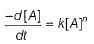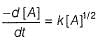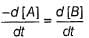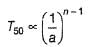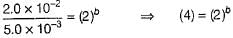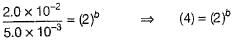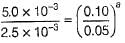Test: Determination of Rate of a Reaction - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 12 - Test: Determination of Rate of a Reaction
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-13) This section contains 13 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
For a given reaction,
A → Product,
rate = 1 x 10-4 Ms-1 at [A] = 0.01 M
rate = 1.41 x 10-4 Ms-1 at [A] = 0.02 M
Hence, rate law is
rate = 1.41 x 10-4 Ms-1 at [A] = 0.02 M
The rate law for a reaction between the substances A and 8 is given by
rate = k[A]n [B]m
If concentration of A is doubled and that of B is halved, the new rate as compared to the earlier rate would be
The rate equation for the reaction,
2A + B → C
is found to be, rate = k[A] [B]
Q. The correct statement in relation to this reaction is that the
For the reaction,
2 A+B → Product
The half-life period was independent of concentration of B. On doubling the concentration A, rate increases two times. Thus, unit of rate constant for this reaction is
Which of the following statements appears to the first order reaction?
2N2O5(CCl4) → 4NO2(CCl4) + O2(g)
For a reaction, time of 75% reaction is thrice of time of 50% reaction. Thus, order of the reaction is
For nth order reaction,
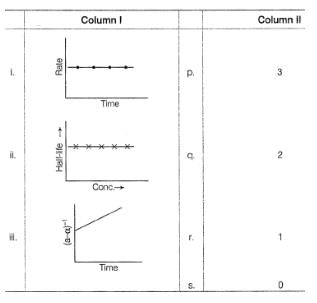
Graphs between log (rate) and log[A0] are of the type ([A0] is the initial concentration)
Lines P, Q, R and S are for the order
nA → Product
For the reaction, rate constant and rate of the reaction are equal, then on doubling the concentration of A, rate becomes,
For the simple reaction,
A → B
When [A] was changed from 0.502 mol dm-3 to 1.004 mol dm-3 half-life dropped from 52 s to 26 s at 300 K. Thus, order of the reaction is
For the following reaction,
Variation of T50 with [A] is shown
Q.
After 10 min volume of N2 (g) is 10 L and after complete reaction, volume of N2 (g) is 50 L. Thus, T50 is
Kinetics of the following reaction,
can be studied by
Graph between [B] and time t of the reaction of the type I for the reaction, A → B
Hence, graph between and time t will be of the type
If in the fermentation of sugar in an enzymatic solution that is 0.12 M, the concentration of sugar is reduced to 0.06 M in 10 h and to 0.03 M in 20 h. Thus, order of the reaction is
Direction (Q. No. 14) Choices for the correct combination of elements from Column I and Column II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which one is correct.
Direction (Q. Nos. 15-20) This section contains 3 paragraphs, each describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Six questions related to the paragraphs have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage I
Peroxy acetyl nitrite is an air pollutant, as it decomposes into radicals :
A sample of polluted air is analysed for its PAN content which is reported as molecules per litre of air at 298 K.
Q.
Determine the order of the PAN decomposition
Passage I
Peroxy acetyl nitrite is an air pollutant, as it decomposes into radicals :
A sample of polluted air is analysed for its PAN content which is reported as molecules per litre of air at 298 K.
Q.
Rate constant of the reaction is
Passage II
H The reaction between nitric oxide (NO) and hydrogen (H2)has been investigated by measuring the initial rate of decrease of pressure in known mixture of gases. The following results were obtained at 1000 K.
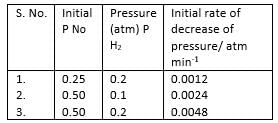
Q.
Overall order of the reaction is
Passage II
H The reaction between nitric oxide (NO) and hydrogen (H2)has been investigated by measuring the initial rate of decrease of pressure in known mixture of gases. The following results were obtained at 1000 K.

Q.
Rate constant of the overall reaction is
Passage III
A reaction between substances A and B is represented as:
A+B → C
Observations on the rate of this reaction are obtained as :
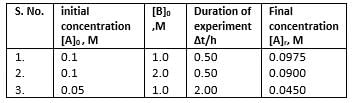
Q.
Order of the reaction w.r.t. A and B respectively are
Passage III
A reaction between substances A and B is represented as:
A+B → C
Observations on the rate of this reaction are obtained as :

Q.
Rate constant of the overall reaction is
|
108 videos|286 docs|123 tests
|