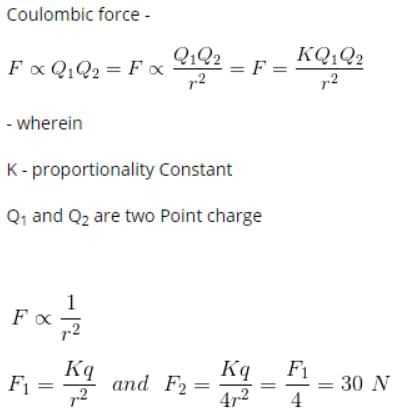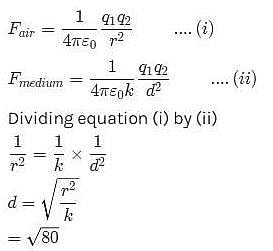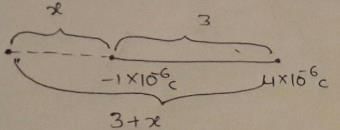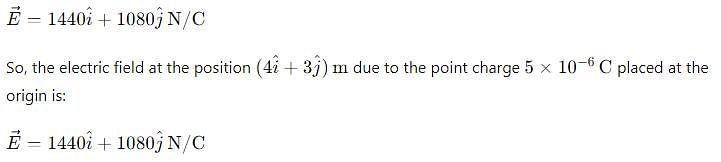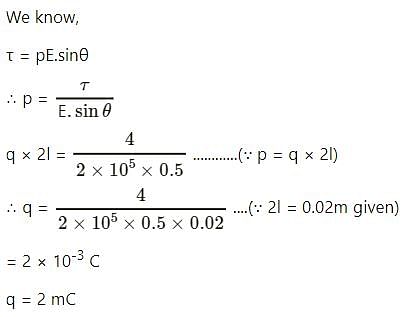Test: Electrostatics - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Physics Class 12 - Test: Electrostatics
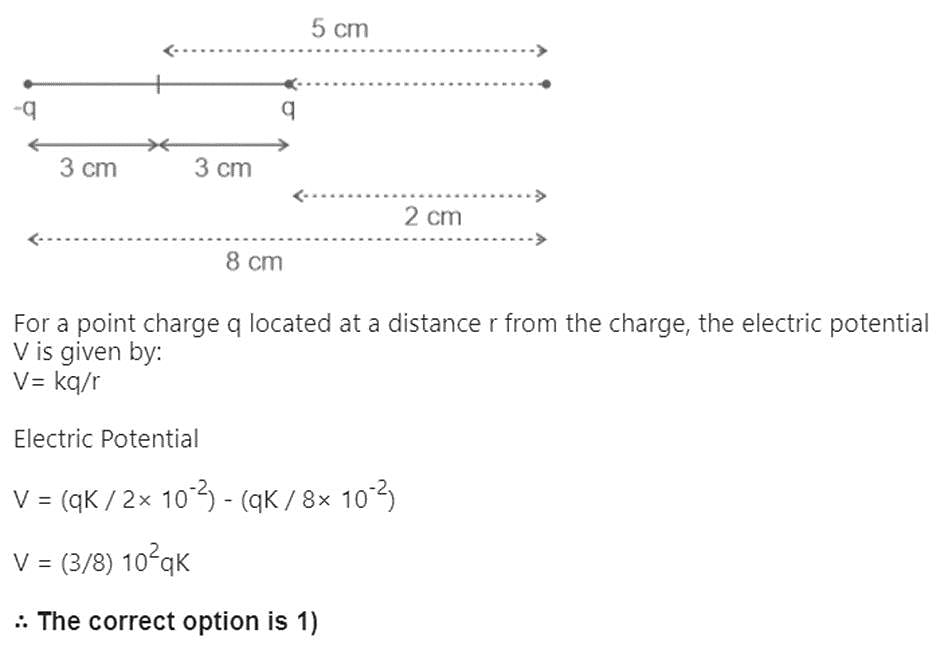
An electric dipole is placed as shown in the figure.
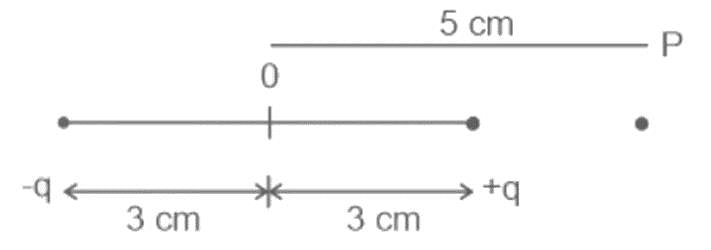
The electric potential (in 102 V) at point P due to the dipole is (ϵ0 = permittivity of free space and 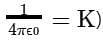 :
:

The electric potential (in 102 V) at point P due to the dipole is (ϵ0 = permittivity of free space and
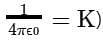 :
:The force between two charges is 120 N. If the distance between the charges is doubled, the force will be
Which one of the following statement regarding electrostatics is wrong ?
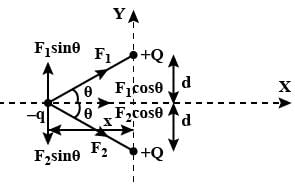
Two similar charge of +Q , as shown in figure are placed at A and B. _q charge is placed at point C midway between A and B. _q charge will oscillate if
When the distance between two charged particle is halved, the force between them becomes
Two point charges in air at a distance of 20 cm. from each other interact with a certain force. At what distance from each other should these charges be placed in oil of relative permittivity 5 to obtain the same force of interaction
A certain charge Q is divided at first into two parts, (q) and (Q-q). Later on the charges are placed at a certain distance. If the force of interaction between the two charges is maximum then
Two small balls having equal positive charge Q (Coulomb) on each are suspended by two insulating strings of equal length 'L' metre, from a hook fixed to a stand. The whole set up is taken in a satellite in to space where there is no gravity (state of weight lessness). Then the angle (q) between the two strings is
Two point charges -1 × 10-6 C and 4 × 10-6 C separated by 3 m distance have zero field location of
Two charges 4q and q are placed 30 cm. apart. At what point the value of electric field will be zero
If Q =2 coloumb and force on it is F=100 newtons , Then the value of field intensity will be
Four equal but like charge are placed at four corners of a square. The electric field intensity at the center of the square due to any one charge is E, then the resultant electric field intensity at centre of square will be
If mass of the electron = 9.1 × 10-31 Kg. Charge on the electron = 1.6 × 10-19coulomb and g = 9.8 m/s2. Then the intensity of the electric field required to balance the weight of an electron is
The electric field intensity at a point situated 4 meters from a point charge is 200 N/C. If the distance is reduced to 2 meters, the field intensity will be
At position of (4i + 3j) by a point charge 5 × 10-6 C placed at origin will produce electric field of
Two identical point charges are placed at a separation of l.P is a point on the line joining the charges, at a distance x from any one charge. The field at P is E. E is plotted against x for values of x from close to zero to slightly less than l. Which of the following best represents the resulting curve ?
A particle of mass m and charge Q is placed in an electric field E which varies with time t ass E = E0 sinwt. It will undergo simple harmonic motion of amplitude
Four charges are arranged at the corners of a square ABCD, as shown. The force on +ve charge kept at the centre of the square is
Two free positive charges 4q and q are a distance l apart. What charge Q is needed to achieve equilibrium for the entire system and where should it be placed form charge q ?
Six charges are placed at the corner of a regular hexagon as shown. If an electron is placed at its centre O, force on it will be
A charged particle of charge q and mass m is released from rest in an uniform electric field E. Neglecting the effect of gravity, the kinetic energy of the charged particle after time 't' seconds is
Two identical positive charges are fixed on the y-axis, at equal distances from the origin O. A particle with a negative charge starts on the x-axis at a large distance from O, moves along the +x-axis, passes through O and moves far away from O. Its acceleration a is taken as positive along its direction of motion. The particle's acceleration a is plotted against its x-coordinate. Which of the following best represents the plot ?
Four equal positive charges are fixed at the vertices of a square of side L. Z-axis is perpendicular to the plane of the square. The point z = 0 is the point where the diagonals of the square intersect each other. The plot of electric field due to the four charges, as one moves on the z-axis.
A small circular ring has a uniform charge distribution. On a far-off axial point distance x from the centre of the ring, the electric field is proportional to
A nonconducting ring of radius R has uniformly distributed positive charge Q. A small part of the ring, of length d, is removed (d<<R). The electric field at the centre of the ring will now be
The electric field intensity at a point situated 4 meters from a point charge is 200 N/C. If the distance is reduced to 2 meters, the field intensity will be
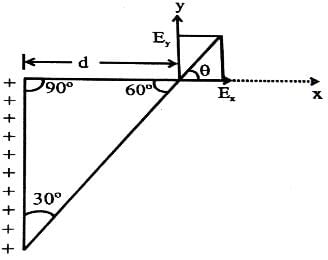
The direction (θ) of E at point P due to uniformly charged finite rod will be -
When charge of 3 coulomb is placed in a Uniform electric field , it experiences a force of 3000 newton, within this field, potential difference between two points separated by a distance of 1 cm is-
An electric dipole is placed at an angle of 30° with an electric field intensity 2 × 105 N/C. It experiences a torque equal to 4 N m. The charge on the dipole, if the dipole length is 2 cm, is
|
98 videos|334 docs|102 tests
|