UGC NET Paper 2 Sociology Mock Test - 3 - UGC NET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test UGC NET Mock Test Series 2025 - UGC NET Paper 2 Sociology Mock Test - 3
Which one of the following pairs is not correctly matched?
The term 'Husband endemic' refers to the residence in which a newly married couple:
The celebrated dictum that “the life of man is ‘solitary, poor, nasty, brutish and short,’ while the condition of man is a condition of war of everyone against everyone”, is assigned to which great philosopher?
The system in which a woman is shared by the whole group is called:
Below are given a number of concepts in Set - I and their descriptions in Set - II. Match the items in Set - I with that of Set - II :
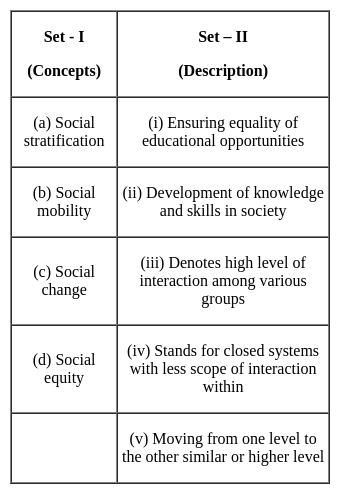
Select the correct code :
Given below are two statements:
Statement I: The modernization hypothesis gained a lot of traction in the 1950s but came under fire at the end of the 1960s.
Statement II: According to modernization ideology, traditional values must be rejected.
Choose the correct option:
Which of the following is not correct one?
Who among the following considered culture as the handiwork of man and as the medium through which he/she achieve his/her ends?
Using the codes given below, select the problems associated with urban areas?
1) Poverty
2) Air Pollution
3) Spreading of Diseases
4) Unemployment
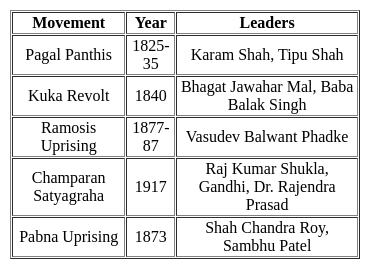
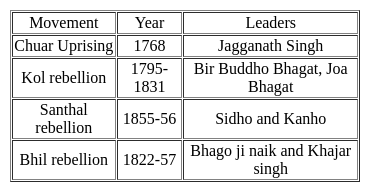
Certain movements of the early twentieth century described as 'Movements from below' were
Who coined the phrase symbolic interactionnism?
In which type of societies are the kings usually defined:
Direction: Given below are two statements, one labelled as Assertion A . and the other are Reason (R). examine the statements and indicate the correct answer by choosing the codes below.
Assertion A: City dwellers satisfy their needs through secondary groups.
Reason (R): The urban problems cannot be solved by primary groups.
What is the current status of the poverty alleviation programme initiated by the Government of India?
(A) Technology dissemination is uneven and slow in rural areas.
(B) There still remains much more to be done to bring prosperity in the lives of the people in rural areas.
(C) There is a lack of participation of different stakeholders.
Which of the following is/are true about plastics?
I. They are organic polymers of high molecular mass.
II. They are mostly derived from fossil fuels.
III. It was used for the first time in Germany and used on a mass scale in New York.
What can be some possible steps to tackle the menace of plastic pollution?
I. Plastic production should be restricted and recycling should be encouraged.
II. We should aim for behavioral changes with household-wise waste segregation being an example.
III. We should eliminate plastic from our daily lives.
As per the passage, what are some ways in which we can act as responsible citizens?
I. Use of cloth/jute/paper bags.
II. Reduce single-use plastic usage.
III. Organize community based drives on recovering plastic waste in the community.
In "Social Statics", Spencer gave ideas on
Who had initiated the work on total communities of India namely "People of India Project"?
In a system of social stratification social rankings are based on certain attributes which may:
|
92 docs|125 tests
|