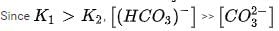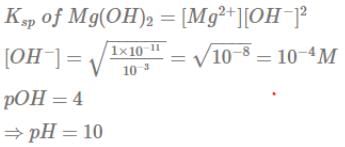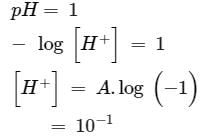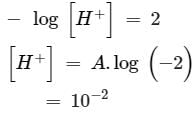Test: JEE Previous Year Questions- Ionic Equilibrium - JEE MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced - Test: JEE Previous Year Questions- Ionic Equilibrium
The solubility of Mg(OH)2 is x mole/ltr. then its solubility product is -
[AIEEE-2002]
The solubility in water of a sparingly soluble salt AB2 is 1.0 × 10-5 mol L-1 . Its solubility product will be -
[AIEEE-2003]
The molar solubility (in mol L-1) of a sparingly soluble salt MX4 is `s'. The corresponding solubility product is KSP. `s' is given in terms of Ksp by the relation -
[AIEEE-2004]
The solubility product of a salt having general formula MX2, in water is 4x10-12. The concentration of M2+ ions in the aqueous solution of the salt is - [AIEEE-2005]
The first and second dissociation constants of an acid H2A are 1.0 x 10-5 & 5.0 x 10-10 respectively. The overall dissociation constant of the acid will be -
[AIEEE-2007]
The pKa of a weak acid (HA) is 4.5. The pOH of an aqueous buffered solution of HA in which 50% of the acid is ionized is- [AIEEE-2007]
In a saturated solution of the sparingly soluble strong electrolyte AgIO3 (molecular mass = 283) the equilibrium which sets in is -
AgIO3(s) Ag+(aq) + IO3¯(aq)
If the solubility product Ksp of AgIO3 at a given temperature is 1.0 x 10-8, what is the mass of AgIO3 contained in 100 ml of its saturated solution ?
[AIEEE-2007]
The pKa of a weak acid, HA, is 4.80. The pKb of a weak base, BOH, is 4.78. The pH of an aqueous solution of the corresponding salt, BA, will be -
[AIEEE-2008]
Solid Ba(NO3)2 is gradually dissolved in a 1.0 x 10-4 M Na2CO3 solution. At what concentration of Ba2+ will a precipitate begin to form ? (Ksp for Ba CO3 = 5.1 x 10-9)
[AIEEE-2009]
In aqueous solution the ionization constants for carbonic acid are K1 = 4.2 x 10-7 and K2 = 4.8 x 10-11 Selection the correct statement for a saturated 0.034 M solution of the carbonic acid.
[AIEEE-2010]
Solubility product of silver bromide is 5.0 x 10-13. The quantity of potassium bromide (molar mass taken as 120 g mol-1) to be added to 1 litre of 0.05 M solution of silver nitrate to start the precipitation of AgBr is
[AIEEE-2010]
Three reactions involving are given below:
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
In which of the above does act as an acid?
[AIEEE-2010]
At 25°C, the solubility product of Mg(OH)2 is 1.0 ×10-11. At which pH, will Mg2+ ions start precipitating in the form of Mg(OH)2 from a solution of 0.001 M Mg2+ions ?
[AIEEE-2010]
The pH of a 0.1 molar solution of the acid HQ is 3. The value of the ionization constant, Ka of this acid is -
[AIEEE-2012]
How many litres of water must be added to litre of an aqueous solution of HCl with a pH of 1 to create an aqueous solution with pH of 2?
[AIEEE-2013]
|
352 videos|596 docs|309 tests
|


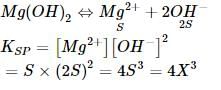

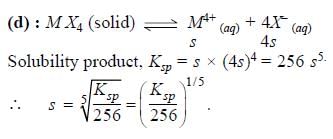
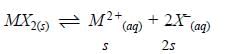


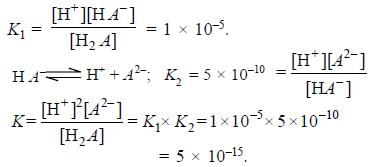

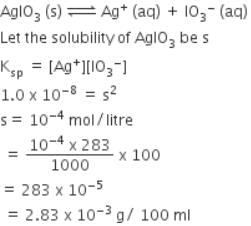
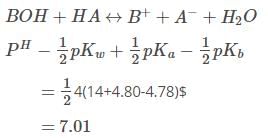
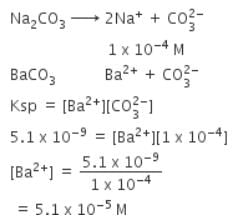
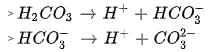
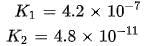
 cannot be 0.034 M as there is no complete dissociation.
cannot be 0.034 M as there is no complete dissociation.