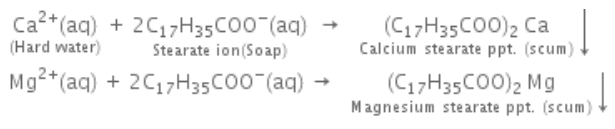Case Based Questions Test: Carbon & Its compounds - 1 - Year 11 MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Case Based Questions Test: Carbon & Its compounds - 1
Read the given passage and answer the question :
A sample of water which gives lather with soap with difficulty is known as hard water, while a sample of water which gives lather with soap easily is known as soft water. Hardness of water is due to the presence of bicarbonates, sulphates and chlorides of calcium and magnesium. Hardness of water is of two types, temporary and permanent hardness. When hardness of water is due to the presence of bicarbonates of magnesium and calcium, it is called temporary hardness. When hardness of water is due to the presence of sulphates and chlorides of magnesium and calcium, it is called permanent hardness.
The amount of hardness causing substances in a certain volume of water measures the extent of hardness or degree of hardness. Hardness of water is always calculated in terms of calcium carbonate although it is never responsible for causing hardness of water because of its insoluble nature. The reason for choosing calcium carbonate as the standard for calculating hardness of water is the ease in calculation as its molecular weight is exactly 100. Degree of hardness is usually expressed as parts per million (ppm).
Q. “A student requires hard water for an experiment in his laboratory which is not available in the neighbouring area. In the laboratory there are some salts, which when dissolved in distilled water can convert it into hard water. Select from the following groups of salts, a group, and each salt of which when dissolved in distilled water will make it hard.”
Read the given passage and answer the question :
A sample of water which gives lather with soap with difficulty is known as hard water, while a sample of water which gives lather with soap easily is known as soft water. Hardness of water is due to the presence of bicarbonates, sulphates and chlorides of calcium and magnesium. Hardness of water is of two types, temporary and permanent hardness. When hardness of water is due to the presence of bicarbonates of magnesium and calcium, it is called temporary hardness. When hardness of water is due to the presence of sulphates and chlorides of magnesium and calcium, it is called permanent hardness.
The amount of hardness causing substances in a certain volume of water measures the extent of hardness or degree of hardness. Hardness of water is always calculated in terms of calcium carbonate although it is never responsible for causing hardness of water because of its insoluble nature. The reason for choosing calcium carbonate as the standard for calculating hardness of water is the ease in calculation as its molecular weight is exactly 100. Degree of hardness is usually expressed as parts per million (ppm).
Q. Hardness of water is calculated in terms of :
Read the given passage and answer the question :
A sample of water which gives lather with soap with difficulty is known as hard water, while a sample of water which gives lather with soap easily is known as soft water. Hardness of water is due to the presence of bicarbonates, sulphates and chlorides of calcium and magnesium. Hardness of water is of two types, temporary and permanent hardness. When hardness of water is due to the presence of bicarbonates of magnesium and calcium, it is called temporary hardness. When hardness of water is due to the presence of sulphates and chlorides of magnesium and calcium, it is called permanent hardness.
The amount of hardness causing substances in a certain volume of water measures the extent of hardness or degree of hardness. Hardness of water is always calculated in terms of calcium carbonate although it is never responsible for causing hardness of water because of its insoluble nature. The reason for choosing calcium carbonate as the standard for calculating hardness of water is the ease in calculation as its molecular weight is exactly 100. Degree of hardness is usually expressed as parts per million (ppm).
Q. Hardness of water is due to :
Read the given passage and answer the question :
A sample of water which gives lather with soap with difficulty is known as hard water, while a sample of water which gives lather with soap easily is known as soft water. Hardness of water is due to the presence of bicarbonates, sulphates and chlorides of calcium and magnesium. Hardness of water is of two types, temporary and permanent hardness. When hardness of water is due to the presence of bicarbonates of magnesium and calcium, it is called temporary hardness. When hardness of water is due to the presence of sulphates and chlorides of magnesium and calcium, it is called permanent hardness.
The amount of hardness causing substances in a certain volume of water measures the extent of hardness or degree of hardness. Hardness of water is always calculated in terms of calcium carbonate although it is never responsible for causing hardness of water because of its insoluble nature. The reason for choosing calcium carbonate as the standard for calculating hardness of water is the ease in calculation as its molecular weight is exactly 100. Degree of hardness is usually expressed as parts per million (ppm).
Q. Which statement is not true:
Read the given passage and answer the question :
A sample of water which gives lather with soap with difficulty is known as hard water, while a sample of water which gives lather with soap easily is known as soft water. Hardness of water is due to the presence of bicarbonates, sulphates and chlorides of calcium and magnesium. Hardness of water is of two types, temporary and permanent hardness. When hardness of water is due to the presence of bicarbonates of magnesium and calcium, it is called temporary hardness. When hardness of water is due to the presence of sulphates and chlorides of magnesium and calcium, it is called permanent hardness.
The amount of hardness causing substances in a certain volume of water measures the extent of hardness or degree of hardness. Hardness of water is always calculated in terms of calcium carbonate although it is never responsible for causing hardness of water because of its insoluble nature. The reason for choosing calcium carbonate as the standard for calculating hardness of water is the ease in calculation as its molecular weight is exactly 100. Degree of hardness is usually expressed as parts per million (ppm).
Q. Why do soaps not form lather (foam) with hard water?
Read the below passage and answer the question :
An organic compound A is a constituent of many medicines and is used as antifreeze. Its molecular formula is C2H6O. Upon the reaction with alk. KMnO4, the compound A is oxidized to another compound B with formula C2H4O2.
Q. Identify the compounds A and B.
Read the below passage and answer the question :
An organic compound A is a constituent of many medicines and is used as antifreeze. Its molecular formula is C2H6O. Upon the reaction with alk. KMnO4, the compound A is oxidized to another compound B with formula C2H4O2.
Q. Choose the correct compound which can be used instead of alk. KMnO4:
Read the below passage and answer the question :
An organic compound A is a constituent of many medicines and is used as antifreeze. Its molecular formula is C2H6O. Upon the reaction with alk. KMnO4, the compound A is oxidized to another compound B with formula C2H4O2.
Q. Which of the following statement is true
Read the below passage and answer the question :
An organic compound A is a constituent of many medicines and is used as antifreeze. Its molecular formula is C2H6O. Upon the reaction with alk. KMnO4, the compound A is oxidized to another compound B with formula C2H4O2.
Q. What is the role of alk. KMnO4.
Read the below passage and answer the question :
An organic compound A is a constituent of many medicines and is used as antifreeze. Its molecular formula is C2H6O. Upon the reaction with alk. KMnO4, the compound A is oxidized to another compound B with formula C2H4O2.
Q. Which of the following statement is true for ethanol:
Study the given experimental set-up and answer the questions:
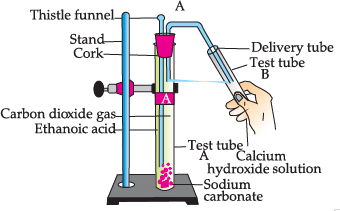
Q. Name the gas released in test tube B:
Study the given experimental set-up and answer the questions:
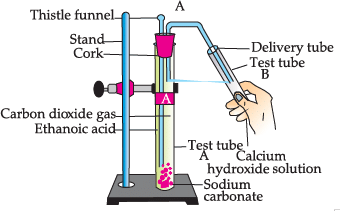
Q. Choose the correct reaction which justifies the above activity:
Study the given experimental set-up and answer the questions:
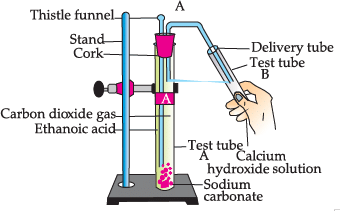
Q. Name the salt produced in the above activity:
Study the given experimental set-up and answer the questions:
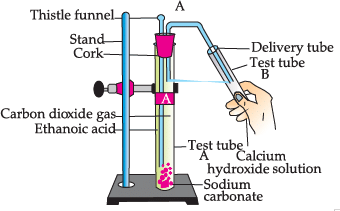
Q. Which gas turns lime water milky:
Study the given experimental set-up and answer the questions:
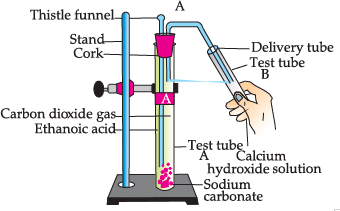
Q. What happens when ethanol is used instead of ethanoic acid: