Test: Kinetic Energy and Molecular Velocities - Chemistry MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Physical Chemistry - Test: Kinetic Energy and Molecular Velocities
What is the ratio of urms to ump in oxygen gas at 298k?
What is the ratio of root mean square speed of 16 grams of Oxygen to 4 grams of hydrogen?
If the root mean square speed of an argon gas atom at temperature T is equal to the average speed of a helium gas atom at -20 °C, then T will be:
Given:- atomic mass of Ar = 39.9 u
Atomic mass of He = 4.0 u
What is the ratio of the rms velocities of 2 moles of hydrogen to five moles of helium?
Calculate the root mean square speed of hydrogen in m/s at 27°C?
The speed of three particles is recorded as 3 m/s, 4 m/s, and 5 m/s. What is a root mean square speed of these particles?
Which of the following is greater for identical conditions and the same gas?
Which among the following options do you think has the highest average speed?
According to kinetic theory of gases , the root mean square velocity is directly proportional to:
The root mean square speed of a gas at a certain condition is 1.128 times greater than the most probable speed.
|
90 videos|144 docs|67 tests
|








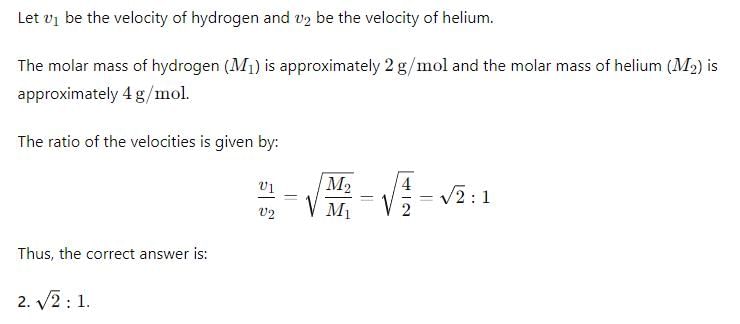
 where R is universal gas constant, T is a temperature in Kelvin and M is the mass in kilograms. From the formula, we understand that the average speed is inversely proportional to the root over the mass. As hydrogen has the least mass among the options it has the highest average speed.
where R is universal gas constant, T is a temperature in Kelvin and M is the mass in kilograms. From the formula, we understand that the average speed is inversely proportional to the root over the mass. As hydrogen has the least mass among the options it has the highest average speed.











