MPTET Varg 1 Biology Mock Test - 1 - MPTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - MPTET Varg 1 Biology Mock Test - 1
Learning and knowledge are the greatest assets of a man.
इस वाक्य का हिंदी रूपांतरण है?
इस वाक्य का हिंदी रूपांतरण है?
निर्देश: इन प्रश्नों में दिए गए वाक्यांशों के सही अर्थ को व्यक्त करने वाला शब्द (अनेक शब्दों के लिए एक शब्द) दिए गए विकल्पों में से चुनिए।
जो ममत्व से रहित हो
जो ममत्व से रहित हो
DIRECTIONS: A sentence with an underlined idiomatic expression is given below. What is the meaning of the idiomatic expression 'A snake in the grass' in the sentence given below?
Raghav was so friendly that we failed to realize he was the snake in the grass.
DIRECTIONS: Fill in the blank with the correct article.
We live _____ few miles from the city.
Consider the following question and decide which of the statements is sufficient to answer the question.
Question:
Ajay is the nephew of Lalit. Determine the present ages of Ajay and Lalit.
Statements:
1. Their mean age is 34.
2. After 14 years, Lalit’s age will be twice that of Ajay’s.
The method of directly injecting a sperm into ovum in Assisted Reproductive Technology is called:
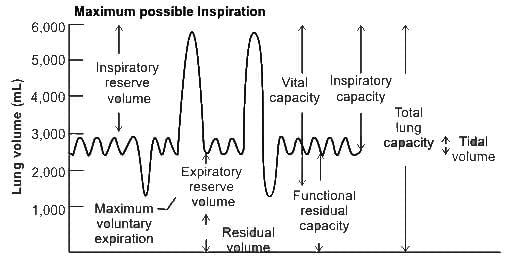
Volume of air inspired or expired during a normal respiration is termed as
Golden rice is genetically modified to produce ß carotene to solve the problem of:
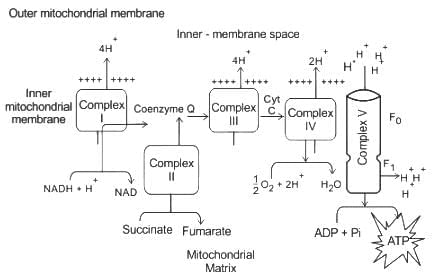
When electrons flow along the electron transport chains of mitochondria, which of the following changes occurs?
Anaphase promoting complex (APC) is a protein degradation machinery necessary for proper mitosis of animal cells. If APC is defective in a human cell, which of the following is expected to occur?
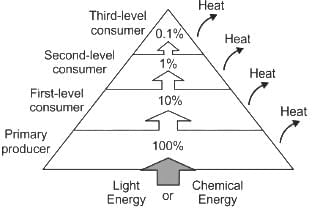
The pyramid that cannot be inverted in a stable ecosystem, is pyramid of
One hormone hastens the maturity period in juvenile conifers, a second hormone controls xylem differentiation, while the third hormone increases the tolerance of plants to various stresses. They are respectively
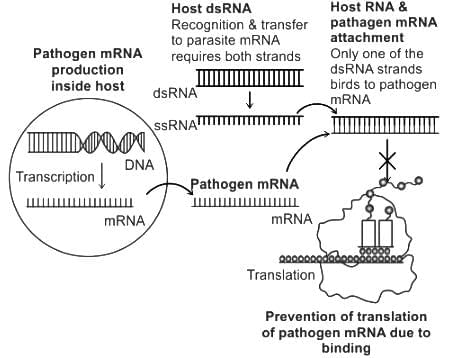
Silencing of a gene could be achieved through the use of
Which of the following can be threats to the biodiversity of any Geographical area?
(A) Global warming
(B) Fragmentation of natural habitat
(C) Invasion by alien species
(D) Promotion of vegetarianism
Select the correct answer by using the codes given below.