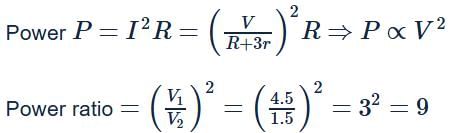NEET Part Test - 2 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - NEET Part Test - 2
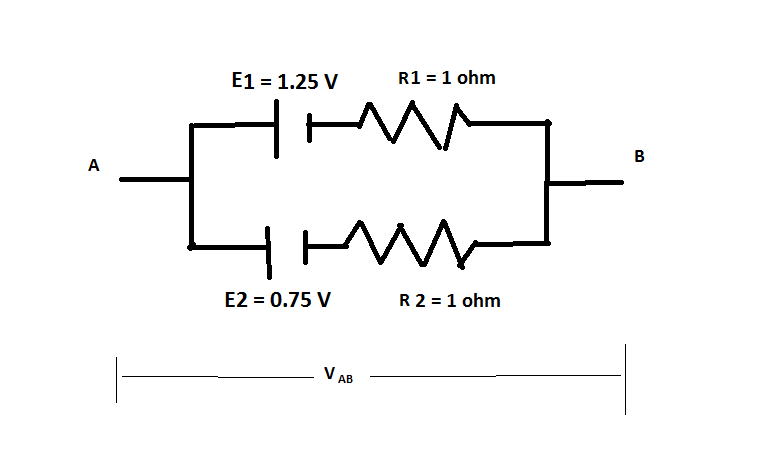
Two cells of emf 1.25V , 0.75V and each of internal resistance 1Ω are connected in parallel. The effective emf will be
Three identical cells, each having an e.m.f. of 1.5 V and a constant internal resistance of 2.0Ω, are connected in series with a 4.0Ω resistor R, first as in circuit (i), and secondly as in circuit (ii).
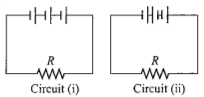
What is the ratio 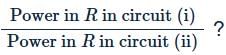

What is the ratio
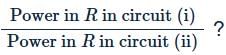
In a meter bridge experiment a balance point is obtained at a distance of 60 cm from the left end when unknown resistance R is in a left gap and 8 ohms resistor is connected in the right gap. When the position of R and 8 ohm resistor is interchanged the balance point will be at distance of
An observer looks at a tree of height 15 metre with a telescope of magnifying power 10. To him, the tree appears
A convex lens forms a real image of an object on a screen; the magnification of the image being 3/2. The object and the screen are kept fixed and the lens is moved through a distance of 16 cm when a sharp image is again formed on the screen; the magnification now being 2/3. What is the focal length of the lens?
An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a co-axial combination of two lenses A and B in contact. The combination forms a real image three times the size of the object. If lens B is concave with a focal length of 30 cm, what is the nature and focal length of lens A ?
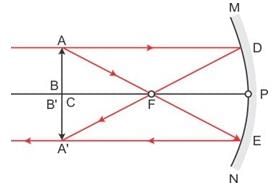
An infinitely long rod lies along the axis of a concave mirror of focal length f. The near end of the rod is at a distance u > f from the mirror. Its image will have a length
In case of concave mirror, the minimum distance between a real object and its real image is :
A concave lens of glass, refractive index 1.5, has both surfaces of same radius of curvature R. On immersion in a medium of refractive index 1.75, it will behave as a:
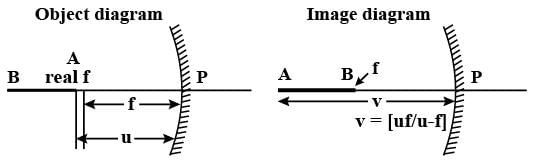
A convex lens produces a real image m times the size of the object. What is the distance of the object from the lens?
A sample of radioactive material contains 1018 atoms. The half life of the material is 2 days, then the activity of the sample is
What is considered as the rivet in the ‘Rivet popper hypothesis’?
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.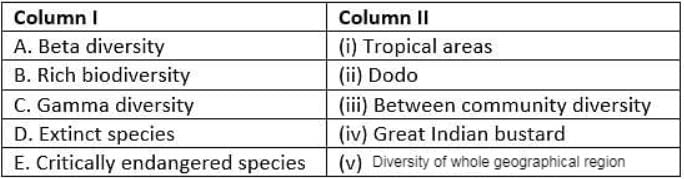
Study the following ecological pyramids carefully.
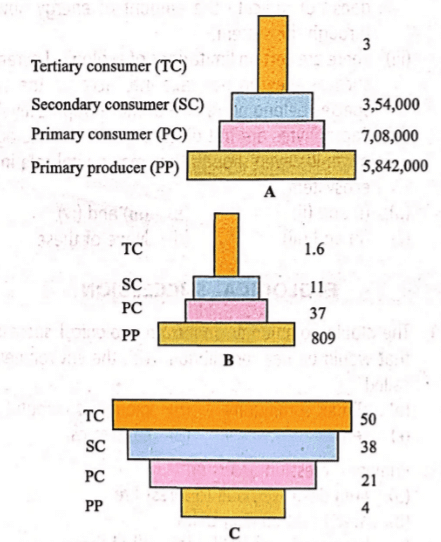
Match the following statements (i),(ii) and (iii) with given pyramids A, B and C and select the correct answer.
(i) Inverted pyramid of biomass depicting small standing crop of phytoplanktons supporting a large standing crop of zooplanktons
(ii) Pyramid of numbers in a grassland ecosystem showing about 6 million producers
(iii) Upright pyramid of biomass
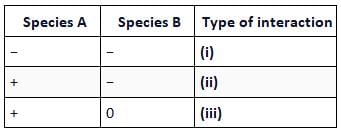
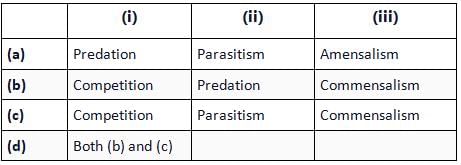
Refer to the given table. If '+' sign has been assigned for beneficial interaction, sign for detrimental interaction and '0' for neutral interaction, identify the type of interaction (i), (ii) and (iii) and select the correct option.
A microbial biocontrol agent that can be used to control butterfly caterpillars is:
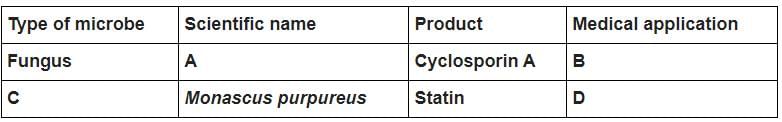
Identify the blank spaces A, B, C and D in the table given below and select the correct answer.
What is the primary purpose of passing effluent into a settling tank after reducing BOD?
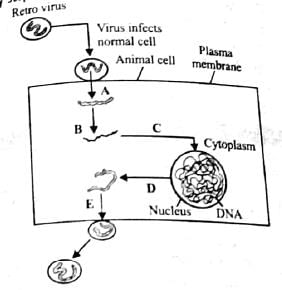
The figure given below shows mode of action of AIDS virus. Identify steps A, B, C, D and E labelled in it.
Elephantiasis, a chronic inflammation that results in grossdeformities is caused by
Which of the following pairs correctly matches a disease and a pathogen causing it?
Consider the following statements and select the option stating which ones are true (T) and which ones are false (F).
(i) There are many side effects of tubectomy and vasectomy.
(ii) Purpose of tubectomy is to prevent egg formation.
(iii) Contraceptive oral pills help in birth control by preventing ovulation.
(iv) Genital warts is a sexually transmitted disease caused by herpes virus.
(v) In India, there is rapid decline in infant mortality rate and MMR.
How do the pills work?
(i) Inhibit ovulation and implantation
(ii) Alter the quality of cervical mucus to prevent or retard the entry of sperms
(iii) Prevent the ejaculated semen from entering the female vagina
(iv) Inhibit spermatogenesis
Match each function below with the associated part or parts of the human male reproductive system shown in the figure.
(i) Produces sperm
(ii) Conducts the sperm through the penis to the outside of the body
(iii) Produces seminal fluid
(iv) Connects the epididymis with the urethra
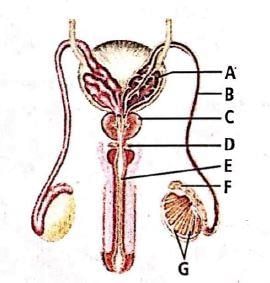
Identify the parts labelled A, B, C and D in the given figure and select the correct option.
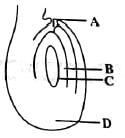
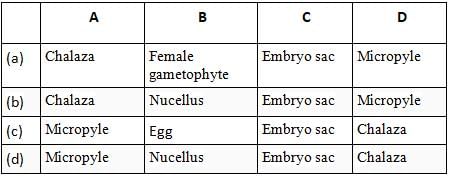
Which of the following are correct?
(i)Diploblastic:Poriferans, Coelenterates
(ii)Triploblastic:Platyheliminthes to Chorodates
(iii)Acoelomate:Poriferans,Coelenterates,Platyhelminthes
(iv)Pseudocoelomate:Aschelminthes /Roundworms
(v)Eucoelomate:Annelids to Chordates
Causal organisms of sleeping sickness belong to which of the following groups of protozoan protists?