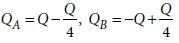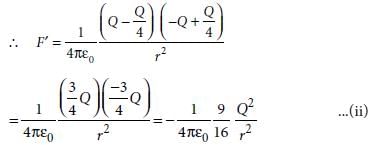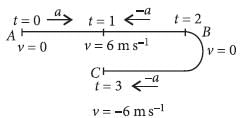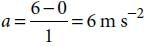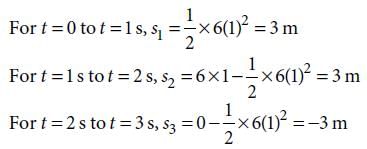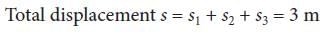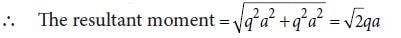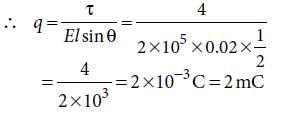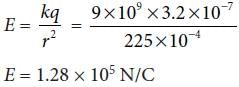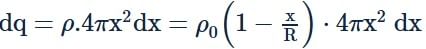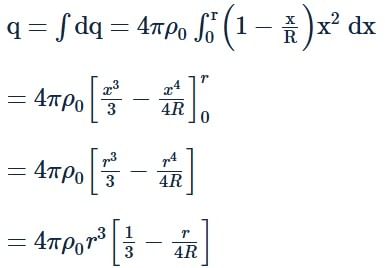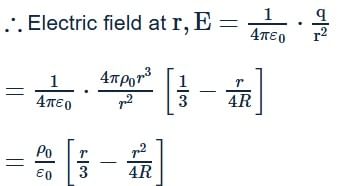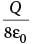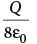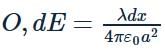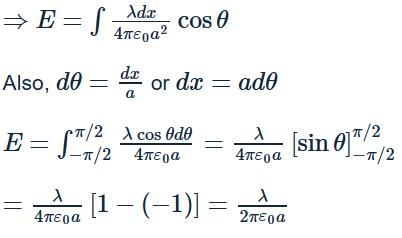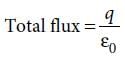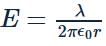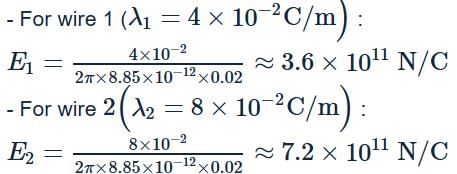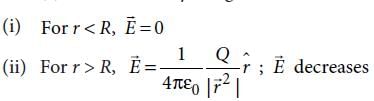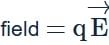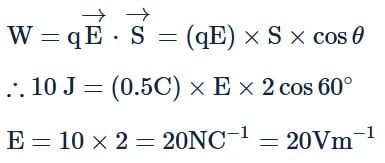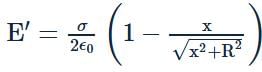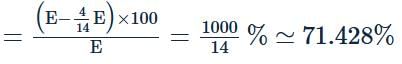Test: Electric Charges & Fields - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Physics Class 12 - Test: Electric Charges & Fields
When a negatively charged conductor is connected to earth,
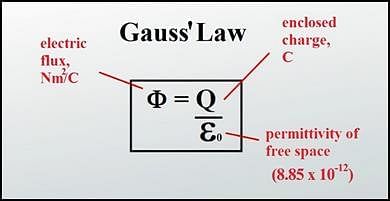
A point charge of 2.0 μC is at the centre of a cubic Gaussian surface 9.0 cm on edge. What is the net electric flux through the surface?
A point charge causes an electric flux of −1.0×103Nm2/C to pass through a spherical Gaussian surface of 10.0 cm radius centred on the charge.
(a) If the radius of the Gaussian surface were doubled, how much flux would pass through the surface?
(b) What is the value of the point charge?
(a) If the radius of the Gaussian surface were doubled, how much flux would pass through the surface?
(b) What is the value of the point charge?
A hollow spherical conductor of radius 2m carries a charge of 500 μ C. Then electric field strength at its surface is
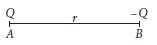
Two point charges A and B, having charges +Q and –Q respectively, are placed at certain distance apart and force acting between them is F. If 25% charge of A is transferred to B, then force between the charges becomes
A toy car with charge q moves on a frictionless horizontal plane surface under the influence of a uniform electric field 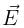 . Due to the force
. Due to the force 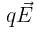 , its velocity increases from 0 to 6 m s–1 in one second duration. At that instant the direction of the field is
, its velocity increases from 0 to 6 m s–1 in one second duration. At that instant the direction of the field is
reversed. The car continues to move for two more seconds under the influence of this field. The average velocity and the average speed of the toy car between 0 to 3 seconds are respectively
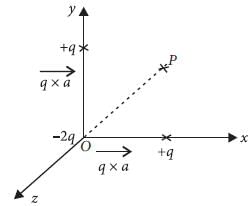
Three point charges +q, –2q and +q are placed at points (x = 0, y = a, z = 0), (x = 0, y = 0, z = 0) and (x = a, y = 0, z = 0) respectively. The magnitude and direction of the electric dipole moment vector of this charge assembly are
An electric dipole is placed at an angle of 30° with an electric field intensity 2 x 105 N C–1.It experiences a torque equal to 4 N m. The charge on the dipole, if the dipole length is 2 cm, is
A spherical conductor of radius 10 cm has a charge of 3.2 x 10–7 C distributed uniformly. What is the magnitude of electric field at a point 15 cm from the centre of the sphere?
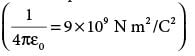
A hollow cylinder has a charge q coulomb within it. If f φ is the electric flux in units of volt meter associated with the curved surface B, the flux linked with the plane surface A in units of V-m will be
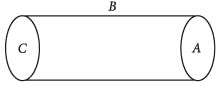
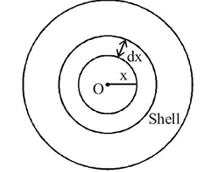
A spherically symmetric charge distribution is characterised by a charge density having the following variations:
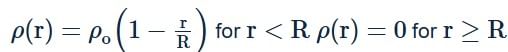
Where r is the distance from the centre of the charge distribution ρ0 is a constant. The electric field at an internal point (r<R) is:
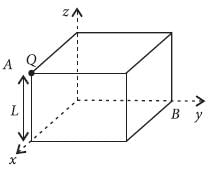
A charge Q is situated at the corner of a cube, the electric flux passed through all the six faces of the cube is
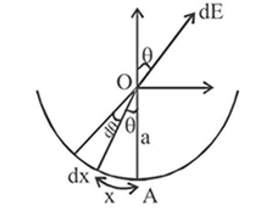
A semi-circular arc of radius ' a ' is charged uniformly and the charge per unit length is λ. The electric field at the centre of this arc is
A point charge + q is placed at the centre of a cube of side l. The electric flux emerging from the cube is
The linear charge densities of two infinitely long thin and parallel wires are 4Cm−1, 8Cm−1 and separation between them is 4 cm. Then the electric field intensity at mid point on the line joining them is
A hollow metal sphere of radius R is uniformly charged. The electric field due to the sphere at a distance r from the centre
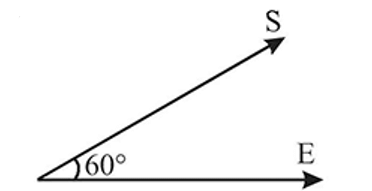
An uniform electric field E exists along positive x-axis. The work done in moving a charge 0.5C through a distance 2 m along a direction making an angle 60∘ with x -axis is 10 J. Then what is the magnitude of electric field (in Vm−1)?
The surface charge density of a thin charged disc of radius R is σ. The value of the electric field at the centre of the disc is σ/2ϵ0. With respect to the field at the centre, the electric field along the axis at a distance R from the centre of the disc reduces (in percent) by _____. Answer should be rounded off to two decimal places.
|
98 videos|332 docs|101 tests
|