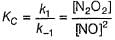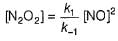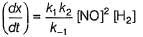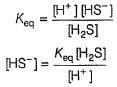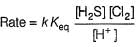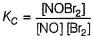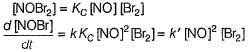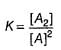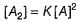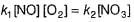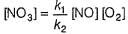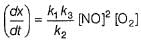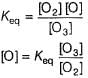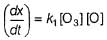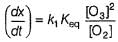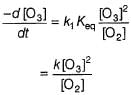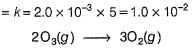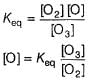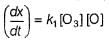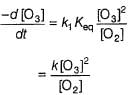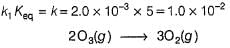Test: Collision Theory & Reaction Mechanism - NEET MCQ
22 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Collision Theory & Reaction Mechanism
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-14) This section contains 14 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
A chemical reaction proceeds through the following steps :
Step I, 2A ⇌ X fast
Step II, X+B ⇌ Y slow
Step III, Y+B ⇌ Product fast
Q. The rate law for the overall reaction is
Step II, X+B ⇌ Y slow
Step III, Y+B ⇌ Product fast
The following reaction obey rate law
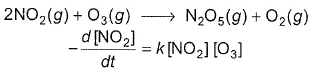
It can follow mechanism
I. NO2 + O3 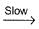 NO3 + O2 ,
NO3 + O2 ,
NO3+NO2 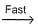 N2O5
N2O5
II. NO2 + O 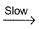 NO3
NO3
NO3+NO2 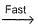 N2O5
N2O5
Select the correct mechanism.
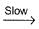 NO3 + O2 ,
NO3 + O2 , 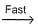 N2O5
N2O5 NO3
NO3 N2O5
N2O5A chemical reaction is said to take place through the various stages with ΔG° values indicated by the graph:
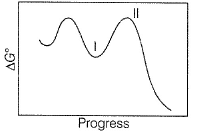
Stages I and II represent respectively
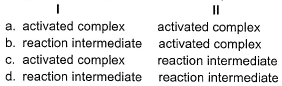
Following reaction takes place by mechanism:
Step I

Step II

Hence for the given reaction is
For the reaction,
A + 2B → C+ D
The rate law is k [A] [B] .
Select the correct statement.
For the reaction,
Mechanism is given by
Rate law is true, if
For the following SN reaction,
Rate-determining step is
Reaction between nitric oxide and hydrogen takes place by the following mechanism:
Q.
Rate of the overall reaction in terms of the concentration of the reactants is
Consider the following reaction,
The rate equation for this reaction is, rate = k[CI2] [H2S]
Which of these mechanisms is/are consistent with this rate equation?
[AIEEE2010]
The following mechanism has been proposed for the reaction,
It involves the following steps:
Q.
The order of the reaction w.r.t. NO(g) is
Consider the three following proposed mechanism for the overall equation.
Q.
Which mechanism predicts a third order reaction?
Consider the following proposed mechanism :
Based on the following steps:
Rate law is
Direction (Q. Nos. 15- 20) This section contains 3 paragraphs, each describing theory, experiments, data, etc., Six questions related to the paragraphs have been given. Each question has ONLY ONE correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage I
The ozone in the earth’s ozone layer decomposes according to the equation,
It involves
(Time is in seconds and concentration in mol L-1)
Q.
Rate of disappearance of O3 is
Passage I
The ozone in the earth’s ozone layer decomposes according to the equation,
It involves
(Time is in seconds and concentration in mol L-1)
Q.
What is the rate at a time of 50% decomposition of O3, when [O3]0 = 1.0 M?
Passage II
N2O5 decomposes according to the following equation:
The following mechanism has been given:
Q.
Rate of formation of O2 is given by
Passage II
N2O5 decomposes according to the following equation:
The following mechanism has been given:
Q.
Half-life period is independent of the concentration of N2O5. Thus,
Passage III
is believed to proceed through the following three step mechanism:
Q.
Identify the false statement.
Passage III
is believed to proceed through the following three step mechanism:
Q.
What is the rate equation of the reaction?
Direction (Q. Nos. 21 and 22) This section contains 2 questions. When worked out will result in one integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Consider the following proposed mechanism:
(rate constant =k ) to describe the overall equations
Q.
What is the order predicted by the proposed mechanism?
For the overall reaction between A and 6 to yield C and D, two mechanisms are proposed.
Q.
At what concentration of A and/or B will the inherent rates be equal?



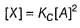
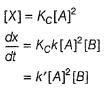
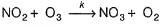
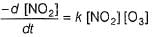
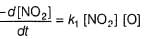
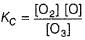
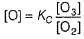
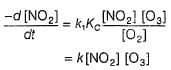

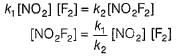
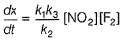
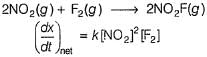

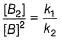
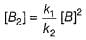
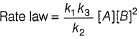
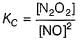
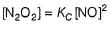
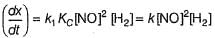
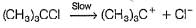
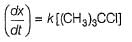
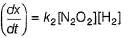 ...(1)
...(1)