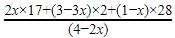Test: Chemical Equation - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET - Test: Chemical Equation
Two flasks A and B of equal volume containing 1 mole and 2 mole of O3 respectively, are heated to the same temperature. When the reaction 2O3 → 3O2 practically stops, then both the flasks shall have
A 10L container at 300K contains CO2 gas at pressure of O.2 atm and an excess solid CaO (neglect the volume of solid CaO). The volume of container is now decreased by moving the movable piston fitted in the container. What will be the maximum volume of container when pressure of CO2 attains its maximum value given that
CaCO3 (s) → CaO(s) + CO2(g) Kph = 0.800 atm
An equilibrium mixture at 700 K of 0.50 M N2, 3.00 M H2 and 2.00 M NH3 is present in a container. Now if this equilibrium is disturbed by adding N2 so that its concentration becomes 1.50 M just after addition then which of the following graphs represents the above situation more appropriately –
At 1400 K, Kc= 2.5x10 +3 for the reaction CH4(g) + 2H2S(g) CS2(g) + 4H2(g) . A 10.0L reaction vessel at 1400 K contains 2.00 mole of CH4, 3.0 mol of CS2, 3.0 mole of H2 and 4.0 mole of H2S. Then
The graph which will be representing all the equilibrium concentrations for the reaction
N2O4 → 2NO2 (g) will be :
(the concentrations of N2O4 (g) and of NO (g) for which the following eaction will be at equilibrium will lie
In a basic aqueous solution chloromethane undergoes a substitution reaction in which Cl is replaced by OH– as.
CH3Cl (aq) + OH- → CH3OH(aq) + Cl(aq)
The equilibrium constant of above reaction C, =1 x 10'6. If a solution is prepared by mixing equal volumes of 0.1 M CH3CI and 0.2 M NaOH (100% dissociated) then [OH-] concentration at equilibrium in mixture will be:
For the chemical equilibrium,
CaCO3 (S) → CaO(s) + CO2 (g)
ΔHf° can be determined from which one of the following plots ?
At a certain temperature the following equilibrium is established, CO(g) + N02(g) → CO(g) + NO(g) One mole of each of the four gas is mixed in one litre container and the reaction is allowed to reach equilibrium state. When excess of baryta water (Ba(OH)2) is added to the equilibrium mixture, the weight of white ppt (BaCO3) obtained is 236.4 gm. The equilibrium constant Cc of the reaction is (Ba = 137)
At temperature T, the compound AB2 (g) dissociates according to the reaction, 2AB2 (g) 2 AB(g) + B2(g).With a degree of dissociation x, which is small compared with unity. Deduce the expression for x in terms of the equilibrium constant, Kp and the total pressure, P.
2 AB(g) + B2(g).With a degree of dissociation x, which is small compared with unity. Deduce the expression for x in terms of the equilibrium constant, Kp and the total pressure, P.
Equilibrium constant for the given reaction is C = 1020 at temperature 300 K
A(s) +2B(aq)  2C (s) + D(aq.)K = 1020
2C (s) + D(aq.)K = 1020
The equilibrium conc. of B starting with mixture of 1 mole of A and 1/3 mote/titre of B at 300 K is
10lt box contain O3 and O2 at equilibrium at 2000 K. The ΔG0 = –534.52 kJ at 8 atm equilibrium
pressure.The following equilibrium is present in the container
2o3(g) 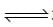 3O2 (g). the partial pressure of O3 will be ( In 10 = 2.3, R = 8.3 J mol-1 K-1)
3O2 (g). the partial pressure of O3 will be ( In 10 = 2.3, R = 8.3 J mol-1 K-1)
Solid ammonium carbamate dissociates to give ammonia and carbon dioxid as follows:
NH2COONH4(s) 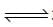 2NH5(g) + CO2(g)
2NH5(g) + CO2(g)
At equilibrium, ammonia is added such that partial pressures of NH5 now equals the original total pressure. Calculate the ratio of the total pressures now to the original total pressure.
The reactions, PCl5 (g) 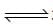 PCl5(g) + Cl2(g) and Cl2(g)
PCl5(g) + Cl2(g) and Cl2(g) CO2(g) + Cl2 (g) are simultaneously in equilibrium in an equilibrium box at constant volume. Afew moles of CO(g) are later introduced into the vessel. After some time, the new equilibrium concentration of
CO2(g) + Cl2 (g) are simultaneously in equilibrium in an equilibrium box at constant volume. Afew moles of CO(g) are later introduced into the vessel. After some time, the new equilibrium concentration of
In the Haber process for the industrial manufacture of ammonia involving the reaction, atm pressure in the presence of a catalyst a temperature of about 500°C is used. This is considered as optimum temperature for the process because
For the equilibrium of the reaction ,kP for the reaction at total pressure of P is:
What is the minimum mass of CaC05 (s), below which it decomposes completely, required to establish equilibrium in a 6.50 litre container for the reaction : [ KC = mole/litre]
CaCO3 (s)  CaO(s) + CO2(g)
CaO(s) + CO2(g)
The value of kp for the reaction at 27°C
is '1 atom'. At equilibrium in a closed container partial pressure of BrCI gas is 0.1 atm and at this temperature the vapour pressure of Br2(l) is also 0.1 atm. Then what will be minimum moles of Br2(l) to be added to 1 mole of C12 , initially, to get above equilibrium situation :
5 mol PCI3(g) and one mole N2 gas is placed in a closed vessel. At equilibrium PCI5(g) decomposes 20% and total pressure in to the container is found to be 1 atm. The kP for equilibrium
Degree of association can be defined as the number of moles of a particular substance associated per mole of the substance taken.
For example : If out of 10 mole of N2 , 3 mol of N2 combine with H2 to form NHL. then degree of association of N2 = 0.3.Consider the equilibrium situation : N2(g) + 3H2(g)  2NH3(g)
2NH3(g)
Initially N2 & H2 were mixed in 1 : 3 molar ratio and after long time the mean molar mass of the mixture was found to be 34/3g. The degree of association of N2 is
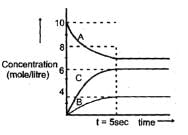
Attainment of the equilibrium A(g)  2C(g) +B(g) gave the gave the followeing graph. Find the correct option. (% dissociation = fraction dissociated x 100)
2C(g) +B(g) gave the gave the followeing graph. Find the correct option. (% dissociation = fraction dissociated x 100)
|
9 docs|1259 tests
|


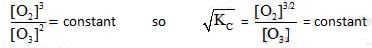
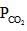 = maximum pressure of CO2 in the container to calculate maximum volume of container the
= maximum pressure of CO2 in the container to calculate maximum volume of container the 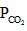 = 0.8 atm and none of
= 0.8 atm and none of 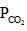 = 0.8 should get converted into CaCO3 (s)
= 0.8 should get converted into CaCO3 (s)
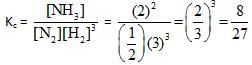
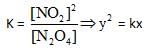
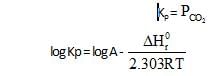
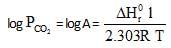
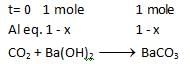
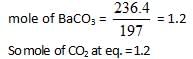
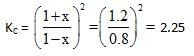
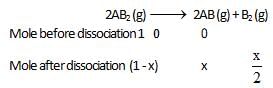
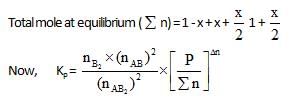
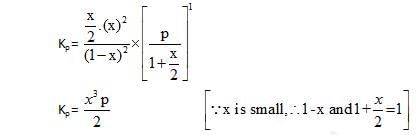
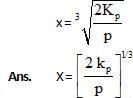
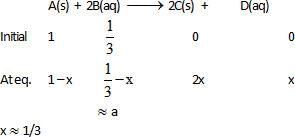
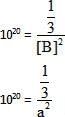
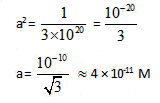
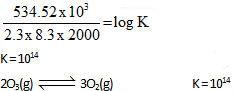
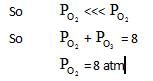
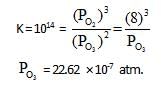
 CaO + Cl2
CaO + Cl2