Economics: CUET Mock Test - 5 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test CUET Mock Test Series - Economics: CUET Mock Test - 5
Foreign travellers defined the finest quality of muslin, a type of cotton textile with its origin in Bengal as ______(Fill up the blank with correct alternative)
On the basis of contribution to GDP in the Indian economy (in decreasing order), choose the correct sequence of the given section-
Consider the following statements and choose their correct order in a market economy.
a. Ginning mill cleans the cotton and makes it into balls
b. Weavers return with cloth
c. Spinning mill buys the cotton and sells yarn to the yarn traders
d. Yarn dealers give the yarn to the weavers.
In the history of population, which year has been termed as the 'Year of Great Divide'?
Match List - I with List - II.
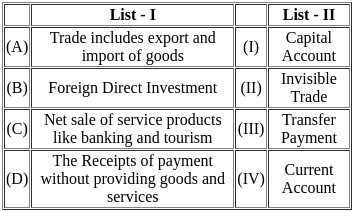
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
When Cash Reserve Ratio is 20% then with the deposit of Rs. 1000, Money creation will be Rs. 5000, Money multiplier is:
Life Expectancy during the British India was ______ (Fill up the blank with correct answer)
British enabled India to be an importer of raw materials and an exporter of finished goods. (Choose the correct alternative)
Whose estimates are considered as more reliable with regard to estimation of national income and per capita income during the colonial period?
The main objective of the zamindars during the land settlement system was to
Indian economy on the eve of independence is characterised as
Indian farmers voluntarily agreed to switch from subsistence farming towards commercialisation of agriculture. The given statement is
The main reason for stagnation of Indian agriculture during the British rule was
The chief casual factor responsible for the decline of handicrafts industry in India was
De-industrialisation acted as a major setback to which Indian industry?
Which of the following does not highlight the status of industrial sector during the colonial period?
The main focus of the Industrial Policy pursued during the colonialperiod
Which of the following industry/ies was/were covered under the public sector during the colonial period?
The major characteristic of India’s foreign trade during the colonial period was
British restricted India’s foreign trade with which of these nations?
The major reason(s) for the alarming mortality rate during British India include
The reason for the Great Bengal Famine of 1943-44 as per Amartya Sen was
Which of the following is false regarding the positive contribution by the British rule?
The share of workforce engaged in industrial and service sector respectively during the colonial rule
Assertion (A): India developed a sound industrial base during the colonial rule.
Reason (R): The industrial sector was crying for modernisation , diversification, capacity building and increased public investment.
Alternatives
|
39 docs|148 tests
|




















