c as
Sb2S3(s) + 3H2(g) 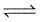 2Sb(s) + 3H2S(g).
2Sb(s) + 3H2S(g).
After equilibrium the H2S formed was analysed by dissolving it in water and treating with excess of Pb2+ to give. 1.195 g of PbS (Molecular weight = 239) precipitate.
What is value of Kc of the reaction at 440°C ?
The equilibrium constant for the reaction
CO(g) + H2O(g) 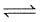 CO2(g) + H2(g) is 3 at 500 K. In a 2 litre vessel 60 gm of water gas [equimolar mixture of CO(g) and H2(g)] and 90 gm of steam is initially taken.
CO2(g) + H2(g) is 3 at 500 K. In a 2 litre vessel 60 gm of water gas [equimolar mixture of CO(g) and H2(g)] and 90 gm of steam is initially taken.
What is the equilibrium concentration of H2(g) at equilibrium (mole/L) ?
At 87°C, the following equilibrium is established
H2(g) + S(s) 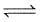 H2S(g) Kp = 7 × 10-2
H2S(g) Kp = 7 × 10-2
If 0.50 mole of hydrogen and 1.0 mole of sulfur are heated to 87°C in 1.0 L vessel, what will be the partial pressure of H2S at equilibrium ?
At certain temperature (T) for the gas phase reaction
2H2O(g)+2Cl2(g)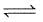 4HCl(g)+O2(g) ; Kp =12×108 atm
4HCl(g)+O2(g) ; Kp =12×108 atm
If Cl2, HCl & O2 are mixed in such a manner that the partial pressure of each is 2 atm and the mixture is brought into contact with excess of liquid water. What would be approximate partial pressure of Cl2 when equilibrium is attained at temperature (T) ?
[Given : Vapour pressure of water is 380 mm Hg at temperature (T)]
At 675 K, H2(g) and CO2(g) react to form CO(g) and H2O(g), Kp for the reaction is 0.16. If a mixture of 0.25 mole of H2(g) and 0.25 mol of CO2 is heated at 675 K, mole% of CO(g) in equilibrium mixture is :
In which of the following reactions, increase in the pressure at constant temperature does not affect the moles at equilibrium.
Change in volume of the system does not alter the number of moles in which of the following equilibrium
The conditions favourable for the reaction :
2SO2(g)+O2(g) 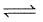 2SO3(g) ; ΔH° = -198 kJ are :
2SO3(g) ; ΔH° = -198 kJ are :
The exothermic formation of ClF3 is represented by the equation :
Cl2(g) + 3F2(g) 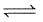 2ClF3(g) ; ΔH = -329 kJ
2ClF3(g) ; ΔH = -329 kJ
Which of the following will increase the quantity of ClF3 in an equilibrium mixture of Cl2, F2 and ClF3 :
Densities of diamond and graphite are 3.5 and 2.3 gm/mL. respectively and for
C(diamond) 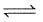 C (graphite) ; ΔH= -1.9 kJ/mole favourable conditions for formation of diamond are
C (graphite) ; ΔH= -1.9 kJ/mole favourable conditions for formation of diamond are
|
9 docs|1259 tests
|





















