MPTET Varg 1 Economics Mock Test - 2 - MPTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test MPTET Varg 1 Mock Test Series 2025 - MPTET Varg 1 Economics Mock Test - 2
निम्नलिखित में से कौन-सा शब्द 'पति' का पर्यायवाची है?
Learning and knowledge are the greatest assets of a man. इस वाक्य का हिंदी रूपांतरण है?
निम्नलिखित में से 'विष्णु' के पर्यायवाची शब्द-समूह का चयन कीजिए -
Directions: A sentence with an underlined idiomatic expression is given below. What is the meaning of the idiomatic expression 'A snake in the grass' in the sentence given below?
Raghav was so friendly that we failed to realize he was the snake in the grass.
Choose the correct word substitute for the following sentence:
One who collects coins as a hobby.
Refer to the following series and answer the question (all numbers are single digit numbers only)
3 7 5 2 8 6 4 1 3 7 4 3 7 6 8 2 6 5 8 9 7 8 6 1 2 7 3
How many such odd digits are there, each of which is immediately preceded by a perfect square and immediately followed by an odd digit? (NOTE: 1 is also a perfect square)
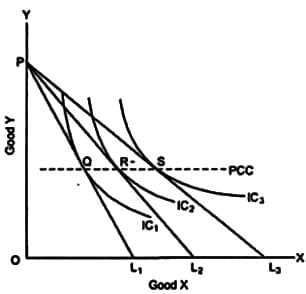
A consumer's demand curve can be obtained from:
Given:
I = 50 + 0.2 Y
S = -150 + 0.4 Y
G = 50
Where I = Investment, S = Savings
G = Government Expenditure
Y = National Income
What is the equilibrium level of national income?
Which of the following incomes are taxable in India?
A) Resident and ordinarily resident
B) Resident but not ordinary resident
C) Non-Resident
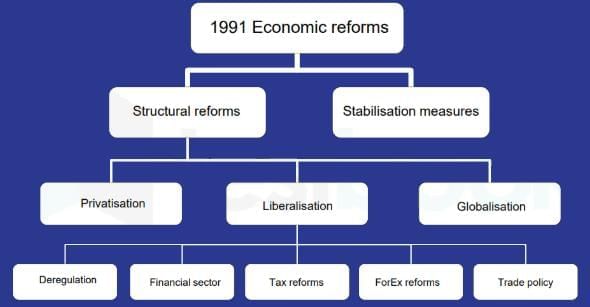
What is the main feature of New Economic Policy launched in the year 1991?
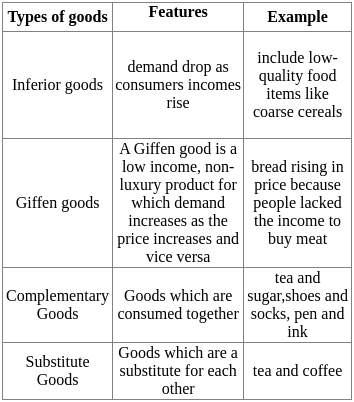
A good for which demand decreases with increase in income of consumer is called
How many languages are there on language panel of Indian currency note?
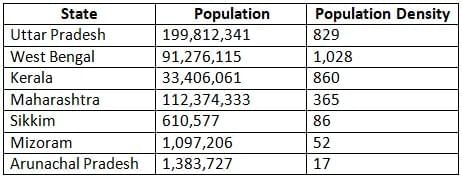
Which among the following states leads in Density of Population according to 2011 census?



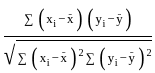 .
.