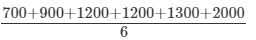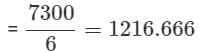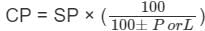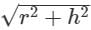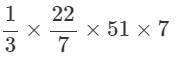MPTET Varg 2 Math Mock Test - 10 - MPTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - MPTET Varg 2 Math Mock Test - 10
The ratio of cost price and selling price of an article is 20 ∶ 21. The gain percent is
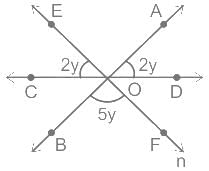
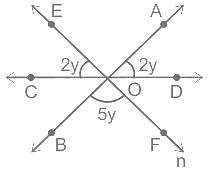
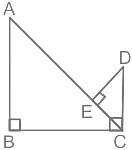
In the figure, AB, CD, and EF are three concurrent at O. find the value of y.

Find the value of k so that the area of triangle ABC with A (k + 1, 1), B (4, -3) and C (7, -k) is 6 square units.
A man loses 10% by selling his watch for Rs. 450. find the cost price of the watch.
The following sentences are steps involved in finding the H.C.F. of 29 and 24 by using Euclid's division algorithm. Arrange in sequential order from first to last.
(a) 5 = 1 × 5 + 0
(b) 29 = 24 × 1 + 5
(c) 24 = 5 × 4 + 1
A train takes 5 seconds to pass an electric pole. If the length of the train is 120 metres, the time taken by it to cross a railway platform 180 metres long, is
The shadow of a tower standing on a level plane is 30 m longer when sun’s elevation changes from 60° to 30°. Find the height of the tower.
Find the area of Rhombus with diagonals 10 cm and 8 cm
When two bodies are in thermal contact, heat flow will occur between them if they differ in ______.
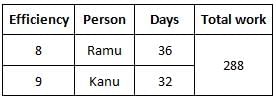
Ramu can do a work in 36 days and Kanu in 32 days. If they work on it together for 12 days, then what fraction of work is left?
"A" and "B" can do a piece of work in 8 days which "A" alone can do in 12 days. In how many days can "B" alone do the same work?
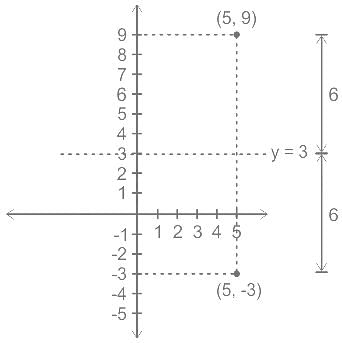
What is the reflection of the point (5, -3) in the line y = 3?
Find the distance between the points A(4,-3) and B(-4,3).
The number of planes of a regular hexagonal prism is
A loan of Rs. 8,925 is to be paid back in two equal half-yearly instalments. How much is each instalment if the interest is compounded half-yearly at 8% per annum?
A can do a work in 6 days. B takes 12 days. C takes as long as A and B would take working together. How long will it take B and C to complete the work together ?
The amount of simple interest on ₹4800 at the rate 5% per annum in 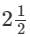 years will be-
years will be-
For how many years, there was more import of X than the average import of X?
An article is sold at a certain price. By selling it at 2/3 of the price one loses 10%. The gain percent at original price is:
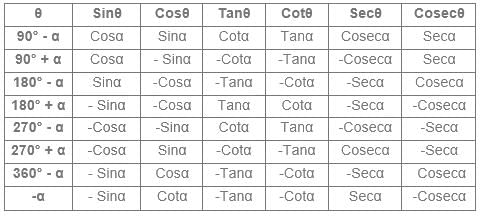
Which one of the following expressions is false ?
a) 9999 < 100
b) 1052 < 1023
c) 958765 > 957865
The volume of a cone of height 7 cm and slant height 10 cm is
The circumference of a circular field is 88 km, find its radius in kilometers.


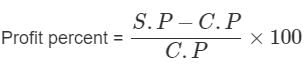
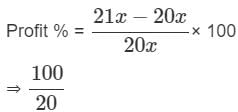

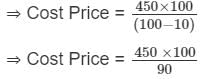
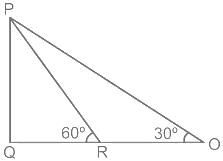
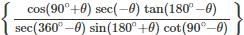 is:
is: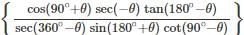
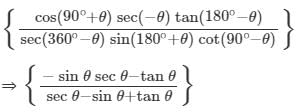
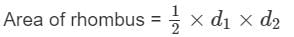
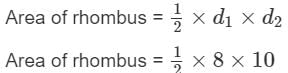
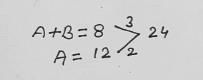
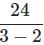
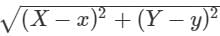
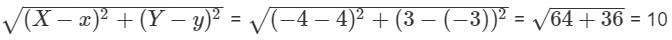
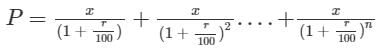
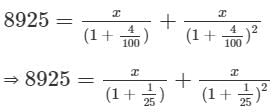
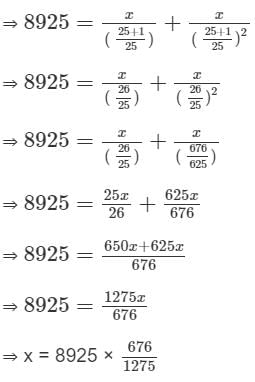

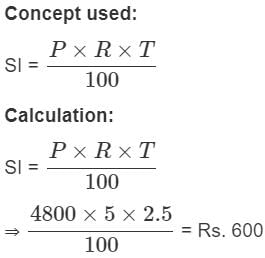
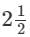 years will be ₹600.
years will be ₹600.