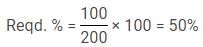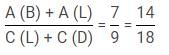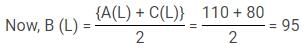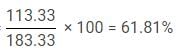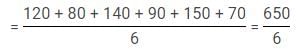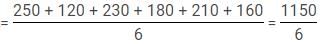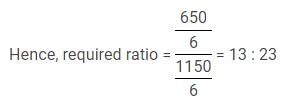IDBI Assistant Manager Mock Test - 4 - Bank Exams MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - IDBI Assistant Manager Mock Test - 4
Directions: A word and number arrangement machine, when given an input line of words and numbers, rearranges them following a particular rule in each step. The following is an illustration of input and rearrangement.
Input: hard 27 nut 14 impossible 54 to 86 crack 62
Step1:54 hard 27 nut 14 impossible 86 crack 62 to
Step2:86 54 hard 27 14 impossible crack 62 to nut
Step3:14 86 54 hard 27 crack 62 to nut impossible
Step4:62 14 86 54 27 crack to nut impossible hard
Step5:27 62 14 86 54 to nut impossible hard crack
Step 5 is the final output.
Find the different steps of output using the above-mentioned logic for the following input.
Input: deeds 39 for 96 humanity 75 give 27 pleasure 62
Q. Which of the following is second to the right of '39' in step 4?
Step1:54 hard 27 nut 14 impossible 86 crack 62 to
Step2:86 54 hard 27 14 impossible crack 62 to nut
Step3:14 86 54 hard 27 crack 62 to nut impossible
Step4:62 14 86 54 27 crack to nut impossible hard
Step5:27 62 14 86 54 to nut impossible hard crack
Find the different steps of output using the above-mentioned logic for the following input.
Input: deeds 39 for 96 humanity 75 give 27 pleasure 62
Directions: A word and number arrangement machine, when given an input line of words and numbers, rearranges them following a particular rule in each step. The following is an illustration of input and rearrangement.
Input: hard 27 nut 14 impossible 54 to 86 crack 62
Step1:54 hard 27 nut 14 impossible 86 crack 62 to
Step2:86 54 hard 27 14 impossible crack 62 to nut
Step3:14 86 54 hard 27 crack 62 to nut impossible
Step4:62 14 86 54 27 crack to nut impossible hard
Step5:27 62 14 86 54 to nut impossible hard crack
Step 5 is the final output.
Find the different steps of output using the above-mentioned logic for the following input.
Input: deeds 39 for 96 humanity 75 give 27 pleasure 62
Q. Four of the following five are alike in a certain way and thus form a group. Which of the following does not belong to the group?
Step1:54 hard 27 nut 14 impossible 86 crack 62 to
Step2:86 54 hard 27 14 impossible crack 62 to nut
Step3:14 86 54 hard 27 crack 62 to nut impossible
Step4:62 14 86 54 27 crack to nut impossible hard
Step5:27 62 14 86 54 to nut impossible hard crack
Find the different steps of output using the above-mentioned logic for the following input.
Input: deeds 39 for 96 humanity 75 give 27 pleasure 62
Directions: A word and number arrangement machine, when given an input line of words and numbers, rearranges them following a particular rule in each step. The following is an illustration of input and rearrangement.
Input: hard 27 nut 14 impossible 54 to 86 crack 62
Step1:54 hard 27 nut 14 impossible 86 crack 62 to
Step2:86 54 hard 27 14 impossible crack 62 to nut
Step3:14 86 54 hard 27 crack 62 to nut impossible
Step4:62 14 86 54 27 crack to nut impossible hard
Step5:27 62 14 86 54 to nut impossible hard crack
Step 5 is the final output.
Find the different steps of output using the above-mentioned logic for the following input.
Input: deeds 39 for 96 humanity 75 give 27 pleasure 62
Q. What is the sum of the digits of the numbers which are second from left end and fourth from right end in step 3?
Step1:54 hard 27 nut 14 impossible 86 crack 62 to
Step2:86 54 hard 27 14 impossible crack 62 to nut
Step3:14 86 54 hard 27 crack 62 to nut impossible
Step4:62 14 86 54 27 crack to nut impossible hard
Step5:27 62 14 86 54 to nut impossible hard crack
Find the different steps of output using the above-mentioned logic for the following input.
Input: deeds 39 for 96 humanity 75 give 27 pleasure 62
Directions: A word and number arrangement machine, when given an input line of words and numbers, rearranges them following a particular rule in each step. The following is an illustration of input and rearrangement.
Input: hard 27 nut 14 impossible 54 to 86 crack 62
Step1:54 hard 27 nut 14 impossible 86 crack 62 to
Step2:86 54 hard 27 14 impossible crack 62 to nut
Step3:14 86 54 hard 27 crack 62 to nut impossible
Step4:62 14 86 54 27 crack to nut impossible hard
Step5:27 62 14 86 54 to nut impossible hard crack
Step 5 is the final output.
Find the different steps of output using the above-mentioned logic for the following input.
Input: deeds 39 for 96 humanity 75 give 27 pleasure 62
Q. In which of the following steps, 96 is seen exactly between 62 and 75 for the first time?
Directions: A word and number arrangement machine, when given an input line of words and numbers, rearranges them following a particular rule in each step. The following is an illustration of input and rearrangement.
Input: hard 27 nut 14 impossible 54 to 86 crack 62
Step1:54 hard 27 nut 14 impossible 86 crack 62 to
Step2:86 54 hard 27 14 impossible crack 62 to nut
Step3:14 86 54 hard 27 crack 62 to nut impossible
Step4:62 14 86 54 27 crack to nut impossible hard
Step5:27 62 14 86 54 to nut impossible hard crack
Step 5 is the final output.
Find the different steps of output using the above-mentioned logic for the following input.
Input: deeds 39 for 96 humanity 75 give 27 pleasure 62
Q. Which of the following elements is third to the left of fifth element from right end in step 3?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given beside.
Three online hotel booking website A,B and C listed some hotels on their websites. The all listed 3 star, 4 star and 5 star hotels. One hotel can be listed on exactly one website.
Further it is known that
- Total number of hotels listed on all three website together is 720.
- Total number of 4 star hotels is twice the total number of 3 star hotels on all the three websites taken together. Further, total number of 5 star hotels is thrice the total number of 4 star hotels on all three sites together.
- Out of 200 hotels listed on Websites A, 30% are 3 star hotels.
- Ratio of 5 star hotels on sites A,B and C are 1 : 1 : 2.
- Number of 5 star hotels on B website is 20% more than number of 4 star hotels on the same website.
- Number of 3 star hotels on website B and C are same.
Q. 4 Star Hotels on Site B is what percent of total number Hotels on Site A ?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given beside.
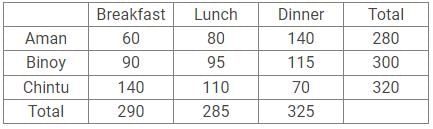
Aman, Binoy and Chintu are three friends who go out to explore the city. They ate their breakfast, lunch and dinner in the market and split the total bill. The amount spent by Aman on breakfast and lunch is in the ratio 3 : 4, while that spent by Chintu on lunch and dinner is in the ratio 11 : 7.
The amount paid by Aman on Dinner and Chintu on breakfast is equal. In lunch, the share of Binoy is the average of Aman and Chintu. The money spent by Aman on Breakfast and lunch is 700/9% of the money spent by Chintu on lunch and dinner. The ratio of breakfast, lunch and dinner in the total bill is 58 : 57 : 65. In the end Aman gives Chintu Rs. 20, to make the share of each of them equal.
Q. The amount spent by Aman on breakfast, Binoy on lunch and Chintu on dinner is what percent of the total expenditure of all three?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given beside.
Aman, Binoy and Chintu are three friends who go out to explore the city. They ate their breakfast, lunch and dinner in the market and split the total bill. The amount spent by Aman on breakfast and lunch is in the ratio 3 : 4, while that spent by Chintu on lunch and dinner is in the ratio 11 : 7.
The amount paid by Aman on Dinner and Chintu on breakfast is equal. In lunch, the share of Binoy is the average of Aman and Chintu. The money spent by Aman on Breakfast and lunch is 700/9% of the money spent by Chintu on lunch and dinner. The ratio of breakfast, lunch and dinner in the total bill is 58 : 57 : 65. In the end Aman gives Chintu Rs. 20, to make the share of each of them equal.
Q. The amount spent on dinner by Binoy is what percent of the total amount spent by him?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given beside.
Aman, Binoy and Chintu are three friends who go out to explore the city. They ate their breakfast, lunch and dinner in the market and split the total bill. The amount spent by Aman on breakfast and lunch is in the ratio 3 : 4, while that spent by Chintu on lunch and dinner is in the ratio 11 : 7.
The amount paid by Aman on Dinner and Chintu on breakfast is equal. In lunch, the share of Binoy is the average of Aman and Chintu. The money spent by Aman on Breakfast and lunch is 700/9% of the money spent by Chintu on lunch and dinner. The ratio of breakfast, lunch and dinner in the total bill is 58 : 57 : 65. In the end Aman gives Chintu Rs. 20, to make the share of each of them equal.
Q. What would have been the ratio of total amount spent by Aman and Binoy, had they split the dinner amount paid by Chintu between them evenly?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given beside.
Aman, Binoy and Chintu are three friends who go out to explore the city. They ate their breakfast, lunch and dinner in the market and split the total bill. The amount spent by Aman on breakfast and lunch is in the ratio 3 : 4, while that spent by Chintu on lunch and dinner is in the ratio 11 : 7.
The amount paid by Aman on Dinner and Chintu on breakfast is equal. In lunch, the share of Binoy is the average of Aman and Chintu. The money spent by Aman on Breakfast and lunch is 700/9% of the money spent by Chintu on lunch and dinner. The ratio of breakfast, lunch and dinner in the total bill is 58 : 57 : 65. In the end Aman gives Chintu Rs. 20, to make the share of each of them equal.
Q. What is the difference between the total amount spent on breakfast and dinner?
Directions: Study the following bar chart carefully and answer the questions given beside.
The number of people who visited four different places in two different years are given.
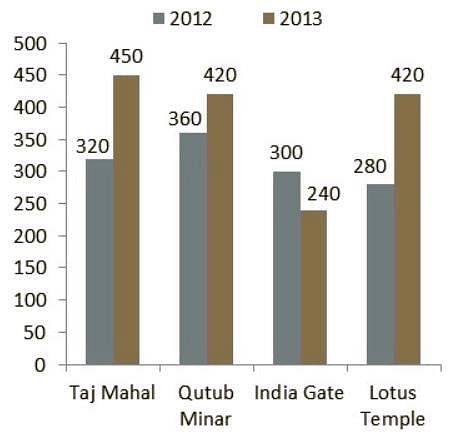
Q. What is the average of the number of people who visited Taj Mahal in 2012, Qutub Minar in 2012, Lotus Temple in 2013 and India Gate in 2013?
Directions: Study the following bar chart carefully and answer the questions given beside.
The number of people who visited four different places in two different years are given.
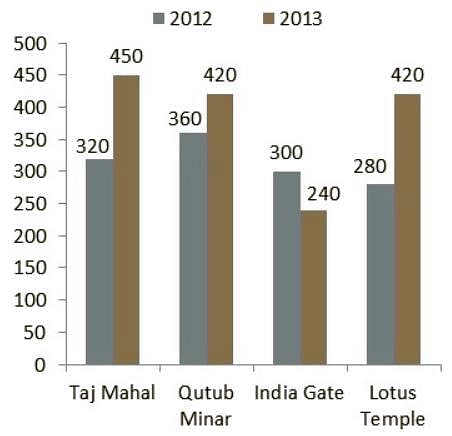
Q. Which place shows maximum percentage increase in number of people who visited from 2012 to 2013?
The given Line graph Data Interpretation Chart shows the sales of shoes (in thousands) from six stores in six different cities Kolkata, Patna, Dhanbad, Ranchi, Asansol, and Gaya during three consecutive years 2014, 2015 and 2016.

Q. What percent of the average sales of Campus shoes on Kolkata store, Patna store and Dhanbad store in 2014 is the average sales of Campus shoes on Ranchi store, Asansol store and Gaya store in 2015?
Directions: Study the following bar chart carefully and answer the questions given beside.
The number of people who visited four different places in two different years are given.
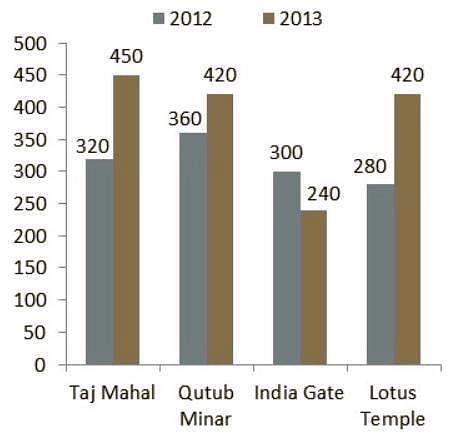
Q. The number of people who visited Taj Mahal in 2013 is how much percent less than the number of people who visited Taj Mahal and Lotus Temple in 2012 together?
The given Line graph Data Interpretation Chart shows the sales of shoes (in thousands) from six stores in six different cities Kolkata, Patna, Dhanbad, Ranchi, Asansol, and Gaya during three consecutive years 2014, 2015 and 2016.

Q. What is the ratio of average sales of Campus shoes of all the stores for the year 2014 to average sales of Campus shoes of all the stores for the year 2015?
The given Line graph Data Interpretation Chart shows the sales of shoes (in thousands) from six stores in six different cities Kolkata, Patna, Dhanbad, Ranchi, Asansol, and Gaya during three consecutive years 2014, 2015 and 2016.

Q. Total number of Campus shoes sales on Gaya store and Patna store together for three years is what percent of the total sales of Dhanbad store and Ranchi store together for three years?
The given Line graph Data Interpretation Chart shows the sales of shoes (in thousands) from six stores in six different cities Kolkata, Patna, Dhanbad, Ranchi, Asansol, and Gaya during three consecutive years 2014, 2015 and 2016.

Q. What is the total number of Campus shoes sales of store Kolkata, store Patna and store Ranchi together for three years?
The given Line graph Data Interpretation Chart shows the sales of shoes (in thousands) from six stores in six different cities Kolkata, Patna, Dhanbad, Ranchi, Asansol, and Gaya during three consecutive years 2014, 2015 and 2016.
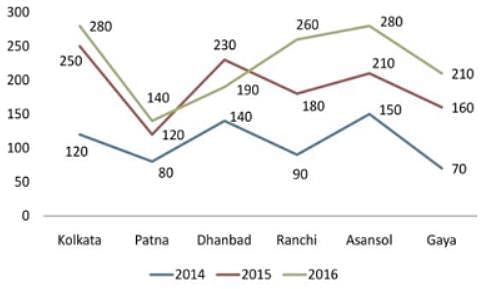
Q. What is the ratio of the total sales of Patna store for three years to the total sales of Asansol store for three years?
Directions: Study the following bar chart carefully and answer the questions given beside.
The number of people who visited four different places in two different years are given.
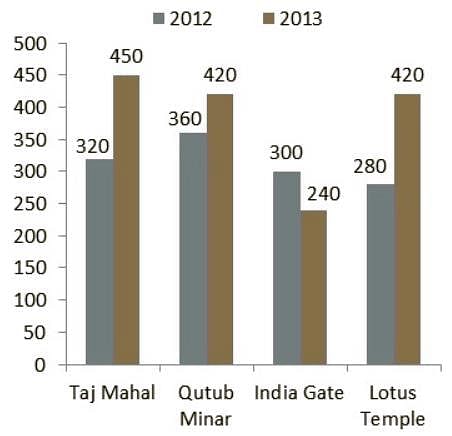
Q. What is the ratio of the number of people who visited Qutub Minar and India Gate in 2013 together and the number of people who visited Lotus Temple and Taj Mahal in 2012 together respectively?
Directions: Study the following bar chart carefully and answer the questions given beside.
The number of people who visited four different places in two different years are given.
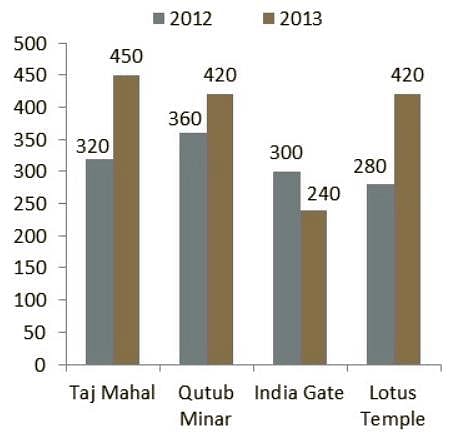
Q. What is difference between the sum of the number of people who visited Qutub Minar and India Gate in 2012 together and the sum of the number of people who visited Lotus Temple and India Gate in 2013 together?
Directions: These questions are based on the following information, read the comprehension carefully to answer the given questions.
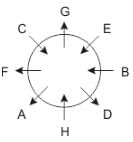
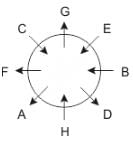
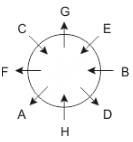
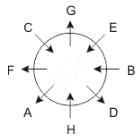
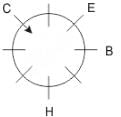
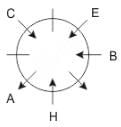
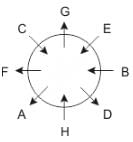
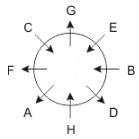
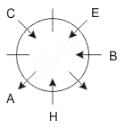
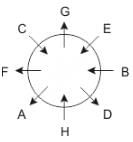
Eight people A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are sitting around a circular table but not necessarily in the same order. Some are facing inside and some are facing outside. Not more than two people facing same direction are sitting together.
H sits third to the right of C who is not facing outside. Immediate neighbours of H are facing same directions with respect to each other but opposite direction with respect to H who is facing inside. B is the immediate neighbor of E and both are facing same direction. E sits second to the left of C who is not the immediate neighbor of B. There are equal number of persons facing inside and outside direction. B sits third to the left of A and both are facing opposite directions to each other. H sits to the immediate right of D. F sits second to the left of G.
Q. If D leaves the group, what will be H's position?
Directions: These questions are based on the following information, read the comprehension carefully to answer the given questions.
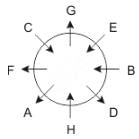
Eight people A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are sitting around a circular table but not necessarily in the same order. Some are facing inside and some are facing outside. Not more than two people facing same direction are sitting together.
H sits third to the right of C who is not facing outside. Immediate neighbours of H are facing same directions with respect to each other but opposite direction with respect to H who is facing inside. B is the immediate neighbor of E and both are facing same direction. E sits second to the left of C who is not the immediate neighbor of B. There are equal number of persons facing inside and outside direction. B sits third to the left of A and both are facing opposite directions to each other. H sits to the immediate right of D. F sits second to the left of G.
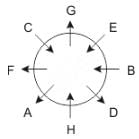
Q. Who is immediate neighbor of F?
Directions: These questions are based on the following information, read the comprehension carefully to answer the given questions.
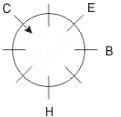
Eight people A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are sitting around a circular table but not necessarily in the same order. Some are facing inside and some are facing outside. Not more than two people facing same direction are sitting together.
H sits third to the right of C who is not facing outside. Immediate neighbours of H are facing same directions with respect to each other but opposite direction with respect to H who is facing inside. B is the immediate neighbor of E and both are facing same direction. E sits second to the left of C who is not the immediate neighbor of B. There are equal number of persons facing inside and outside direction. B sits third to the left of A and both are facing opposite directions to each other. H sits to the immediate right of D. F sits second to the left of G.
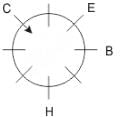
Q. If all the persons sitting are equidistant and if H faces south direction, what direction will B be facing?
Directions: These questions are based on the following information, read the comprehension carefully to answer the given questions.
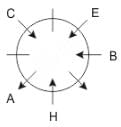
Eight people A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are sitting around a circular table but not necessarily in the same order. Some are facing inside and some are facing outside. Not more than two people facing same direction are sitting together.
H sits third to the right of C who is not facing outside. Immediate neighbours of H are facing same directions with respect to each other but opposite direction with respect to H who is facing inside. B is the immediate neighbor of E and both are facing same direction. E sits second to the left of C who is not the immediate neighbor of B. There are equal number of persons facing inside and outside direction. B sits third to the left of A and both are facing opposite directions to each other. H sits to the immediate right of D. F sits second to the left of G.
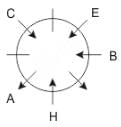
Q. What is the position of F with respect to E?
Directions: These questions are based on the following information, read the comprehension carefully to answer the given questions.
Eight people A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are sitting around a circular table but not necessarily in the same order. Some are facing inside and some are facing outside. Not more than two people facing same direction are sitting together.
H sits third to the right of C who is not facing outside. Immediate neighbours of H are facing same directions with respect to each other but opposite direction with respect to H who is facing inside. B is the immediate neighbor of E and both are facing same direction. E sits second to the left of C who is not the immediate neighbor of B. There are equal number of persons facing inside and outside direction. B sits third to the left of A and both are facing opposite directions to each other. H sits to the immediate right of D. F sits second to the left of G.
Q. How many persons are sitting between A and G while counting from left of G?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the given question.
In a certain code:
'chest teeth gap limb' is coded as Q&2 C%3 U#4 I?4
'borrow some corn people' is coded as F@3 0#3 X!5 F*5
'eat bank scheme tomato' is coded as P?5 L!3 U^2 F@5
'gossible come person gones' is coded as F#3 T&4 F&7 O*5
What will be the code for 'linguist paraglide emperor'?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the given question.
In a certain code:
'chest teeth gap limb' is coded as Q&2 C%3 U#4 I?4
'borrow some corn people' is coded as F@3 O#3 X!5 F*5
'eat bank scheme tomato' is coded as P?5 L!3 U^2 F@5
'gossible come person gones' is coded as F#3 T&4 F&7 O*5
What will be the code for 'shaker prospectus trick'?
Directions: In the question given below, there is a group of letters followed by combinations of digits/symbols lettered (1), (2), (3) and (4). You have to find out which of the combinations correctly represents the group of letters based on the coding system and mark the letter of that combination as your answer.

Conditions:
(i) If both the first and the last letters are consonants, then all the vowels are to be coded as the code of E.
(ii) If both the first and the last letters are vowels, then both are to be coded by &.
(iii) If the first letter is a vowel and the last letter is a consonant, then their codes are to be interchanged.
PTUWT
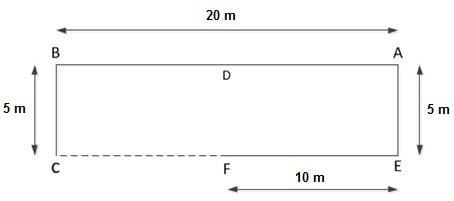
Point A is 20 m to the east of point B. Point B is 5 m to the north of point C. Point D is 10 m to the east of point B. Point E is 5 m to the south of point A. Point F is 10 m to the west of point E.
Which of the following points lie in a straight line?
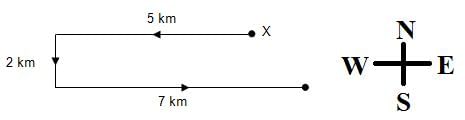
Suraj started from point X and walked 5 km towards west. He then turned left and walked 2 km, after which he turned left again and walked 7 km.
In which direction was he in the end with respect to point X?