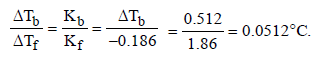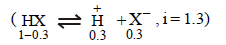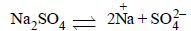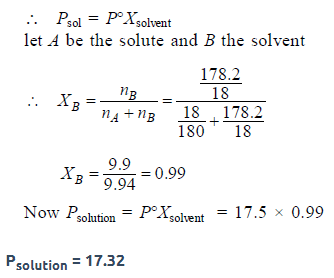Test: JEE Main 35 Year PYQs- Solutions - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced - Test: JEE Main 35 Year PYQs- Solutions
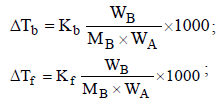
Freezing point of an aqueous solution is (–0.186)°C. Elevationof boiling point of the same solution is Kb = 0.512°C, Kf = 1.86°C, find the increase in boiling point. [2002]
In mixture A and B components show -ve deviation as [2002]
If liquids A and B form an ideal solution [2003]
In a 0.2 molal aqueous solution of a weak acid HX the degreeof ionization is 0.3. Taking kf for water as 1.85, the freezingpoint of the solution will be nearest to [2003]
A pressure cooker reduces cooking time for food because[2003]
Which one of the following aqueous solutions will exihibithighest boiling point ? [2004]
For which of the following parameters the structural isomersC2H5OH and CH3OCH3 would be expected to have the samevalues?(Assume ideal behaviour) [2004]
Which of the following liquid pairs shows a positivedeviation from Raoult’s law ? [2004]
Which one of the following statements is FALSE? [2004]
Benzene and toluene form nearly ideal solution. At 20°C,the vapour pressure of benzene is 75 torr and that of tolueneis 22 torr. The partial vapour pressure of benzene at 20°C fora solution containing 78 g of benzene and 46 g of toluene intorr is [2005]
Equimolar solutions in the same solvent have [2005]
Among the following mixtures, dipole-dipole as the majorinteraction, is present in [2006]
18 g of glucose (C6H12O6) is added to 178.2 g of water. Thevapour pressure of water for this aqueous solution at 100ºC is [2006]
A mixture of ethyl alcohol and propyl alcohol has a vapourpressure of 290 mm at 300 K. The vapour pressure of propylalcohol is 200 mm. If the mole fraction of ethyl alcohol is0.6, its vapour pressure (in mm) at the same temperature willbe [2007]
Equal masses of methane and oxygen are mixed in an emptycontainer at 25°C. The fraction of the total pressure exertedby oxygen is [2007]
A 5.25% solution of a substance is isotonic with a 1.5% solutionof urea (molar mass = 60 g mol–1) in the same solvent. If thedensities of both the solutions are assumed to be equal to 1.0g cm–3, molar mass of the substance will be [2007]
At 80° C, the vapour pressure of pure liquid ‘A’ is 520 mmHg and that of pure liquid ‘B’ is 1000 mm Hg. If a mixturesolution of ‘A’ and ‘B’ boils at 80° C and 1 atm pressure, theamount of ‘A’ in the mixture is (1 atm = 760 mm Hg) [2008]
The vapour pressure of water at 20° C is 17.5 mm Hg. If 18 gof glucose (C6H12O6) is added to 178.2 g of water at 20° C,the vapour pressure of the resulting solution will be [2008]
A binary liquid solution is prepared by mixing n-heptaneand ethanol. Which one of the following statements iscorrect regarding the behaviour of the solution? [2009]
Two liquids X and Y form an ideal solution. At 300 K, vapourpressure of the solution containing 1 mol of X and 3 mol ofY is 550 mmHg. At the same temperature, if 1 mol of Y isfurther added to this solution, vapour pressure of thesolution increases by 10 mmHg. Vapour pressure ( in mmHg)of X and Y in their pure states will be, respectively: [2009]
If sodium sulphate is considered to be completelydissociated into cations and anions in aqueous solution,the change in freezing point of water (ΔTf), when 0.01 molof sodium sulphate is dissolved in 1 kg of water, is(Kf = 1.86 K kg mol–1) [2010]
On mixing, heptane and octane form an ideal solution. At 373 K, the vapour pressures of the two liquid components(heptane and octane) are 105 kPa and 45 kPa respectively.Vapour pressure of the solution obtained by mixing 25.0 gof heptane and 35 g of octane will be(molar mass of heptane = 100 g mol–1 and of octane = 114 gmol–1) [2010]
A 5.2 molal aqueous solution of methyl alcohol, CH3OH, issupplied. What is the mole fraction of methyl alcohol in thesolution? [2011]
Ethylene glycol is used as an antifreeze in a cold climate.Mass of ethylene glycol which should be added to 4 kg ofwater to prevent it from freezing at –6°C will be : (Kf forwater = 1.86 K kg mol–1, and molar mass of ethylene glycol= 62 g mol–1) [2011]
The degree of dissociation (a) of a weak electrolyte, AxBy is related to van’t Hoff factor (i) by the expression [2011]
The density of a solution prepared by dissolving 120 g ofurea (mol. mass = 60 u) in 1000 g of water is 1.15 g/mL. Themolarity of this solution is : [2012]
Kf for water is 1.86 K kg mol–1. If your automobile radiatorholds 1.0 kg of water, how many grams of ethylene glycol(C2H6O2) must you add to get the freezing point of thesolution lowered to –2.8ºC ? [2012]
The molarity of a solution obtained by mixing 750 mL of 0.5(M) HCl with 250 mL of 2(M) HCl will be : [JEE M 2013]
Consider separate solutions of 0.500 M C2H5OH(aq),0.100 M Mg3(PO4)2 (aq), 0.250 M KBr(aq) and 0.125 MNa3PO4(aq) at 25 C ° . Which statement is true about thesesolutions, assuming all salts to be strong electrolytes? [JEE M 2014]
The vapour pressure of acetone at 20°C is 185 torr. When1.2 g of a non-volatile substance was dissolved in 100 g ofacetone at 20°C, its vapour pressure was 183 torr. The molarmass (g mol–1) of the substance is : [JEE M 2015]
|
446 docs|930 tests
|