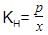Test: Henry's Law - NEET MCQ
29 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 12 - Test: Henry's Law
Only One Option Correct Type
This section contains 11 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct
An unopened soda has an aqueous concentration of C02 at 25° C equal to 0.0506 molal. Thus, pressure of C02 gas in the can is (KH = 0.034 mol/kg bar)
This section contains 11 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct
An unopened soda has an aqueous concentration of C02 at 25° C equal to 0.0506 molal. Thus, pressure of C02 gas in the can is (KH = 0.034 mol/kg bar)
CO(g)is dissolved in H2Oat 25°C and 0.010 atm. Henry’s law constant for this system is 5.80 x104 atm. Thus, mole fraction of CO(g)is
H2S gas is used in qualitative analysis of inorganic cations. Its solubility in water at STP is 0.195 mol kg-1. Thus, Henry’s law constant (in atm molar-1) for H2S is
Variation of Kh (Henry’s law constant) with temperature T is shown by following graphs I - IV.
Correct representation is
Concentration of C02 (in mole fraction) in fat when partial pressure of C02 is 55 kPa at 25° C, is (Henry’s law constant of C02 = 8.6 x 104 torr)
What is the concentration of 02 in a fresh water stream in equilibrium with air at 25° C and 1.0 bar? Given, KH (Henry’s law constant) of 02 = 1.3 x 10-3 mol/kg bar at 25° C.
Following data has been given for C02 for the concentration in H20.
If solution of C02 in H20 is heated from 273 to 333 K, pressure ( p2 ) needed to keep C02 in the solution is
Relation between the volume of gas (2) that dissolves in a fixed volume of solvent(1) and the partial pressure of gas (2) is (nt = total moles, K1and K2 are Henry’s constants)
Henry’s law constant for N2 at 293 K is 76.48 kbar. N2 exerts a partial pressure of 0.987 bar. If N2 gas is bubbled through water at 293 K, then number of millimoles of N2 that will dissolve in 1 L of water is
A handbook lists the solubility of carbon monoxide in water at 0° C and 1 atm pressure as 0.0354 mL CO per mL of H20. What should be the pressure of CO(g) above the solution to obtain 0.010 M CO solution?
One or More than One Options Correct Type
This section contains 2 multiple type questions. Each question has 4 choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Select the correct statement(s).
Statement Type
This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct anser from the codes given below
Statement I Solubility of gases in liquids decreases with rise in temperature.
Statement II CO2(g) + H20 ( / ) ----- » H2CO3(aq ); ΔH = - ve
Statement I: People living at high altitudes have symptoms of a condition known as anoxia.
Statement II: At high altitudes, the partial pressure of oxygen is less than that at the ground level.
Assertion: Soft drinks and soda water bottles are sealed under high pressure.
Reason: High pressure maintains the taste and texture of soft drinks.
Statement I Scuba (instrum ent used for breathing) divers must cope with high concentration of dissolved gases while breathing at high pressure under water.
Statement II Formation of bubbles in blood blocks capillaries and creates bends which are painful and dangerous to life.
Matching List Type
Choices for the correct combination of elements from Column I and Column II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which one is correct
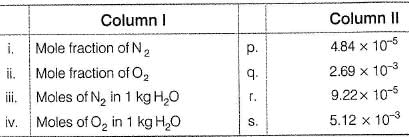
The major components of air are 02 and N2 with approximate proportion of 21% and 79% by volume at 298 K. The water is in equilibrium with air at a pressure of 10 atm. At 298 K, KH(N2 ) = 6.5 1 x 107 mm, KH( 02 ) = 3.30 x 107 mm Match the parameters in Column I with their values in Column II and select the answer from the codes given below.
Codes:

This section contains a graph describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer out of the given 4 options (a), (b), (c) and (d)
Passage
Q. Henry’s law constant for HCI gas is (in torr)
The value for Henry’s constant for helium, hydrogen, nitrogen and oxygen at 293 K are 144.97 kbar, 69.16 kbar, 76.48 kbar and 34.86 kbar respectively. Which of the gas will be having maximum solubility?
A solution in which no more solute can be dissolved at a given temperature and pressure is called a saturated solution. At saturated solution stage equilibrium gets established among which two processes?
A solution in which no more solute can be dissolved at the given temperature and pressure is called a
Some solute particles in solution collide with other solid solute particles present and get separated out of solution. This process is known as
The value for Henry’s constant for argon, carbon dioxide, methane and vinyl chloride at 298 K are 40.3 kbar, 1.67 kbar, 0.413 kbar and 0.611 kbar respectively. Which of the gas will be having least solubility?
According to Henry’s Law at a constant temperature the solubility of gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the
When a large amount of solute dissolves in a given amount of solvent it forms
|
108 videos|286 docs|123 tests
|