Economics: CUET Mock Test - 6 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test CUET UG Mock Test Series 2026 - Economics: CUET Mock Test - 6
Read the following statements regarding National Income estimates and select the correct answer using codes given below :
A. Capital gains and losses are included in National Income.
B. Incomes from illegal activities are not included in National Income.
C. Imputed values of the self occupied houses are included in the National Income.
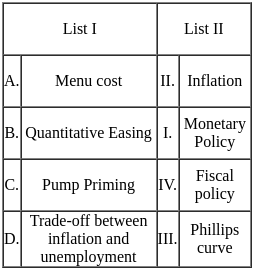
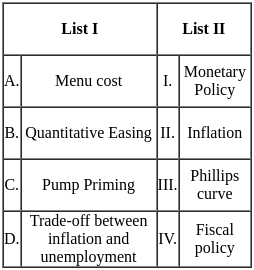
Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
The expenditure made on education, training and health is called :
Which of the following international organizations helps its member countries during the Balance of Payment Crisis?
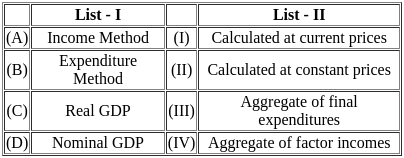
Match List - I with List - II.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
What does the equilibrium output in the economy represent?
What factors influence aggregate demand in an economy?
What happens when the economy is at equilibrium output?
Which of the following will shift the aggregate demand curve?
Why is equilibrium output important in macroeconomics?
What happens when aggregate demand exceeds the economy’s potential output?
Which of the following tools can policymakers use to manage aggregate demand?
Why is managing aggregate demand crucial for economic stability?
Consider the following statements:
(A) Scarcity of resources leads to the need for allocating limited resources.
(B) In a market economy, resources are allocated centrally by the government.
(C) Individuals in society make choices about the goods and services they want to produce and consume.
(D) Scarcity does not lead to opportunity cost.
Choose the correct answer from the following:
Consider the following statements:
(A) The allocation of scarce resources is a fundamental problem for all economies.
(B) In a centrally planned economy, decisions regarding the production and consumption of goods are made by the market.
(C) A market economy solves the problem of allocation by relying on price signals and competition.
(D) Governments do not play a significant role in a market economy.
Choose the correct answer from the following:
Consider the following statements:
(A) Positive economics is concerned with what ought to be.
(B) Normative economics deals with evaluating the desirability of different economic mechanisms.
(C) Positive economics explains how economic mechanisms function without considering their desirability.
(D) Normative economics deals with facts and figures.
Choose the correct answer from the following:
Consider the following statements:
(A) Microeconomics studies individual decision-making units like consumers and producers.
(B) Macroeconomics focuses on the behavior of the economy as a whole, including aggregate output and unemployment.
(C) Microeconomics examines national income and inflation.
(D) Macroeconomics deals with the study of individual markets and firms.
Choose the correct answer from the following:
Following were the main land tenure system prevailing during British colonial period:
________ was developed by the British Raj as a means to enlarge the size of market for the British goods
When was the first census data collected during British India
Opening of Suez Canal in ____ significantly reduced the cost f transportation of goods between Britain and India
The estimate given by Dr Rao regarding per capita output was
|
39 docs|145 tests
|