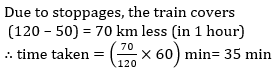Super TET Mock Test - 4 - Super TET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Super TET Mock Test - 4
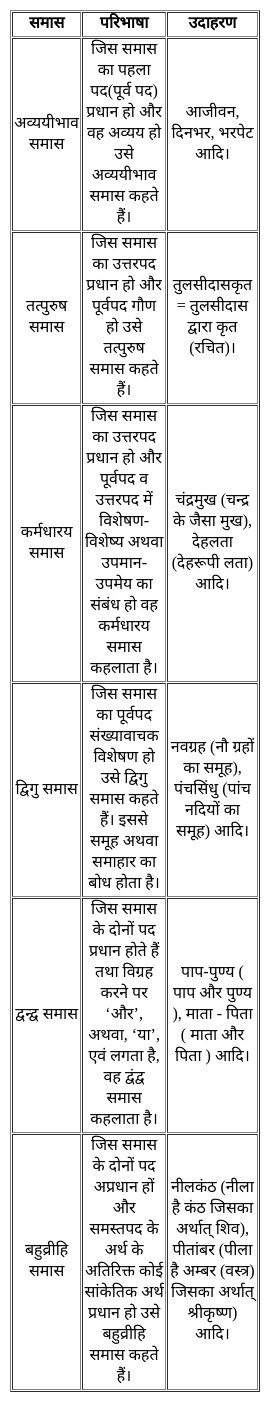
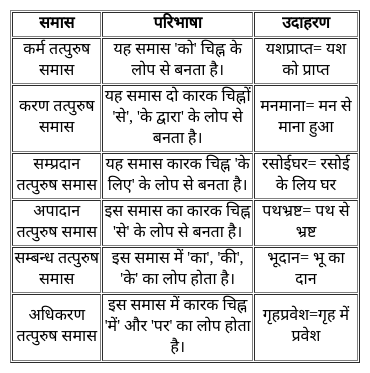
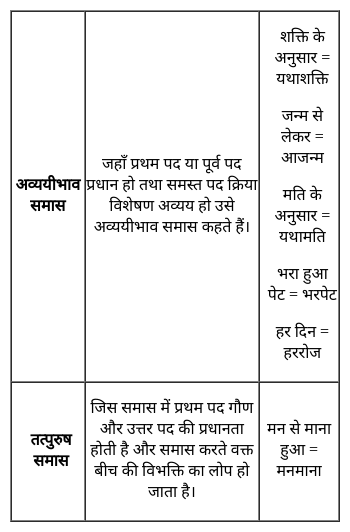
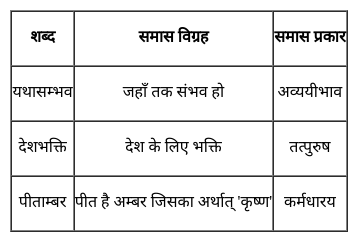
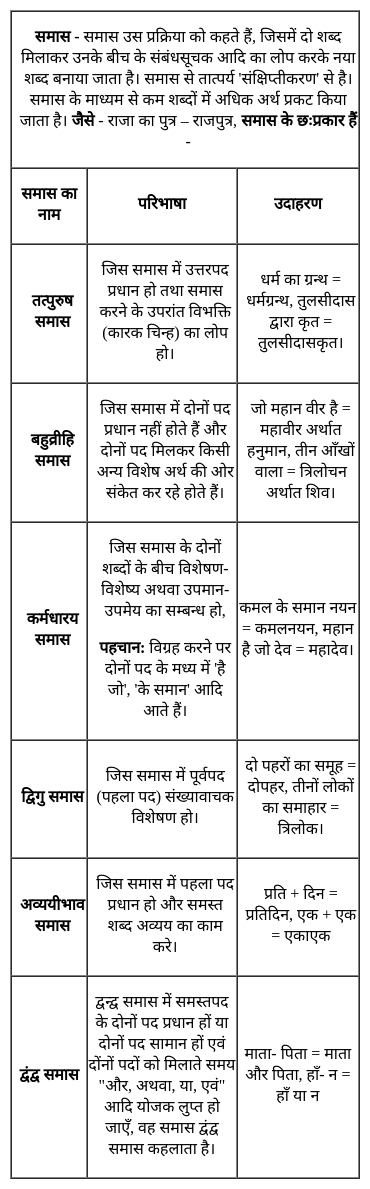
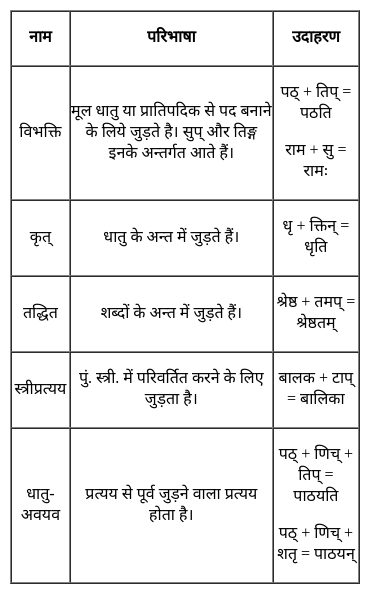
निम्नलिखित प्रश्न में, चार विकल्पों में से, उस विकल्प का चयन करें जो दिए गए शब्द के लिए सही द्विगु समास के विग्रह का विकल्प हो ।
पंचसिंधु
Improve the bracketed part of the sentence with the parts given below.
Q. Although I (did) my homework the teacher punished me.
What is the area of the largest square that can be made in a rectangle with 10 meters length and 4 meters width?
Excluding stoppages, the average speed of a train is 120 kmph and including stoppages, it is 50 kmph. For how many minutes does the train stop per hour?
Assertion (A) - The Ahoms migrated to the Brahmaputra valley from present-day Sri Lanka in the thirteenth century.
Reasoning (R) - In 1662, the Mughals under Asaf Khan attacked the Ahom kingdom.
Choose the correct option.
Which of the following sentences is correct about multicropping?
Outcome-oriented student learning model in Social Sciences will focus primarily on which of the following?
How are monthly or quarterly seminars by students helpful in senior classes?
What is the trend of India's Wholesale Price Index (WPI) for the past seven months?
Which badminton player has clinched the Japan Open 2023 singles men’s title?
The First Cotton Textile Mill was established in India at
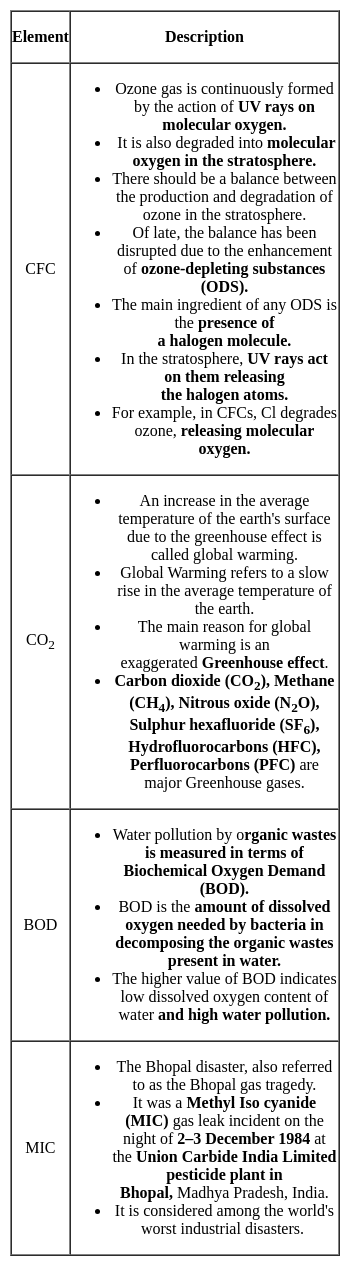
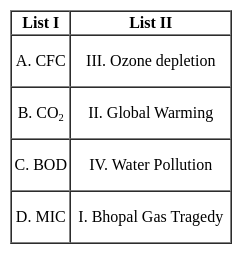
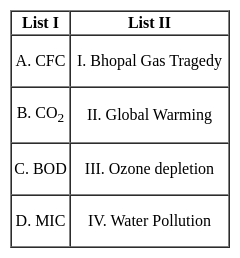
Match the items in List I with List II and select the correct answer using the codes given below:
Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions that follow.
A blacksmith has five iron articles A, B, C, D and E each having a different weight.
I. A weight is twice as much as of B.
II. B weight is four and half times as much as of C.
III. C weight is half times as much as of D.
IV. D weight is half as much as of E.
V. E weight is less than A but more than C.
Q. E is lighter in weight than which of the other two articles?
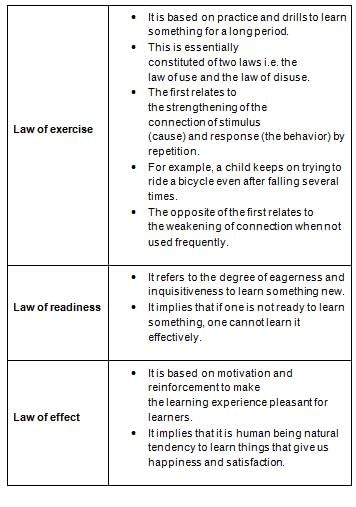
The psychologist who developed first three laws of learning - readiness, exercise and effect
Problem of ‘wastage’ and ‘stagnation’ is primarily related to which level of education ?