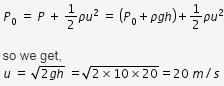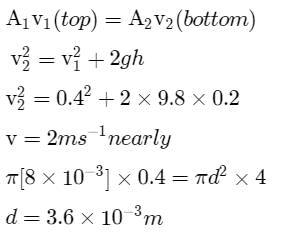JEE Previous Year Questions: Fluid Mechanics - JEE MCQ
5 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Previous Year Questions: Fluid Mechanics
A cylinder of height 20 m is completely filled with water. The velocity of efflux of water (in ms-1) through a small hole on the side wall of the cylinder near its bottom, is
[AIEEE 2002]
A jar is filled with two non-mixing liquids 1 and 2 having densities 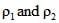 respectively. A solid ball, made of a material of density
respectively. A solid ball, made of a material of density 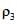 , is dropped in the jar. It comes to equilibrium in the position shown in the figure.
, is dropped in the jar. It comes to equilibrium in the position shown in the figure.
Which of the following is true for 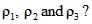
[AIEEE 2008]
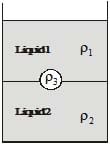
A ball is made of a material of densityr where, representing the densities of oil and water, respectively. The oil and water are immiscible. If the above ball is in equilibrium in a mixture of this oil and water, which of the following pictures represents its equilibrium positions?
representing the densities of oil and water, respectively. The oil and water are immiscible. If the above ball is in equilibrium in a mixture of this oil and water, which of the following pictures represents its equilibrium positions?
[AIEEE 2010]
Water is flowing continuously from a tap having an internal diameter 8 × 10-3m. The water velocity as it leaves the tap is 0.4 ms-1. The diameter of the water stream at a distance 2 × 10-1 m below the tap is close to
[AIEEE 2011]
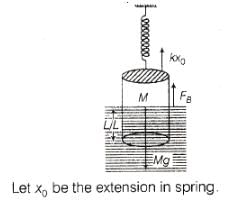
A uniform cylinder of length L and mass M having cross - sectional area A is suspended, with its length vertical, from a fixed point by a massless spring, such that it is half submerged in a liquid of density s at equilibrium position. The extension x0 of the spring when it is in equilibrium is :
[JEE Main 2013]


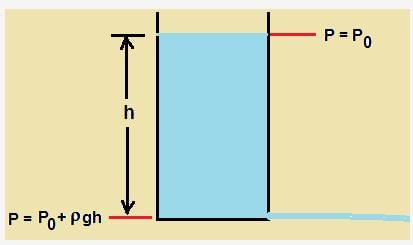 As per bernauli's equation p+(1/2)ρu2 is constant.
As per bernauli's equation p+(1/2)ρu2 is constant.