Test: Carbohydrates - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 12 - Test: Carbohydrates
The following is a reaction of glucose with Fehling’s reagent. What will happen in the reaction?
The oxide linkage formed by the loss of a water molecule when two monosaccharides are joined together through oxygen atom is called:
Glucose + Tollen’s reagent → Silver mirror. The process shows:
In polysaccharides, the linkage connecting monosaccharides is called:
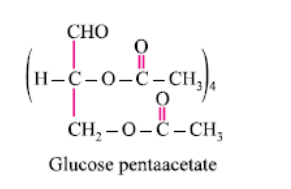
What does the following reaction of glucose with HI elucidates about the structure of glucose?
The Molisch test is a chemical test that determines the presence of:
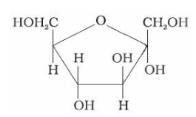
What does the following reaction shows about the structure of glucose?
Which of the following carbohydrates is called an invert sugar?
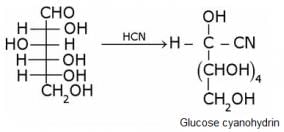
What is the relation between the following pairs of monosaccharides?
Which of the following carbohydrate is an example of an oligosaccharide?
|
108 videos|286 docs|123 tests
|