Test: Hydrogen Spectrum - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Hydrogen Spectrum
Calculate the wavelength of light that corresponds to the radiation that is given off during the transition of an electron from the n = 5 to n = 2 state of the hydrogen atom.
Which of the following subatomic particles is responsible for the spectrum of radiation emitted by an element or compound?
The total energy of an electron in the nth orbit of a hydrogen atom is given by the formula En = -13.6 eV/n2. What does the negative energy for an electron indicate?
Which of the following is not true about Bohr’s model of the atom?
In the absorption spectrum, the wavelengths which are absorbed, are missing and they appear as:
Many home bathrooms have infrared light fixtures to help warm the room, and this light is not cancer causing. Which of the following quality make it so useful?
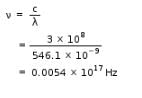
By use of a suitable filter, the green mercury emission line can be isolated. This line has a wavelength of 546.1 nm. What is the frequency? [1 Hz = 1 s-1]
An electron falls from one energy level to another; it releases a certain amount of light with a frequency of 5.100 x 1014 Hz. What energy is associated with this electron?
The energy associated with the transition of an electron from the n=1 state to the n=3 state of H atoms is:
Zeeman effect is the splitting of spectral line in presence of:
EM spectrum shows all forms of radiation except one of the followings:
Which of the following is not a type of electromagnetic radiation?
How much energy is needed to ionize a hydrogen atom if electron is present in n=1 orbit?