MPTET Varg 1 History Mock Test - 3 - MPTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - MPTET Varg 1 History Mock Test - 3
'मेघ आए बड़े बन - ठन के सँवर के' काव्य पंक्ति में प्रयुक्त अलंकार बताइए-
"लक्ष्मी + छाया" का संधि-पद निम्नलिखित में से किस संधि का सही उदाहरण होगा?
DIRECTIONS: Fill in the blank with the correct article.
We live _____ few miles from the city.
Raja Bhoj was a majestic king, he settled Bhojtal and Bhojpur town near Bhopal. Raja Bhoj was the ruler of which dynasty?
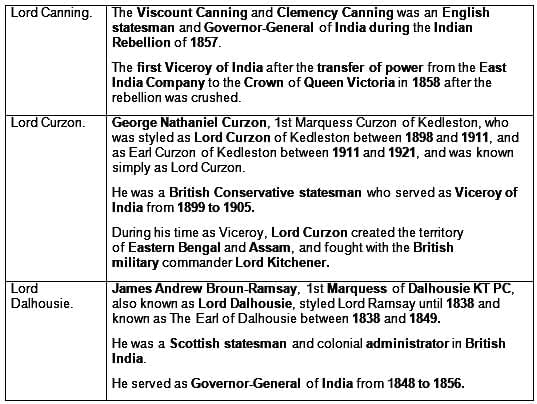
Who was the Viceroy of India at the time of the formation of the Indian National Congress?
Where did the Swadeshi movement formally start?
Which of the following Gupta kings stopped the Hunas from invading India?
Identify the iminent personality who presided over the Indian National Congress's historic Lahore session who approved the resolution for "Poorna Swaraj held in 1929?
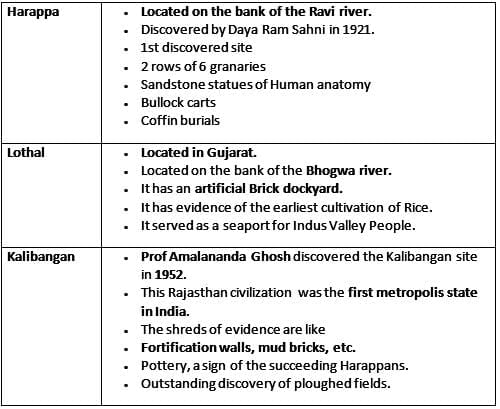
The Great Granary has been found in which of the following Indus Vally Civilization site?