Test: Common Ion Effect - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test NCERT Based Tests for NEET - Test: Common Ion Effect
The following equilibrium exists in aqueous solution
CH3COOH 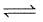 CH3COO- + H+
CH3COO- + H+
If dilute HCl is added:
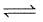 CH3COO- + H+
CH3COO- + H+If dilute HCl is added:
Consider KA, the potassium salt of a weak acid, HA. If a sample of KA is dissolved in water, with no other substances added, which of the following statements is true (approximately)?
If the value of the solubility product for AgBr is 4.0 x 10-12 at 25°C, calculate the solubility of AgBr(s) in water.
Role of NH4Cl in qualitative analysis of third group cations
A mixture of NH4Cl and NH4OH shows no change in pH upon addition small amount of HCl. This is because it is
We eat a variety of foods still pH of our blood does not change every time. The reason is
For HF, pKa = 3.45. What is the pH of an aqueous buffer solution that is 0.1M HF (aq) and 0.300 M KF (aq)?
|
684 tests
|



















