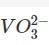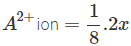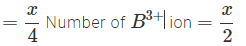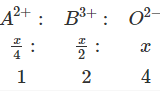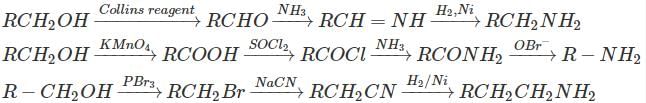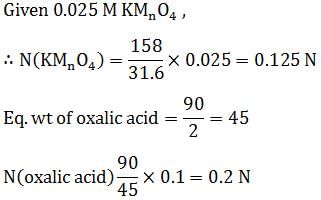JEE Main Practice Test- 2 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Main Practice Test- 2
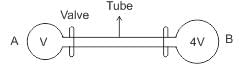
The volumes of containers A and B, connected by a tube and a closed valve are V and 4 V, respectively. Both the containers A and B have the same ideal gas at pressures (temperatures) 5.0 ×105 Pa(300 K) and 1.0 ×105Pa (400 K), respectively. The valve is opened to allow the pressure to equalise, but the temperature of each container is kept constant at its initial value. Find the common pressure in the containers.
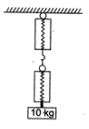
A block of mass 10 kg is suspended through two light spring balances as shown in figure

If E = 100 sin (100t) volt and 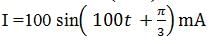 are the instantaneous values of voltage and current, then the R.M.S values of voltage and current are respectively.
are the instantaneous values of voltage and current, then the R.M.S values of voltage and current are respectively.
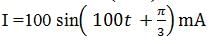 are the instantaneous values of voltage and current, then the R.M.S values of voltage and current are respectively.
are the instantaneous values of voltage and current, then the R.M.S values of voltage and current are respectively.Two spherical bodies of mass M and 5 M and radii R and 2 R, respectively are released in free space with initial separation between their centres equal to 12 R. If they attract each other due to gravitational force only, then the distance covered by the smaller body just before collision is
The length of a given cylindrical wire is increased by 100%. Due to the consequent decrease in diameter the change in the resistance of the wire will be
Students I, II and III perform an experiment for measuring the acceleration due to gravity (g) using a simple pendulum. They use different lengths of the pendulum and /or record time for different number of oscillations. The observations are shown in the table.
Least count for length = 0.1 cm
Least count for time = 0.1 s
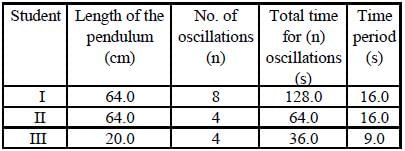
If EI, EII and EIII are the percentage errors in g, i.e.,
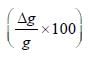 for students I, II and III, respectively, then
for students I, II and III, respectively, then
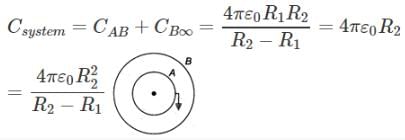
Write down the expression for capacitance of a spherical capacitor whose conductors radii are R1 and R2(R2>R1),when inner sphere is grounded.
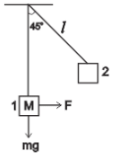
A mass of M kg is suspended by a weightless string. The horizontal force that is required to displace it until the string makes an angle of 45° with the initial vertical direction is
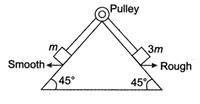
Acceleration of each block is given as g/5√2. Find the magnitude and direction of force exerted by string on pulley. (μ = 0.4)
A pipe of length 85 cm is closed from one end. Find the number of possible natural oscillations of air column in the pipe whose frequencies lie below 1250 Hz. The velocity of sound in air is 340 m/s.
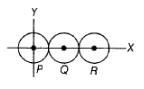
Three identical spheres, each of mass 1 kg are kept as shown in the figure below, touching each other, with their centres on a straight line. If their centres are marked P, Q, R respectively, the distance of centre of mass of the system from P is
A resistor R and 2μF capacitor in series is connected through a switch to 200 V direct supply. Across the capacitor is a neon bulb that lights up at 120 V. Calculate the value of R to make the bulb light up 5 s after the switch has been closed (log10 2.5 = 0.4)
A α−particle passes through a potential difference of 2×106V and then it becomes incident on a silver foil. The charge number of silver is 47. The energy of incident particles will be: (in joule)
Direction: Question is based on the following paragraph.
A wire of length L, mass m and carrying a current is suspended from point O as shown. An infinitely long wire carrying the same current I is at a distance L below the lower end of the wire. Given, I = 2A, L= 1m and m = 0.1 kg (ln 2 = 0.693)
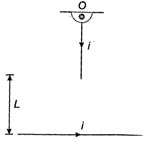
What is angular acceleration of the wire just after it is released from the position shown?
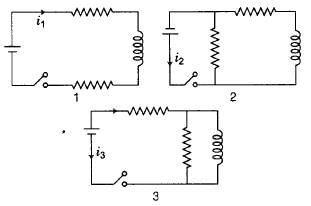
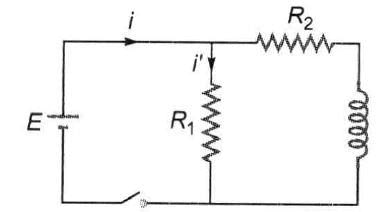
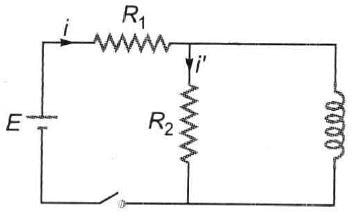
The figure shows three circuits with identical batteries, inductors and resistances. Rank the circuits according to the currents through the battery just after the switch is closed, greatest first
A bullet when fired into a fixed target loses half of its velocity after penetrating 20 cm.How much further it will penetrate before coming to rest?
Directions: Question are Assertion - Reaction type each of these contains two statements: Statement I (Assertion), Statement II (Reason) Each of these questions also has four alternative choices, only one of which is correct. You have to select the correct choices from the codes a, b, c and d given below:
Statement I : The isothermal curves intersect each other at a certain point
Statement II: The isothermal changes takes place slowly, so the isothermal curves have very little slope.
A parallel plate air capacitor has a capacitance C. When it is half filled with a dielectric of dielectric constant 5, the percentage increase in the capacitance will be
A ball is dropped from a bridge at a height of 176.4 m over a river. After 2s, a second ball is thrown straight downwards. What should be the initial velocity of the second ball so that both hit the water simultaneously? (Take g=10m/s2)
Directions: The answer to this question is a single-digit integer, ranging from 0 to 9. Enter the correct digit in the box given below.
Q. A 40 cm diameter pipe branches into two pipes of diameters 10 cm and 20 cm each. If the average velocities of water that flows through 10 cm and 20 cm pipes are 6 m/s and 2 m/s, respectively, then the speed of the water that flows through the 40 cm pipe (in m/s) is
(Answer up to nearest integer)
Directions: The answer to this question is a single-digit integer, ranging from 0 to 9. Enter the correct digit in the box given below.
Q. Two point objects A and B are 40 cm apart. A convex lens L of focal length 15 cm should be placed in between them such that the images due to the two point objects coincide. If the least distance between L and A is x, then the value of x – 1 is
Directions: The answer to this question is a single-digit integer, ranging from 0 to 9. Enter the correct digit in the box given below.
Q. An air-filled parallel plate capacitor having circular plates has a capacitance of 10 pF. When the radii of the plates are increased two times, the distance between them is halved and if a medium of dielectric constant k is introduced, the capacitance increases 16 times. The value of k is
Directions: The answer to this question is a single-digit integer, ranging from 0 to 9. Enter the correct digit in the box given below.
Q. Two parallel identical plates carry equal and opposite charges having a uniform charge of 88.9 C. Positive plate is fixed on the ceiling of a box and the negative plate has to be suspended. If the area of the plates is 6.35 sq. m and 'm' is the mass of the negative plate, then the value of [m] in kg, where [ ] stands for maximum integer value, is
Directions: The answer to the following question is a single digit integer ranging from 0 to 9. Enter the correct digit in the box given below.
A radioactive sample S1 having an activity of 5 μ Ci and half life of 20 years has twice the number of nuclei as another sample S2, which has an activity of 10 μCi. The half lives (in years) of S2 is
Directions: Questions are based on the following paragraph.
When ammonium vanadate is heated with oxalic add solution, a compound Z is formed. A sample of Z was titrated with KMnO4 solution in hot acidic solution. The resulting liquid was reduced with SO2, the excess SO2 boiled off, and the liquid again titrated with KMnO4. The ratio of the volumes of KMnO4 used in the two titrations was 5 : 1. KMnO4 oxidises all oxidation state of vanadium to Vanadium (+V) and SO2 reduces vanadium (+V) to vanadium (+IV). Read the above experiment and answer the following questions. If vanadium exists as 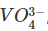 , reduced species by SO2 would be
, reduced species by SO2 would be
In a cubic dosed packed structure of mixed oxides, the lattice is made up of oxide ions, one eighth of tetrahedral/voids are occupied by divalent ions (A2+), while one half of the octahedral voids are occupied by trivalent ions(B3+)What is the formula of the oxide ?
Which of the following sequence of reaction is the best means to furnish the conversion RCH2OH→RCH2NH2
The standard heat of combustion of carbon(s), sulphur (s) and carbon disulphide (l) are -393.3, -293.72 and - 1108.76 kJ/mol respectively. The standard heat of formation of carbon disulphide(l) is
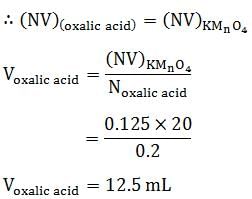
The volume of 0.1 M oxalic acid that can be completely oxidised by 20 mL of 0.025 M KMnO4 solution is


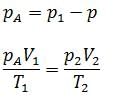
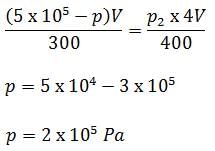

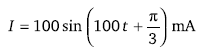
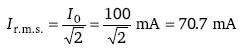
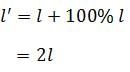
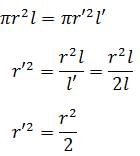
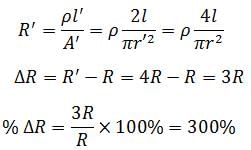
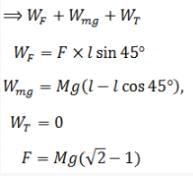
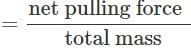
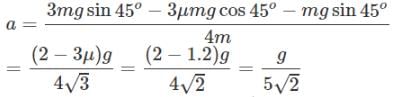
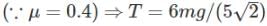
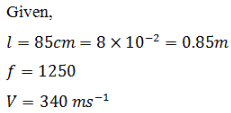
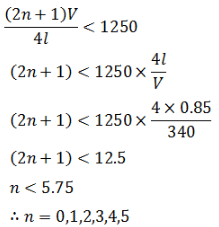

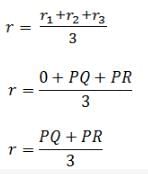
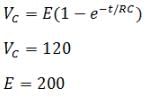
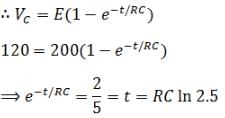
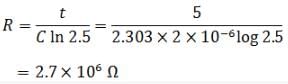
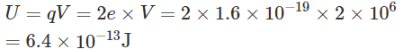
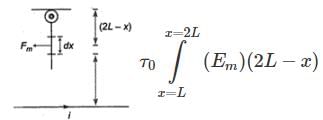
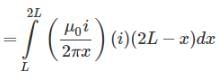
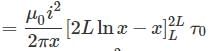
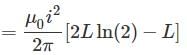
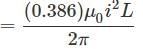

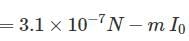
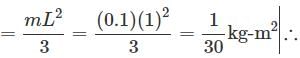
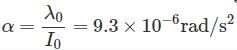
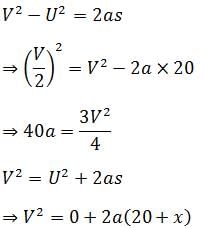
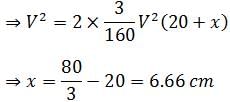
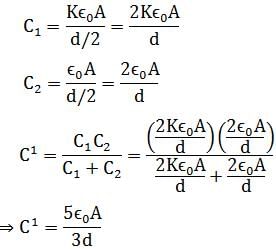
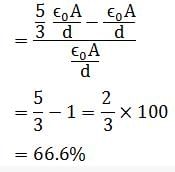
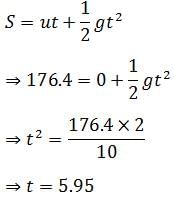
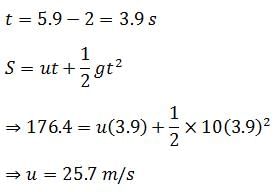
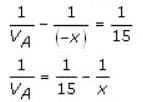
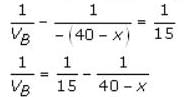
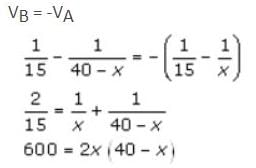
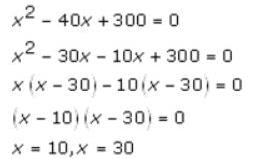
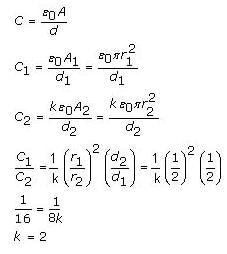
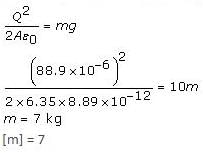
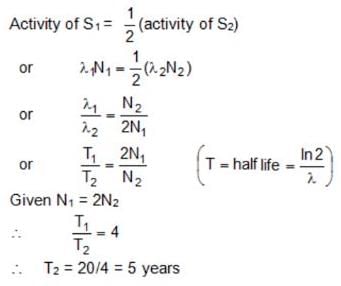
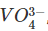 is reduced to +4 oxidation state which is
is reduced to +4 oxidation state which is