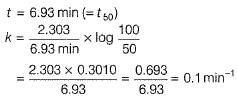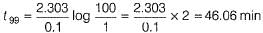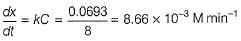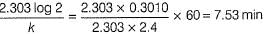Test: Zero Order & First Order Reactions - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 12 - Test: Zero Order & First Order Reactions
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-21) This section contains 21 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q. For zeroth order reaction,
A → B
[A]0 = 0.01 M, [A]t = 0.008Matter 10 min.
Thus, half-life is
A Certain Zeroth Order reaction has k = 0.025 Ms-1 for the disappearance of A. What will be the concentration of A after 15s, if the intial concentration is 0.50 M?
For Zeroth Order Reaction, variation of x with time is shown as
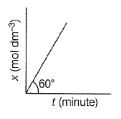
Q. At initial concenration of the reactant as 17.32 min dm-1 , half - life period is

For the first order reaction, rate constant k is given by
kt = logC0 - log Ct
where, C0 is the intial concenration and Ct is the concentration at time t. Graph between log Ct and time t is
In a first order reaction, the concentration of the reactant decreases from 0.8 M to 0.4 M is 15 min. The time taken for the concentration to change from 0.1 M to 0.025 M is
For the First order reaction, concentration of the reactant after two averagelives is reduced to
The half-life period of a first order chemical reaction is 6.93 min. The time required for the completion of 99% of the chemical reaction will be (log2 = 0.3010)
[AIEEE 2009]
For the first order reaction,
A → Product
Q. The concentration of A changes from 0.1 M to 0.025 M in 40 min. The rate of the reaction when the concentration of A is 0.01 M is
[AIEEE 2012]
For the reaction,
A → Products, 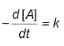
Concentration of A at different time intervals are given :
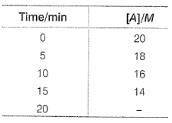
At 20 min, rate will be
For the first order reaction with, C0 as the initial concentration and C at time t, (C0 - C) =
The radioisotope N-13 which has a half-life of 10 min is used to image organs in the body. If the injected sample has an activity of 40 μCi (microcurie), what is the activity after 30 min?
The following data were obtained during the first order decomposition of
2A(g) → B(g) + C(s)
at constant volume and at a particular temperature :

Thus, rate constant is
A G .M. Counter is used to study the process of first order of radioactive disintegration. In the absence of radioactive substance A, it counts 3 dps (disintegration per second). When A is placed in G.M Counter it records 23 dps at the start and 13 dps after 10 min. It records x dps after next 10 min. Half-life period of A is y min. Thus, x and y are
Inversion of sucrose (C12H22O11) is a first order reaction and is studied by measuring angle of rotation at different interval of time
r0 = angle of rotation at the start, rt = angle of rotation at time t
r∞ = angle of rotation at the complete reaction
There is 50% inversion, when
Following radioactive disintegration follows first order kinetics :
Starting with 1 mol of A in a 1L flask at 300 K, pressure set up after two half-lifes is approximately
For the first order reaction Tav (average life), T50 (half-life) and T75 (time 75% reaction) are in the ratio of
For the first order reaction,
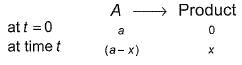
Following equations are given :
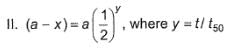
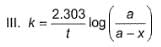
Select the correct equations.
Rate constant of a first order reaction (A → B) is 0.0693 min-1. If initial concentration is 1.0 M, rate after 30 min is
Following reaction is pseudo-unimolecular w.r.t. C6H5N2CI (A)
50 mL of 1M benzene diazonium chloride (A) is taken. After 1 h, 1.226 L of N2 gas at 1 atm and 300 K is obtained. Thus, half-life of the reaction is (log 250 = 2.40)
Minimum half-life of an isotope needed so that not more than 0.1 % of the nuclei undergo decay during a 3.0 h laboratory experiment is
Naturally occurring potassium consists of 0.01% at 40 K which has a half-life of 1.28 x 109 yr. Activity of 1.00 g sample of KCl is
Direction (Q. Nos. 22-27) This section contains a passage describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer out of the given 4 options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage l
Isotope of oxygen with mass number less than 16 undergoes β+ -emission. Assume an equimolar mixture of 14O and 15O, Also t50 (14O) = 71s, t50 (15O) = 124s.
Q. Ratio of rate constants of 14O to 15O is
Passage l
Isotope of oxygen with mass number less than 16 undergoes β+ -emission. Assume an equimolar mixture of 14O and 15O, Also t50 (14O) = 71s, t50 (15O) = 124s.
Q. Ratio of 14O to 15O left after 1.00 h is
Passage II
Consider acid-hydrolysis of ester which is first order reaction.
CH3COOC2H5 + H2O 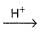 CH3COOH + C2H5OH
CH3COOH + C2H5OH
Kinetics is studied by titration of the acid with NaOH at a given time.
V0 = Volume of NaOH at start, Vt = Volume of NaOH at time t, V∞ = Volume of NaOH at the end of the complete hydrolysis.
Q.
Rate constant k is given by
Passage II
Consider acid-hydrolysis of ester which is first order reaction.
CH3COOC2H5 + H2O 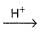 CH3COOH + C2H5OH
CH3COOH + C2H5OH
Kinetics is studied by titration of the acid with NaOH at a given time.
V0 = Volume of NaOH at start, Vt = Volume of NaOH at time t, V∞ = Volume of NaOH at the end of the complete hydrolysis.
Q.
If ester is 50% hydrolysed, then
Passage III
I, II and III are three vessels of equal volumes containing molecules of A as shown and in each A decomposes into products.
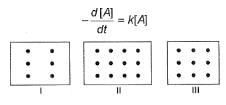
Q.
Initial rate of decomposition of A will be in order in these three vessels as
Passage III
I, II and III are three vessels of equal volumes containing molecules of A as shown and in each A decomposes into products.

Q.
Time of 50% decomposition is in order
Direction (Q. Nos. 28-30) This section contains 3 questions. When worked out will result in one integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).This section contains 3 questions, when worked out will result in an integer value from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
Q. A radioactive element gets spilled over the floor of a room. Its half-life period is 30 days. If the initial activity is ten times the permissible value, it will be safer to enter the room after 10n days. What is the value of n?
For the first order reaction, variation of log10(a - x)vs time (t) is shown below.
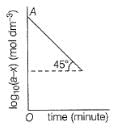
Q.
Its half-life period is logx. What is the value of x?
For the first order reaction,
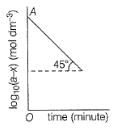
Q.
If OA = 1.3010 then reactant left after 0.6021 min i s .......unit.
|
108 videos|286 docs|123 tests
|