Shankar IAS Test: Marine Organisms - UPSC MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Environment for UPSC CSE - Shankar IAS Test: Marine Organisms
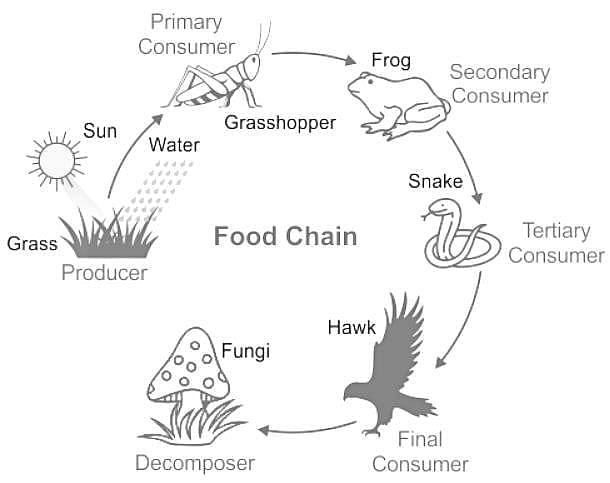
Select the food chain found in forest/grassland ecosystem:
Quinine is used for treatment of which disease ?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Coal, limestone, petroleum, animal shells are all related to:
Which of the following is not an artificial ecosystem?
Which of the following describes a lentic ecosystem?
Consider the following statements:
1. Estuaries, intertidal zones, rocky and sandy shores, tropical reefs and regions of the open ocean are major marine ecosystems.
2. Lentic ecosystem includes river, stream or spring.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Which of the following statement is/are correct?
1. The non-living constituents are said to include the producers, consumers and decomposers.
2. The living organisms may include habitat, gases, solar radiation, temperature, moisture and inorganic and organic nutrients.
Choose the correct option from below.
Which of the following ecosystems has the highest net primary productivity?
Consider the following statements regarding biodiversity hotspots:
1. A biodiversity hotspot is a biogeographic region that is both a significant reservoir of biodiversity and is threatened with destruction.
2. Globally, the total number of biodiversity hotspots has witnessed a decline over the years.
3. The Himalayas and the Western Ghats are the only two biodiversity hotspots in India.
Which of the statements given above is/are not correct?
Very minute plants floating in the water are called
Which of the following regions has maximum bio-diversity?
|
97 videos|203 docs|53 tests
|
|
97 videos|203 docs|53 tests
|