Test: Polity- 1 - UPSC MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Polity- 1
Consider the following statements:
According to our Constitution, the State governments can legislate on the residuary subjects.
The Parliament can on its own change the arrangement of sharing of powers between the Union
Government and the State governments.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
According to our Constitution, the State governments can legislate on the residuary subjects.
The Parliament can on its own change the arrangement of sharing of powers between the Union
With reference to the ‘Advisory Jurisdiction’ of Supreme Court, consider the following statements:
The President of India can refer any matter that is of public importance, or that involves interpretation of the Constitution to the Supreme Court for advice.
The Supreme Court is bound to advise on such matters, though the President is not bound to accept such advice.
Which of the statements given above is/are not correct?
The President of India can refer any matter that is of public importance, or that involves interpretation of the Constitution to the Supreme Court for advice.
The Supreme Court is bound to advise on such matters, though the President is not bound to accept such advice.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
With reference to Federalism in India, consider the following statements:
Preamble mentions India to be a Federal state.
The constitution of India under the Article 1 has described India as a federation.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Preamble mentions India to be a Federal state.
The constitution of India under the Article 1 has described India as a federation.
"This writ is issued when the court finds that a particular office holder is not doing legal duty and thereby is infringing on the right of an individual." The above description refer to?
Which of the following functions are served by the Constitution of India?
It serves as guide to the state to institute laws and policies to reduce poverty.
It provides a set of basic rules for coordination amongst members of a society.
It helps judiciary to decide the legality of the laws framed by the legislatures.
It helps in ensuring that people with good morals and values reach to power.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Democracy’s superior virtue lies in the fact that it calls into activity
Which of the following is essentially not a feature of a federal polity?
Consider the following statements with reference to the Conditions of the Governor's office.
-
The office of governor of a state is an employment under the Central government.
-
The emoluments and allowances of the Governor shall not be diminished during his term of office.
Which of the statements given above is/are not correct?
Which of the following statements is correct with reference to Fundamental rights in India?
With reference to certain features of the Indian Constitution, consider the following pairs:
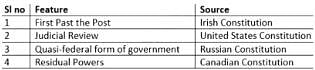
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
The Constituent Assembly was composed roughly along the lines suggested by which of the following?
With reference to the Directive Principles provided under part IV of the Indian Constitution, consider the following statements:
Promoting cottage industries on an individual or cooperation basis in rural areas.
Public assistance in case of old age, sickness, and disablement, and right to work.
Promoting the educational and economic interests of SCs, STs, and other weaker sections of the society.
Promoting the voluntary formation of cooperative societies.
Which of the directive principles given above are based on Gandhian ideology?
This rule allows judges to add or ignore any of the words in the statute while interpreting in order to protect the purpose of creating that law and give fair and equal justice to everyone. Which of the following doctrines resemble this?
Extension of Maternity benefits under Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana to the second child, a girl child, is in consonance with which of the following part of the Indian Constitution?
With reference to administrative relations in India, which one of the following is not correct?
national waterways with prior approval of state government
Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the Objective Resolution by Jawaharlal Nehru?
1. India is an independent, sovereign, republic.
2. The land would make a full and willing contribution to the promotion of world peace and the welfare of mankind.
3. The minorities, backward and tribal areas, depressed and other backward classes shall be provided adequate safeguards.
4. All powers and authority of sovereign and independent India and its constitution shall flow from the people.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Consider the following statements:
-
Article 125(1) of the Constitution provides that the salaries and allowances of the Judges are not subjected to the Legislature's approval.
-
A Judge of the Supreme Court or High Court can be removed only on the ground of violation of the Constitution.
Which of the statements given above is/are not correct?
Consider the following statements regarding the National Commission for Scheduled Castes (NCSC):
It seeks to provide safeguards against the exploitation of Scheduled Castes and Anglo Indian communities.
It specifies the inclusion or exclusion of castes in the list of Scheduled Castes.
It presents to the President an annual report on the working on safeguards for Scheduled Castes.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
With reference to the Election Commission of India (ECI), consider the following statements:
The Election Commissioners enjoy the same status as available to the Chief Justice of the High Court.
The Chief Election Commissioner can be removed from office only through impeachment by Parliament.
The decisions of the ECI can be challenged only in the the Supreme Court of India by appropriate petitions.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
In the context of India, which one of the following is the characteristic appropriate for bureaucracy?
Consider the following statements with respect to ‘office of profit’:
It has been explicitly defined in the Constitution.
The Constitution provides immunity to legislators in case of certain specified offices.
Which of the statements given above is/are not correct?
With reference to rights of minorities in India, consider the following statements:
Article 30 of Indian Constitution provides for reverse discrimination in favour of minorities.
No citizen shall be denied admission into any educational institution maintained by the State.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following statements about ‘preventive detention’ in India
The authority that has detained the person is obligated to provide the reasons for his detention before his arrest.
The period of detention cannot be extended beyond three months under any circumstances.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Which of the following statements most correctly describes the term citizenship?
Which one of the following statements about Constitutional Amendment Bill is not correct?
The concept of ‘Principled Distance’ is closely related to which among the following?
Which of the following statements in the context of the Fundamental Duties is not correct?
Imposition of President’s rule in a state would be improper under which of the following situations?
In case of hung assembly after general elections.
Where a ministry resigns and no other party is able to form ministry commanding majority.
Maladministration in the state due to allegations of corruption.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Which of the following bill when passed by both the Houses of the Parliament puts an obligation on the Indian President to give his/her assent?

















