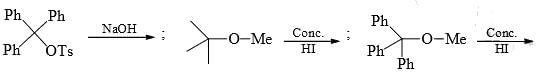Test: Reaction Mechanism Level - 7 - Chemistry MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Organic Chemistry - Test: Reaction Mechanism Level - 7
Among the following, the number of reaction(s) that produce(s) benzaldehyde is:
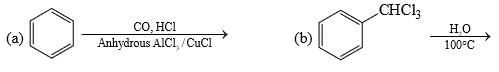
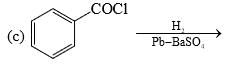
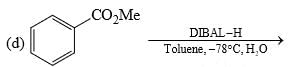

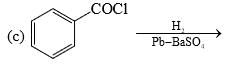
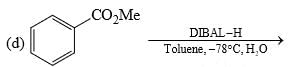
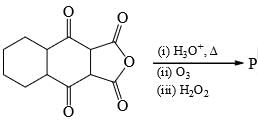
The total number of carboxylic acid groups in the product P is:

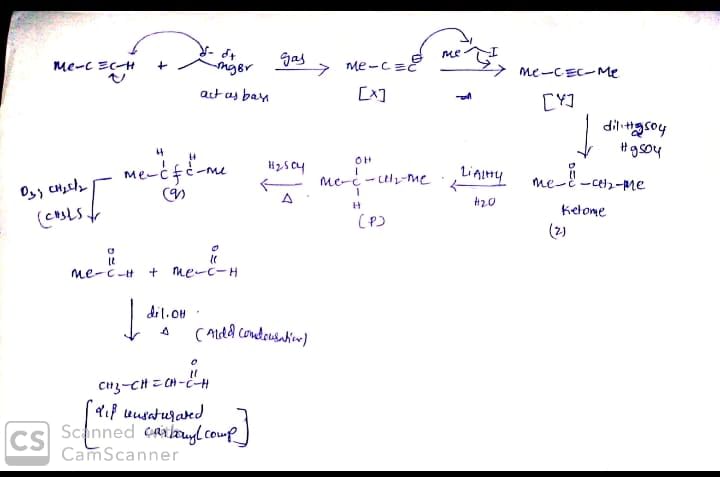
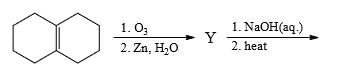
In the scheme given below, the total number of intramolecular Aldol condensation products formed from ‘Y’ is:

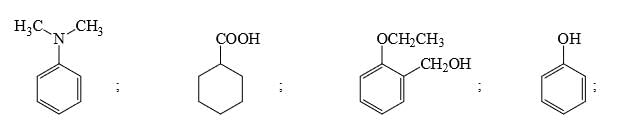
Amongst the following, the total number of compounds soluble in aqueous NaOH is:
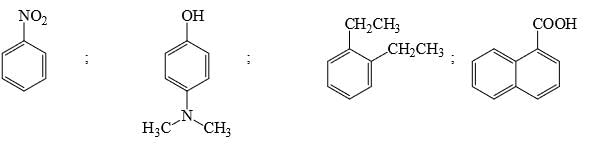
Among the following, how many compounds can form most stable hydrates:
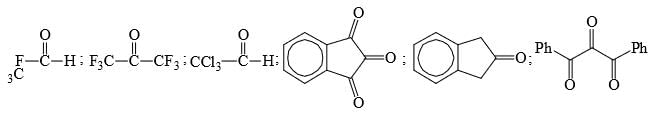
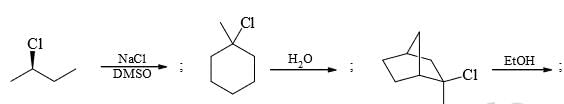
Identify total number of ‘β’-elimination reactions:
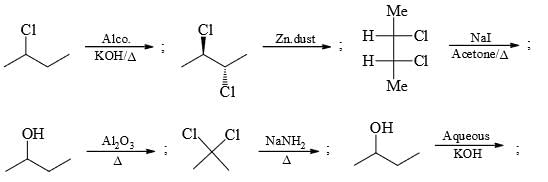
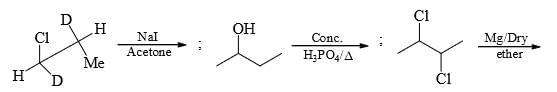
Calculate percentage of SN1 product if (R)-2-chloro butane on reaction with NaOH/H2O and acetone gives 98 per cent inverted product.
Calculate total number of alkene products when 2-chloro-2-cyclobutyl hexane react with alcoholic KOH and heat.
Calculate total number of α-H present in alkene formed when, 2,3-dimethyl butanol react with concentrated H2SO4/Δ.
For the given sequence of reaction
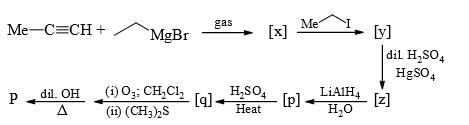
How many products are obtained finally?
Identify the total number of compounds that give positive test with Tollen’s reagent:
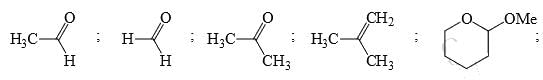
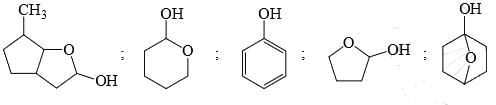
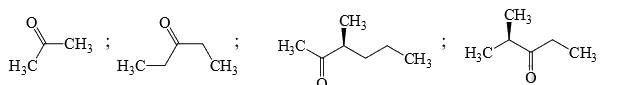
Identify the total number of compounds that give positive Iodoform test:
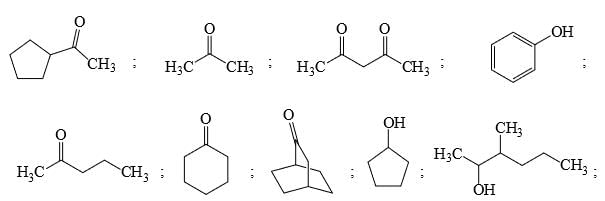
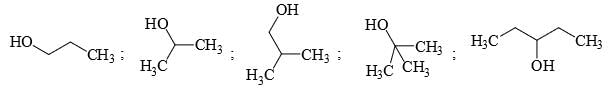
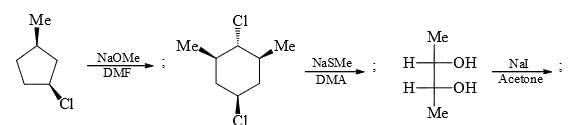
Identify the total number of compounds that give diastereomeric product on reaction with MeMgCl.
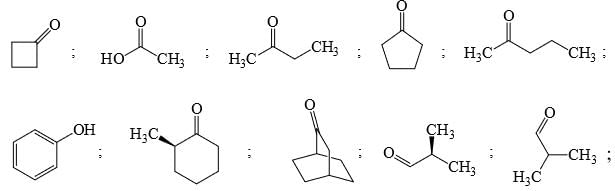
Identify that compounds that give Cannizaro reaction:



|
44 videos|102 docs|52 tests
|