Test: Matrices- 2 - JEE MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Matrices- 2
If A any square matrix then which of the following is not symmetric ?
Let a, b, c, d, u, v be integers. If the system of equations, a x + b y = u, c x + dy = v, has a unique solution in integers, then
The system of equations, x + y + z = 1, 3 x + 6 y + z = 8, αx + 2 y + 3z = 1 has a unique solution for
The system of equations, x + y + z = 6, x + 2 y + 3 z = 14, x + 3 y + 5z = 20 has
The matrix of the transformation ‘reflection in the line x + y = 0 ‘ is
A square matrix A = [aij]n×n is called a diagonal matrix if aij = 0 for
If a square matrix A has two identical rows or columns , then det.A is :
For a skew symmetric odd ordered matrix A of integers, which of the following will hold true:
Matrix A when multiplied with Matrix C gives the Identity matrix I, what is C?
Let for any matrix M ,M−1exist. Which of the following is not true.
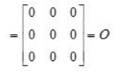
If for a matrix A, A2+I = O where I is the identity matrix, then A equals
The system of linear equations x + y + z = 2, 2x + y - z = 3, 3x + 2y - kz = 4 has a unique solution if ,
The value of k for which the system of equations, x + k y + 3 z = 0, 3 x + k y – 2 z = 0, 2 x + 3 y – 4 z = 0, have a non-trival solution is


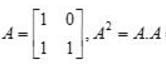
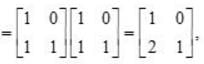
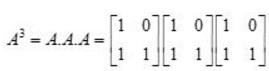
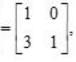
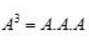
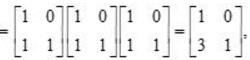

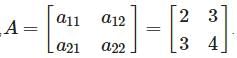
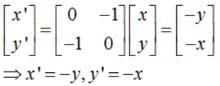
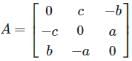 and
and 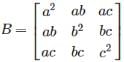 then AB =
then AB =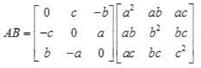
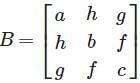 and C = [xyt]t, then ABC is
and C = [xyt]t, then ABC is










