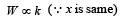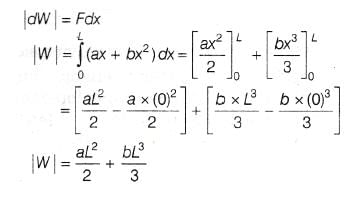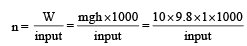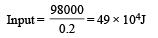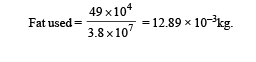Test: JEE Main 35 Year PYQs- Work, Energy & Power - JEE MCQ
26 Questions MCQ Test Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced - Test: JEE Main 35 Year PYQs- Work, Energy & Power
Consider the following two statements : A Linear momentum of a system of particles is zero B. Kinetic energy of a system of particles is zero.Then
A wire suspended vertically from one of its ends is stretched by attaching a weight of 200N to the lower end. The weight stretches the wire by 1 mm. Then the elastic energy stored in the wire is
A spring of spring constant 5 × 103 N/m is stretched initially by 5cm from the unstretched position. Then the work required to stretch it further by another 5 cm is
A body is moved along a straight line by a machine delivering a constant power. The distance moved by the body in time ‘t’ is proportional to
A particle moves in a straight line with retar dation proportional to its displacement. Its loss of kinetic energy for any displacement x is proportional to
A uniform chain of length 2 m is kept on a table such that a length of 60 cm hangs freely from the edge of the table. The total mass of the chain is 4 kg. What is the work done in pulling the entire chain on the table ?
A force 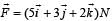 is applied over a particle which displaces it from its origin to the point
is applied over a particle which displaces it from its origin to the point 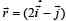 m. The work done on the particle in joules is
m. The work done on the particle in joules is
A body of mass ‘m’, accelerates uniformly from rest to ‘v1’ in time ‘t1’. The instantaneous power delivered to the body as a function of time ‘t’ is
A Particle is acted upon by a force of constant magnitude which is always perpendicular to the velocity of the particle, the motion of the particles takes place in a plane. It follows that
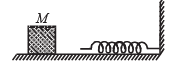
The block of mass M moving on the frictionless horizontal surface collides with the spring of spring constant k and compresses it by length L. The maximum momentum of the block after collision is
A spherical ball of mass 20 kg is stationary at the top of a hill of height 100 m. It rolls down a smooth surface to the ground, then climbs up another hill of height 30 m and finally rolls down to a horizontal base at a height of 20 m above the ground. The velocity attained by the ball is
A body of mass m is accelerated uniformly from rest to a speed v in a time T. The instantaneous power delivered to the body as a function of time is given by
A particle of mass 100g is thrown vertically upwards with a speed of 5 m/s. The work done by the force of gravity during the time the particle goes up is
The potential energy of a 1 kg particle free to move along
the x-axis is given by
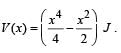
The total mechanical energy of the particle is 2 J. Then, the maximum speed (in m/s) is
A 2 kg block slides on a horizontal floor with a speed of 4m/s.It strikes a uncompressed spring, and compresses it till the block is motionless. The kinetic friction force is 15N and spring constant is 10,000 N/m. The spring compresses by
An athlete in the olympic games covers a distance of 100 m in 10s. His kinetic energy can be estimated to be in the range
A block of mass 0.50 kg is moving with a speed of 2.00 ms–1 on a smooth surface. It strikes another mass of 1.00 kg and then they move together as a single body. The energy loss during the collision is
The potential energy function for the force between two atoms in a diatomic molecule is approximately given by  where a and b are constants and x is the distance between the atoms. If the dissociation energy of the molecule is
where a and b are constants and x is the distance between the atoms. If the dissociation energy of the molecule is 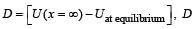 is
is
This question has Statement 1 and Statement 2. Of the four choices given after the Statements, choose the one that best describes the two Statements.
If two springs S1 and S2 of force constants k1 and k2, respectively, are stretched by the same force, it is found that more work is done on spring S1 than on spring S2.
STATEMENT 1 : If stretched by the same amount work done on S1, Work done on S1 is more than S2
STATEMENT 2 : k1 < k2
When a rubber-band is stretched by a distance x, it exerts restoring force of magnitude F = ax + bx2 where a and b are constants. The work done in stretching the unstretched rubber-band by L is:
A person trying to lose weight by burning fat lifts a mass of 10 kg upto a height of 1 m 1000 times. Assume that the potential energy lost each time he lowers the mass is dissipated. How much fat will he use up considering the work done only when the weight is lifted up? Fat supplies 3.8 × 107 J of energy per kg which is converted to mechanical energy with a 20% efficiency rate. Take g = 9.8 ms–2 :
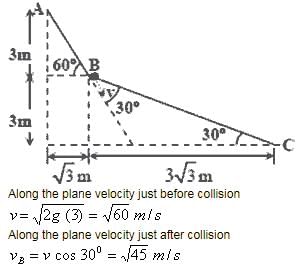
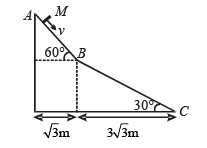
A small block of mass M moves on a frictionless surface of an inclined plane, as shown in figure. The angle of the incline suddenly changes from 60° to 30° at point B. The block is initially at rest at A. Assume that collisions between the block and the incline are totally inelastic (g = 10 m/s2).
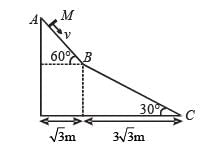
Q.1. The speed of the block at point B immediately after it strikes the second incline is –
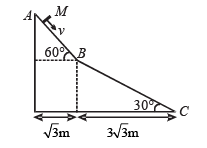
A small block of mass M moves on a frictionless surface of an inclined plane, as shown in figure. The angle of the incline suddenly changes from 60° to 30° at point B. The block is initially at rest at A. Assume that collisions between the block and the incline are totally inelastic (g = 10 m/s2).
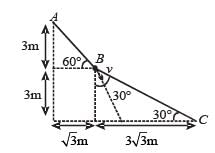
Q.2. The speed of the block at point C, immediately before it leaves the second incline is
A small block of mass M moves on a frictionless surface of an inclined plane, as shown in figure. The angle of the incline suddenly changes from 60° to 30° at point B. The block is initially at rest at A. Assume that collisions between the block and the incline are totally inelastic (g = 10 m/s2).
Q.3. If collision between the block and the incline is completely elastic, then the vertical (upward) component of the velocity of the block at point B, immediately after it strikes the second incline is –
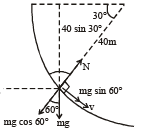
A small block of mass 1 kg is released from rest at the top of a rough track. The track is a circular arc of radius 40 m. The block slides along the track without toppling and a frictional force acts on it in the direction opposite to the instantaneous velocity. The work done in overcoming the friction up to the point Q, as shown in the figure below, is 150 J. (Take the acceleration due to gravity, g = 10 ms–2)
Q.4. The magnitude of the normal reaction that acts on the block at the point Q is
A small block of mass 1 kg is released from rest at the top of a rough track. The track is a circular arc of radius 40 m. The block slides along the track without toppling and a frictional force acts on it in the direction opposite to the instantaneous velocity. The work done in overcoming the friction up to the point Q, as shown in the figure below, is 150 J. (Take the acceleration due to gravity, g = 10 ms–2)
Q.5.The speed of the block when it reaches the point Q is
|
446 docs|930 tests
|




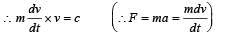
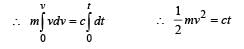
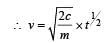
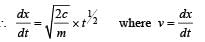

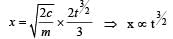
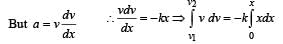

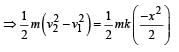
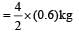
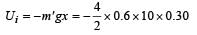
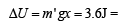 Workdone in putting the en tire chain on the table.
Workdone in putting the en tire chain on the table.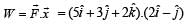


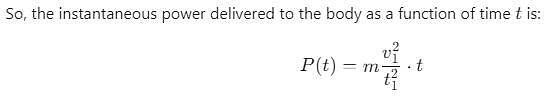
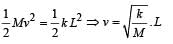
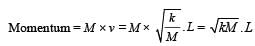

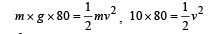

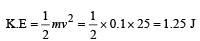
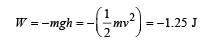
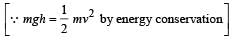
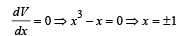
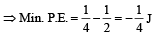
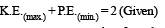
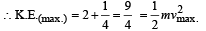


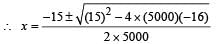
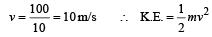
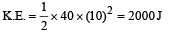
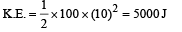
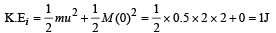
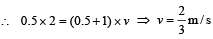
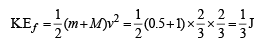
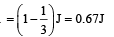
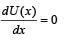
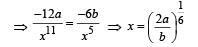
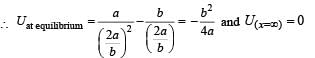
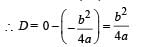
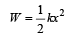
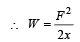 .
.