Test: Ionic Bonds & Fajans' Rule - JEE MCQ
23 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced - Test: Ionic Bonds & Fajans' Rule
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-16) This section contains 16 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. The correct statement for the molecule Csl-3 is
Lewis structure of the elements M and Z are shown below.
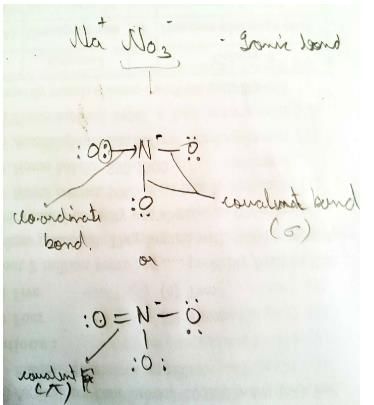
Compound formed is
Different kinds of bonds and interaction present within CuSO4 • 5H2O. They can be
I. σ-bond
II. π-bond
III. coordinate bond
IV. electrostatic force of attraction
V. H-bond due to dipole-dipole interaction
VI. H-bond due to ion-dipole interaction
Select the correct types of bonds/interactions.
Consider the following compounds
I. K4[Fe(CN)6]
II. NH4Cl
III. H2SO4
IV. [Ni (CO)4]
Q.
Ionic, covalent and coordinate bonds are present in
Out of the following, maximum covalent nature is in
Arrange NaCI, MgCI2, AICI3, SiCI4 in increasing solubility in ether (non-polar solvent).
Covalent nature of NaF, Na2O and Na3N in the increasing order is
Solubility of CuS(l), ZnS (II) and Na2S (III) in water is in the order
Which pair is not in the correct order of lattice energy?
Out of the following ions, which pair wil make the compound most covalent?
Aqueous solution of a mixture contains LiCI, CuCI, NaCI and AICI3. This is shaken with ether. What is/are left in water?
Direction (Q. Nos. 17-20) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.
Q. Which of the following can be calculated based on Born-Haber cycle of formation of a lattice A+B- (s) from A(s) and 6 (g) ?
Which of the following Lewis acid-Lewis base interactions are associated with the expansion of octet?
An ionic compound A+B- is most like to be formed from A and B when
Consider following types of bonds.
I. Ionic bond
II. Covalent σ - bond
III. Coordinate bond
IV. Covalent π - bond
Q.
All these bonds are present in
Direction (Q. Nos. 21-22) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given options (a),(b),(c),(d)
A+B- (ionic) is formed in the following steps from gaseous atoms
Q.
How much energy is required to transfer one electron from A to B?
A+B- (ionic) is formed in the following steps from gaseous atoms
Q. What is the maximum size of A+ that would lend itself for the formation of an energetically stable bond?
Direction (Q. Nos. 23) This section contains 1 question. when worked out will result in an integerfrom to 9 (both inclusive)
Q.
An ionic bond is established between a positive ion A+ and negative ion B- . How many times strength of the ionic bond is affected by doubling the charge on A+ and making the radius halved?
|
352 videos|596 docs|309 tests
|