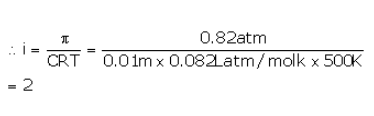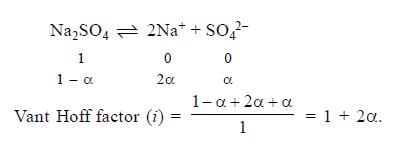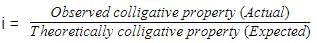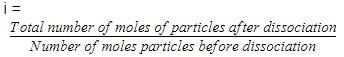Test: Association & Dissociation - JEE MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced - Test: Association & Dissociation
The osmotic pressure of a 0.010 M MgSO4 solution at 500 K is 0.82 atm. Calculate , the van’t Hoff factor, for this MgSO4 solution.
Benzoic acid dissolved in benzene will show a molecular weight of
Molar mass that is either lower or higher than expected or normal molar mass is called as
0.01 M solution of common salt (NaCl) and (CH3COOH ) is taken. If their osmotic pressures are p1and p2 resp., what will be the correct statement correlating their osmotic pressures?
If α is the degree of dissociation of Na2SO4, the vant Hoff’s factor (i) used for calculating the molecular mass is
Increasing the temperature of solution of a weak electrolyte will cause
What is the freezing point of 0.1 m glucose solution in water? For water Kf is 1.86 K kg/mol?
The ratio of osmotic pressure of a 1:1 electrolyte AB to that of a non electrolyte solute of same concentration is
|
446 docs|930 tests
|