Practice Test: Quantitative Aptitude - 5 - SSC CGL MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test SSC CGL Tier 1 and Tier 2 Mock Test Series 2026 - Practice Test: Quantitative Aptitude - 5
A is thrice as fast as B and is therefore able to finish a work in 40 days less than that of B. Find the time in which they can do it working together.
Area of the circle inscribed in a square of diagonal 4 cm is
The original price of a TV set is Rs. 4,000.If the price is discounted by 10% and then raised by 5% for service contract, the price charged by the shopkeeper is
A certain sum of money was divided between A, B and C in the ratio 1 : 3 : 5.If A received Rs. 500 the sum divided was
By selling a bag at Rs. 300, profit of 10% is made. The selling price of the bag, when it is sold at 15% profit would be
The weights of two iron balls are 5 kg and 7 kg. What is the percentage weight of the 1st ball with respect to 2nd ball.
A Bus travels at the speed of 40 km/hr, then the distance covered by it in 5 second is
∆XYZ and ∆PQR are two similar triangles and the perimeter of ∆XYZ and ∆PQR are 160 cm and 40 cm respectively. If length of PQ = 20 cm, then length of XY is
If the length of a chord of a circle is equal to that of the radius of the circle, then the angle subtended, in radians, at the center of the circle by chord is
The value of (sin2 60° - cosec2 45°) + (cot2 30° + tan2 45°)
The average salary of male employees in a firm was Rs. 6000 and that of females was Rs. 5600. The mean salary of all the employees was Rs. 5800. What is the % of female employees?
In ∆PQR, ∠Q is right angle, S is the mid-point of the side PR. If PQ = 4 cm, QR = 6 cm, then the length of PS is
The diagonals of two squares are in the ratio 5 : 7. The ratio of their area is
The angle of elevation of a ladder leaning against a wall is 30° and the foot of the ladder is 5 m away from the wall. The length of the ladder is
The product of two numbers is 1800 and their HCF is 15. The numbers are
The difference between simple and compound interests compounded annually on a certain sum of money for 2 years at 2% per annum is Rs. 3. The sum (in Rs.) is:
In a mixture of 20 litres, the ratio of milk to water is 3 : 2. Another 2 litres of water is added to the mixture. The ratio of milk to water in new mixture is
Direction: The pie chart given below represents the modes of transport for 1400 officers of the Staff Selection Commission, Kolkata. Study the chart and answer the following questions.

Question: The number of officers who go to office by Bus is
Direction: The pie chart given below represents the modes of transport for 1400 officers of the Staff Selection Commission, Kolkata. Study the chart and answer the following questions.

Question: The number of officers who go to office by Metro Rail is
Direction: The pie chart given below represents the modes of transport for 1400 officers of the Staff Selection Commission, Kolkata. Study the chart and answer the following questions.

Question: Write down the difference of officers availing train and the officers availing car as mode of transport?
Direction: The pie chart given below represents the modes of transport for 1400 officers of the Staff Selection Commission, Kolkata. Study the chart and answer the following questions.

Question: The ratio of two - wheelers and trains being used as modes of transport is
|
325 docs|152 tests
|






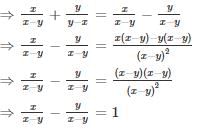


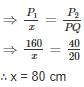
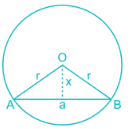

 ⟹ m/n = 1
⟹ m/n = 1