JEE Previous Year Questions: Centre of Mass - JEE MCQ
11 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Previous Year Questions: Centre of Mass
Two block of masses 10 kg and 4 kg are connected by a spring of negligible mass and placed on a frictionless horizontal surface. An impulse gives a velocity of 14 m/s to the heavier block in the direction of the lighter block. The velocity of the centre of mass is
[IIT(Scr.)-2002]
STATEMENT-1 In an elastic collision between two bodies, the relative speed of the bodies after collision is equal to the relative speed before the collision.
because
STATEMENT-2 In an elastic collision, the linear momentum of the system is conserved
The balls, having linear momenta 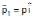 and
and 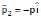 , undergo a collision in free space. There is no external force acting on the balls. Let and be their final momenta. The following options(s) is (are) NOT allowed for any non-zero value of p, a1, a2, b1, b2, c1 and c2
, undergo a collision in free space. There is no external force acting on the balls. Let and be their final momenta. The following options(s) is (are) NOT allowed for any non-zero value of p, a1, a2, b1, b2, c1 and c2
[JEE 2008]
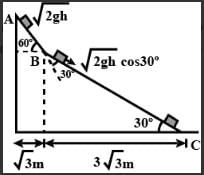
A small block of mass M moves on a frictionless surface of an inclined plane, as shown in figure. The angle of the incline suddenly changes from 60° to 30° at point B. The block is initially at rest at A. Assume that collisions between the block and the incline are totally inelastic (g = 10 m/s2). Figure :
The speed of the block at point B immediately after it strikes the second incline is
[JEE 2008]
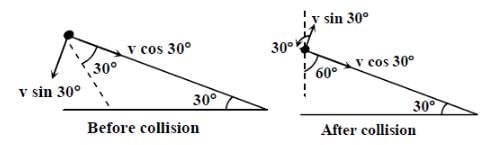
A small block of mass M moves on a frictionless surface of an inclined plane, as shown in figure. The angle of the incline suddenly changes from 60° to 30° at point B. The block is initially at rest at A. Assume that collisions between the block and the incline are totally inelastic (g = 10 m/s2). Figure :
The speed of the block at point C, immediately before it leaves the second incline is
[JEE 2008]
A small block of mass M moves on a frictionless surface of an inclined plane, as shown in figure. The angle of the incline suddenly changes from 60° to 30° at point B. The block is initially at rest at A. Assume that collisions between the block and the incline are totally inelastic (g = 10 m/s2). Figure :
[JEE 2008]
If collision between the block and the incline is completely elastic, then the vertical (upward) component of the velocity of the block at point B, immediately after it strikes the second incline is
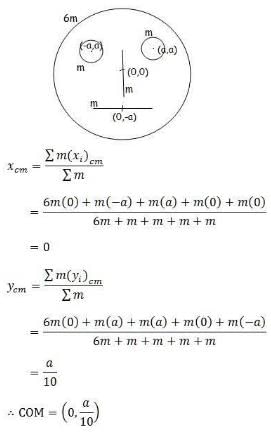
Look at the drawing given in the figure which has been drawn with ink of uniform line-thickness. The mass of ink used to draw each of the two inner circles, and each of the two line segments is m. The mass of the ink unsed to draw the outer circle is 6m. The coordinates of the centres of the different parts are outer circle (0, 0), left inner circle (_a, a), right inner circle (a, a), vertical line (0, 0) and horizontal line (0, _ a). The y-coordinate of the centre of mass of the ink in this drawing is
[JEE 2009]
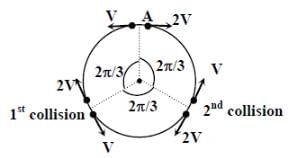
Two small particles of equal masses start moving in opposite directions from a point A in a horizontal circle orbit. Their tangential velocities are v and 2v, respectively, as shown in the figure. Between collisions, the particles move with constant speeds. After making how many elastic collisions, other than that at A, these two particulars will again reach the point A ?
[JEE 2009]
Three objects A, B and C are kept in a straight line on a frictionless horizontal surface. These have masses m, 2m and m, respectively. The object A moves towardsB with a speed 9 ms-1 and makess an elastic collision with it. There after, B makes completely inelastic collision with C. All motions occur on the same straight line. Find the final speed (in ms-1 ) of the object C.
[JEE 2009]
A point mass of 1 kg collides elastically with a stationary point mass of 5 kg. After their collision, the 1 kg mass reverse its direction and moves with a speed of 2 ms-1. Which of the following statement(s) is (are ) correct for the system of these two masses ?
[JEE 2010]
A ball of mass 0.2 kg rests on a vertical post of height 5 m. A bullet of mass 0.01 kg traveling with a velocity V m/s in a horizontal direction, hits the centre of the ball. After the collision, the ball and bullet travel independently. The ball hits the ground at a distance of 20 m and the bullet at a distance of 100 m from the foot of the post. The initial velocity V of the bullet is
[JEE 2011]