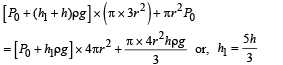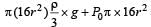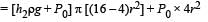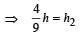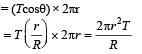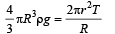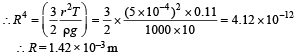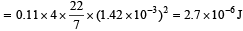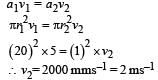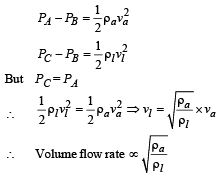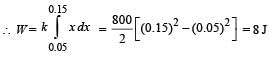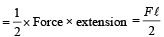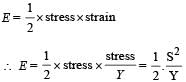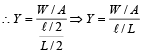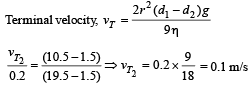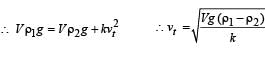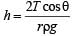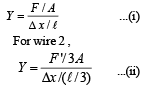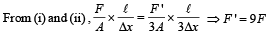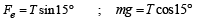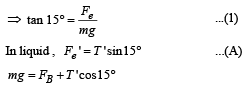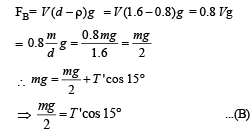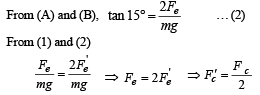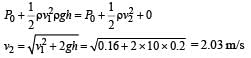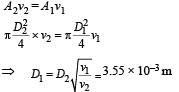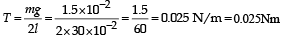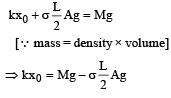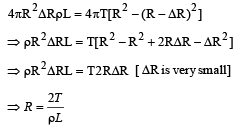Test: JEE Main 35 Year PYQs- Mechanical Properties of Solids & Fluids - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: JEE Main 35 Year PYQs- Mechanical Properties of Solids & Fluids
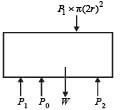
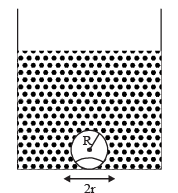
A cylindrical tank has a hole of diameter 2r in its bottom. The hole is covered wooden cylindrical block of diameter 4r, height h and density ρ/3.
Situation I : Initially, the tank is filled with water of density ρ to a height such that the height of water above the top of the block is h1 (measured from the top of the block).
Situation II : The water is removed from the tank to a height h2 (measured from the bottom of the block), as shown in the figure.
The height h2 is smaller than h (height of the block) and thus the block is exposed to the atmosphere.
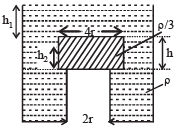
Q. Find the minimum value of height h1 (in situation 1), for which the block just starts to move up?
The height h2 is smaller than h (height of the block) and thus the block is exposed to the atmosphere.

A cylindrical tank has a hole of diameter 2r in its bottom. The hole is covered wooden cylindrical block of diameter 4r, height h and density ρ/3.
Situation I : Initially, the tank is filled with water of density ρ to a height such that the height of water above the top of the block is h1 (measured from the top of the block).
Situation II : The water is removed from the tank to a height h2 (measured from the bottom of the block), as shown in the figure.
The height h2 is smaller than h (height of the block) and thus the block is exposed to the atmosphere.

Q. Find the height of the water level h2 (in situation 2), for which the block remains in its original position without the application of any external force
The height h2 is smaller than h (height of the block) and thus the block is exposed to the atmosphere.

A cylindrical tank has a hole of diameter 2r in its bottom. The hole is covered wooden cylindrical block of diameter 4r, height h and density ρ/3.
Situation I : Initially, the tank is filled with water of density ρ to a height such that the height of water above the top of the block is h1 (measured from the top of the block).
Situation II : The water is removed from the tank to a height h2 (measured from the bottom of the block), as shown in the figure.
The height h2 is smaller than h (height of the block) and thus the block is exposed to the atmosphere.

Q. In situation 2, if h2 is further decreased, then
The height h2 is smaller than h (height of the block) and thus the block is exposed to the atmosphere.

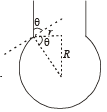
When liquid medicine of density ρ is to put in the eye, it is done with the help of a dropper. As the bulb on the top of the dropper is pressed, a drop forms at the opening of the dropper. We wish to estimate the size of the drop. We first assume that the drop formed at the opening is spherical because that requires a minimum increase in its surface energy. To determine the size, we calculate the net vertical force due to the surface tension T when the radius of the drop is R. When this force becomes smaller than the weight of the drop, the drop gets detached from the dropper.
Q. If the radius of the opening of the dropper is r, the vertical force due to the surface tension on the drop of radius R (assuming r << R) is
When liquid medicine of density ρ is to put in the eye, it is done with the help of a dropper. As the bulb on the top of the dropper is pressed, a drop forms at the opening of the dropper. We wish to estimate the size of the drop. We first assume that the drop formed at the opening is spherical because that requires a minimum increase in its surface energy. To determine the size, we calculate the net vertical force due to the surface tension T when the radius of the drop is R. When this force becomes smaller than the weight of the drop, the drop gets detached from the dropper.
Q. If r = 5 × 10–4 m, ρ = 103 kgm–3 , g = 10 ms–2 ,T= 0.11Nm –1, the radius of the drop when it detaches from the dropper is approximately
When liquid medicine of density ρ is to put in the eye, it is done with the help of a dropper. As the bulb on the top of the dropper is pressed, a drop forms at the opening of the dropper. We wish to estimate the size of the drop. We first assume that the drop formed at the opening is spherical because that requires a minimum increase in its surface energy. To determine the size, we calculate the net vertical force due to the surface tension T when the radius of the drop is R. When this force becomes smaller than the weight of the drop, the drop gets detached from the dropper.
Q. After the drop detaches, its surface energy is
A spray gun is shown in the figure where a piston pushes air out of a nozzle. A thin tube of uniform cross section is connected to the nozzle. The other end of the tube is in a small liquid container.
As the piston pushes air through the nozzle, the liquid from the container rises into the nozzle and is sprayed out. For the spray gun shown, the radii of the piston and the nozzle are 20 mm and 1 mm respectively. The upper end of the container is open to the atmosphere.

Q. If the piston is pushed at a speed of 5 mms–1, the air comes out of the nozzle with a speed of
A spray gun is shown in the figure where a piston pushes air out of a nozzle. A thin tube of uniform cross section is connected to the nozzle. The other end of the tube is in a small liquid container.
As the piston pushes air through the nozzle, the liquid from the container rises into the nozzle and is sprayed out. For the spray gun shown, the radii of the piston and the nozzle are 20 mm and 1 mm respectively. The upper end of the container is open to the atmosphere.
Q. If the density of air is ρa, and that of the liquid ρl, then for a given piston speed the rate (volume per unit time) at which the liquid is sprayed will be proportional to
STATEMENT-1 : The stream of water flowing at high speed from a garden hose pipe tends to spread like a fountain when held vertically up, but tends to narrow down when held vertically down.
STATEMENT-2 : In any steady flow of an incompressible fluid, the volume flow rate of the fluid remains constant.
A spring of force constant 800 N/m has an extension of 5 cm. The work done in extending it from 5 cm to 15 cm is
A wire fixed at the upper end stretches by length ℓ by applying a force F. The work done in stretching is
Spherical balls of radius ‘R’ are falling in a viscous fluid of viscosity ‘η’ with a velocity ‘v’. The retarding viscous force acting on the spherical ball is
If two soap bubbles of different radii are connected by a tube.
If ‘S’ is stress and ‘Y’ is young’s modulus of material of a wire, the energy stored in the wire per unit volume is
A 20 cm long capillary tube is dipped in water. The water rises up to 8 cm. If the entire arrangement is put in a freely falling elevator the length of water column in the capillary tube will be
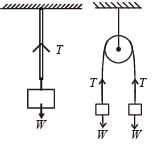
A wire elongates by l mm when a load W is hanged from it.
If the wire goes over a pulley and two weights W each are hung at the two ends, the elongation of the wire will be (in mm)
If the terminal speed of a sphere of gold (density = 19.5 kg/m3) is 0.2 m/s in a viscous liquid (density = 1.5 kg/m3), find the terminal speed of a sphere of silver (density = 10.5 kg/m3) of the same size in the same liquid
A spherical solid ball of volume V is made of a material of density ρ1. It is falling through a liquid of density ρ2 (ρ2< ρ1). Assume that the liquid applies a viscous force on the ball that is proportional to the square of its speed v, i.e., Fviscous = –kv2 (k > 0). The terminal speed of the ball is
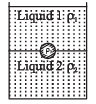
A jar is filled with two non-mixing liquids 1 and 2 having densities ρ1 and, ρ2 respectively. A solid ball, made of a material of density ρ3, is dropped in the jar. It comes to equilibrium in the position shown in the figure.Which of the following is true for ρ1, ρ1 and ρ3?
A capillary tube (A) is dipped in water. Another identical tube (B) is dipped in a soap-water solution. Which of the following shows the relative nature of the liquid columns in the two tubes?
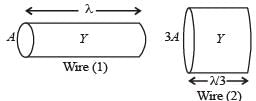
Two wires are made of the same material and have the same volume. However wire 1 has cross-sectional area A and wire 2 has cross-sectional area 3A. If the length of wire 1 increases by Δx on applying force F, how much force is needed to stretch wire 2 by the same amount?
A ball is made of a material of density ρ where ρoil <ρ< ρwater with ρoil and ρwater representing the densities of oil and water, respectively. The oil and water are immiscible. If the above ball is in equilibrium in a mixture of this oil and water, which of the following pictures represents its equilibrium position?
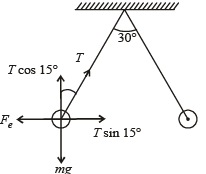
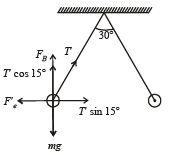
Two identical charged spheres are suspended by strings of equal lengths. The strings make an angle of 30° with each other. When suspended in a liquid of density 0.8g cm–3, the angle remains the same. If density of the material of the sphere is 1.6 g cm–3 , the dielectric constant of the liquid is
Work done in increasing the size of a soap bubble from a radius of 3 cm to 5 cm is nearly (Surface tension of soap solution = 0.03 Nm–1)
Water is flowing continuously from a tap having an internal diameter 8 × 10–3 m. The water velocity as it leaves the tap is 0.4 ms–1. The diameter of the water stream at a distance 2 × 10–1 m below the tap is close to:
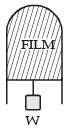
A thin liquid film formed between a U-shaped wire and a light slider supports a weight of 1.5 × 10–2 N (see figure). The length of the slider is 30 cm and its weight negligible. The surface tension of the liquid film is
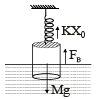
A unifor m cylinder of length L and mass M having crosssectional area A is suspended, with its length vertical, from a fixed point by a massless spring such that it is half submerged in σ liquid of density s at equilibrium position. The extension x0 of the spring when it is in equilibrium is:
Assume that a drop of liquid evaporates by decrease in its surface energy, so that its temperature remains unchanged.What should be the minimum radius of the drop for this to be possible? The surface tension is T, density of liquid is ρ and L is its latent heat of vaporization.
On heating water, bubbles being formed at the bottom of the vessel detach and rise. Take the bubbles to be spheres of radius R and making a circular contact of radius r with the bottom of the vessel. If r << R and the surface tension of water is T, value of r just before bubbles detach is: (density of water is ρ w)
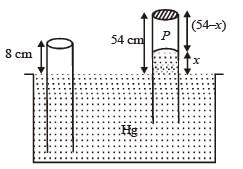
An open glass tube is immersed in mercury in such a way that a length of 8 cm extends above the mercury level. The open end of the tube is then closed and sealed and the tube is raised vertically up by additional 46 cm. What will be length of the air column above mercury in the tube now? (Atmospheric pressure = 76 cm of Hg)