MPTET Varg 1 Biology Mock Test - 2 - MPTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - MPTET Varg 1 Biology Mock Test - 2
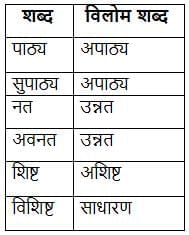
निम्नलिखित में से कौन-सा शब्द 'पति' का पर्यायवाची है?
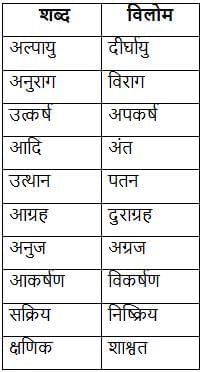
निम्नलिखित में से सही विलोम शब्द-युग्म कौन सा है?
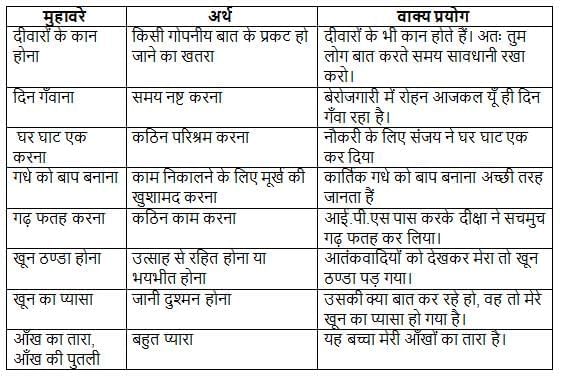
'अपना उल्लू सीधा करना' मुहावरे का अर्थ निम्न विकल्पों में से कौन सा है?
Where is the the Gupta Vishnu Temple located in Jabalpur district?
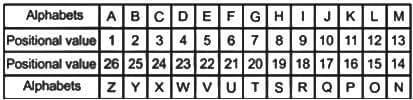
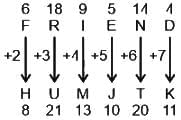
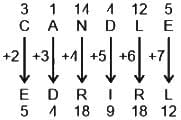
If FRIEND is coded as HUMJTK, how can CANDLE be written in that code?
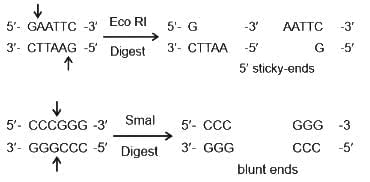
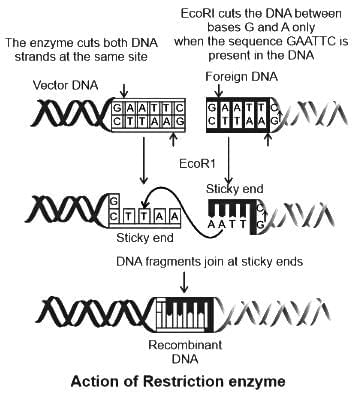
The single-stranded overhanging ends of DNA produced by the restriction endonuclease through offset cuts in the DNA strands are called
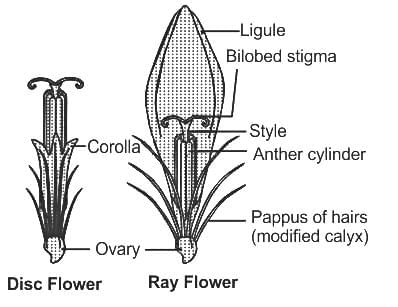
In which of the following families, the calyx is modified into a pappus ?
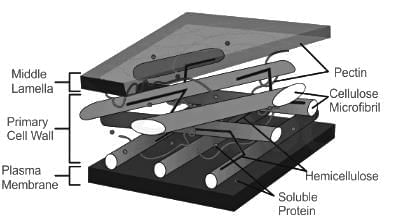
What is the middle lamella of cell wall made up of?
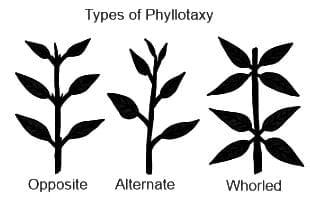
Which of the following shows a whorled phyllotaxy?
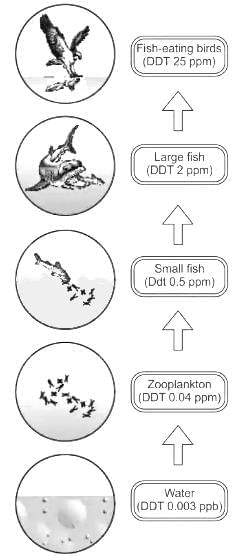
Biomagnification of DDT in an aquatic food chain starting from the water having concentration of 0.003 ppb may go in fish-eating birds up to
In immune response mechanism clonal selection is a process in which:
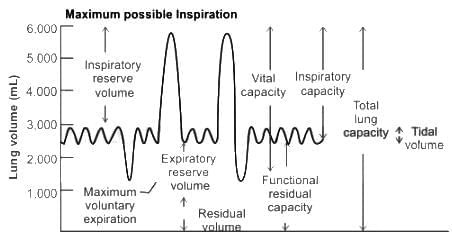
The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after a forced expiration is known as :