MPTET Varg 1 Mathematics Mock Test - 3 - MPTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - MPTET Varg 1 Mathematics Mock Test - 3
Consider the following statements:
1. India's nuclear energy strategy involves the development of Pressurized Heavy Water Reactors (PHWRs) as a central component.
2. The Three-Stage Nuclear Programme in India is hindered by the slow progress of Thorium-based Molten Salt Reactors (MSRs).
3. India's target for achieving net zero carbon emissions by 2070 necessitates a reliance on imported uranium to meet its nuclear energy demands.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
If A and B are the domain and range respectively for the relation R such that R = {(5, 3), (6, 4), (7, 5)} then which of the following option is true ?
Point A divides segment BC in the ratio 4 : 1. Co - ordinates of B are (6, 1) and C are (7/2, 6). What are the coordinates of point A?
In a moderately skewed distribution, the median is given as 10 and the mean is 12.5.Find the approximate value of the mode.
The position vectors of points P, Q, R and S are a, b, (2a + 3b) and (a – 2b) respectively. Which of the following is the position vector of SQ?
If A is an invertible skew-symmetric matrix, then A-1 is a:
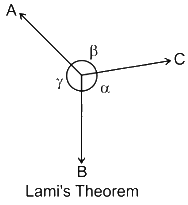
According to Lami’s theorem, if three coplanar forces are acting at a point b in equilibrium, then each force is proportional to the ______ of the angle between the other two.
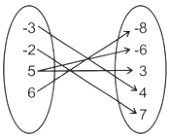
In the ordered set of pairs {(-3, 4), (5, -6), (-2, 7), (5, 3), (6, -8)} the domain and range will form ________.
If sin θ + cos θ = 1, then the value of sin 2θ is:
If a is a whole number and p is a prime number then according to Fermat's theorem:
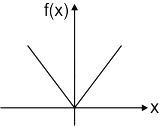
For f(x) = |x|, with df/dx denoting the derivative, the mean value theorem is not applicable because
The solution to the ordinary differential equation 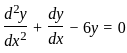 is
is
The value of k so that the function 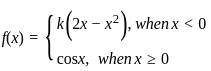 is continuous at x = 0, is
is continuous at x = 0, is
If x = 2/3 and x = -3 are the roots of the equation ax2 + 7x + b = 0, find the values of a and b.



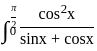 dx = _______
dx = _______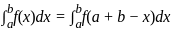
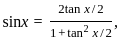
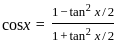
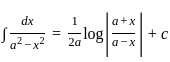
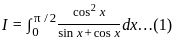
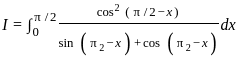
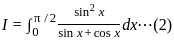
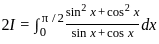
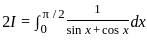
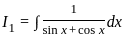
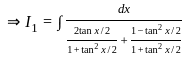
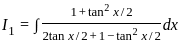
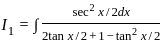
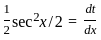
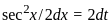
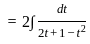
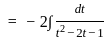
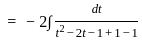
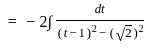
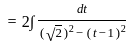
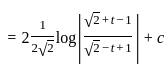
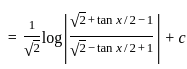
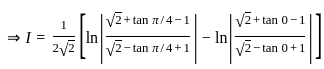
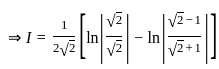
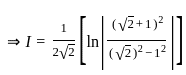
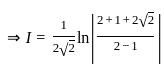
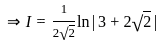
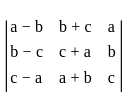
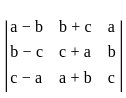
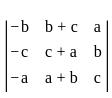
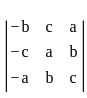
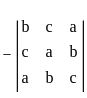
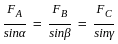
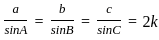
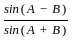
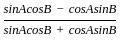
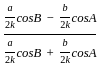
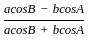
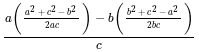
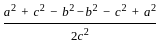
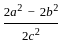
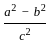
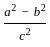
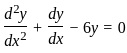
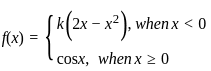 is continuous at x = 0,
is continuous at x = 0,